Nth-party risk extends beyond direct suppliers to include the entire network of vendors and their subcontractors, revealing hidden vulnerabilities in your supply chain. Managing this risk involves comprehensive visibility, continuous monitoring, and a collaborative approach to ensure security and compliance at every level. Explore the full article to understand strategies for identifying and mitigating nth-party risks effectively.
Table of Comparison
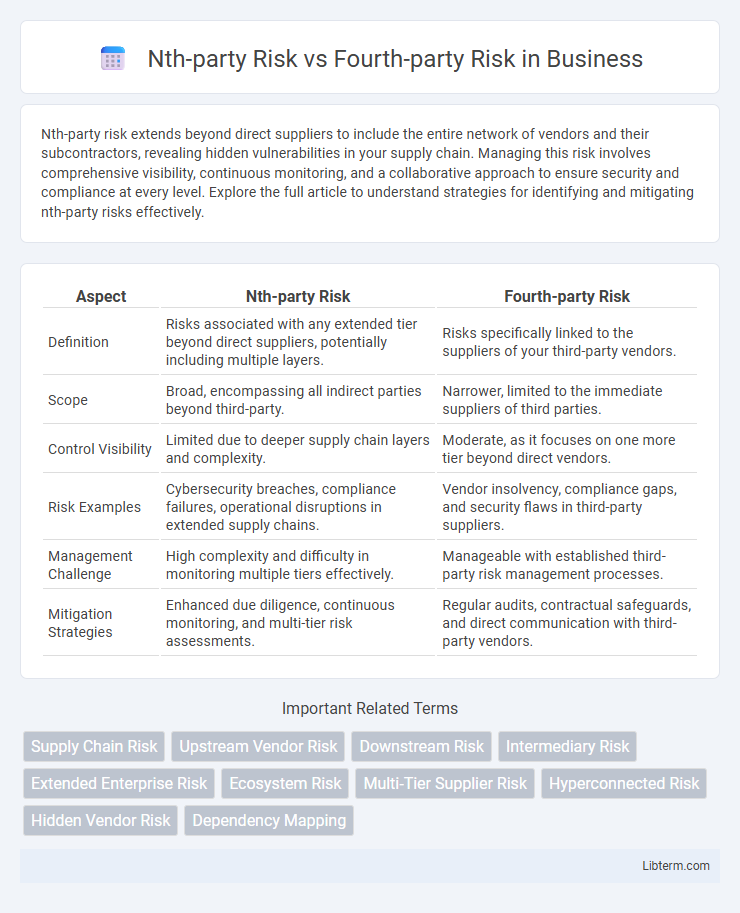
| Aspect | Nth-party Risk | Fourth-party Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risks associated with any extended tier beyond direct suppliers, potentially including multiple layers. | Risks specifically linked to the suppliers of your third-party vendors. |
| Scope | Broad, encompassing all indirect parties beyond third-party. | Narrower, limited to the immediate suppliers of third parties. |
| Control Visibility | Limited due to deeper supply chain layers and complexity. | Moderate, as it focuses on one more tier beyond direct vendors. |
| Risk Examples | Cybersecurity breaches, compliance failures, operational disruptions in extended supply chains. | Vendor insolvency, compliance gaps, and security flaws in third-party suppliers. |
| Management Challenge | High complexity and difficulty in monitoring multiple tiers effectively. | Manageable with established third-party risk management processes. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Enhanced due diligence, continuous monitoring, and multi-tier risk assessments. | Regular audits, contractual safeguards, and direct communication with third-party vendors. |
Understanding Nth-party Risk: Definition and Scope
Nth-party risk refers to the potential vulnerabilities originating beyond an organization's direct suppliers or vendors, extending into deeper tiers of the supply chain, including fourth-party and beyond. Understanding Nth-party risk involves identifying and managing exposures from indirect service providers, subcontractors, or partners that influence the security, compliance, and operational stability of the primary business. This broad scope requires robust risk assessment frameworks and continuous monitoring to mitigate cascading impacts from distant but critical third-party connections.
What is Fourth-party Risk? Key Concepts Explained
Fourth-party risk refers to the potential vulnerabilities and threats posed by the vendors and service providers that a third-party supplier relies on to deliver services or products. It extends beyond direct third-party risk by encompassing the entire supply chain, including subcontractors and their subcontractors, which can impact an organization's security and operational continuity. Managing fourth-party risk involves robust due diligence, continuous monitoring, and collaboration across all tiers of suppliers to mitigate unforeseen exposures.
The Evolving Landscape of Supply Chain Risks
Nth-party risk extends beyond traditional fourth-party risk by encompassing multiple layers of the supply chain, including all subcontractors and service providers involved in the delivery of products or services. The evolving landscape of supply chain risks requires organizations to implement more comprehensive risk management strategies that assess vulnerabilities across these extended networks, leveraging advanced analytics and continuous monitoring tools. Understanding the distinctions between fourth-party and Nth-party risks enhances an organization's ability to anticipate disruptions, enforce compliance, and safeguard operational continuity.
Differences Between Nth-party and Fourth-party Risk
Nth-party risk encompasses all extended risks across multiple layers of suppliers and service providers beyond direct vendors, whereas fourth-party risk specifically refers to the risks associated with a fourth-level subcontractor or service provider. The key difference lies in scope; Nth-party risk includes any tier beyond the first-party supplier, covering diverse and often undefined levels, while fourth-party risk targets the particular risks from the fourth tier in the supply chain hierarchy. Managing Nth-party risk requires comprehensive visibility and assessment tools across infinite layers, whereas fourth-party risk management focuses on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities linked to a single, fourth-tier entity.
Real-world Examples of Nth-party vs Fourth-party Risk
Nth-party risk involves vulnerabilities introduced when an organization's direct third-party vendor outsources tasks to additional vendors, creating multiple layers of risk exposure. For example, a financial institution relying on a cloud service provider (third-party) may face fourth-party risk if that provider uses subcontractors for data storage, potentially leading to unchecked security gaps. Real-world incidents like the Target data breach illustrate how vulnerabilities in fourth-party vendors compromised customer data through a third-party HVAC contractor.
Why Nth-party Risk Is Growing in Importance
Nth-party risk is growing in importance due to increasing supply chain complexity and extended digital ecosystems, where organizations rely on multiple layers of vendors beyond direct fourth-party relationships. This expanded dependency amplifies vulnerabilities as each additional tier introduces more potential points of failure, cyber threats, and compliance challenges. Risk management strategies now prioritize thorough assessment of these indirect partners to safeguard operational resilience and data security across the entire value chain.
Key Challenges in Managing Fourth-party Risk
Managing fourth-party risk presents key challenges including limited visibility into the extended supply chain, making it difficult to assess and mitigate risks effectively. Organizations often struggle with insufficient control over fourth-party vendors' security practices and compliance standards, increasing vulnerabilities and potential operational disruptions. Additionally, the complexity of tracking multiple layers of subcontractors complicates risk assessment processes and slows response times during incidents.
Best Practices for Identifying Nth-party and Fourth-party Risks
Identifying Nth-party and fourth-party risks requires comprehensive vendor risk management programs that extend beyond direct suppliers to include their subcontractors and service providers. Organizations should implement continuous monitoring tools, maintain an updated inventory of all third, fourth, and Nth-party relationships, and utilize risk assessment frameworks such as NIST or ISO 27001 to evaluate security posture across the extended supply chain. Collaboration with vendors to enforce transparent communication, regular due diligence, and contractual obligations related to cybersecurity is essential for mitigating cascading risks in multi-tiered vendor ecosystems.
Technologies and Tools for Mitigating Extended Supply Chain Risks
Technologies like advanced Zero Trust frameworks and AI-driven continuous monitoring platforms play a critical role in mitigating Nth-party and Fourth-party risks by providing real-time visibility into extended supply chains. Tools such as blockchain for immutable audit trails and automated risk assessment software enhance transparency and enable rapid identification of vulnerabilities beyond primary vendors. Integrating Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) solutions further strengthens defenses by streamlining incident response across multiple tiers of third-party relationships.
Future Trends in Nth-party and Fourth-party Risk Management
Future trends in Nth-party and Fourth-party risk management emphasize advanced automation and AI-driven analytics to enhance visibility into extended supply chains. Organizations increasingly adopt blockchain technology to ensure transparency and verify compliance across multiple tiers of vendors. Enhanced regulatory frameworks and continuous monitoring solutions are expected to drive proactive risk mitigation strategies for both Nth-party and Fourth-party relationships.
Nth-party Risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com