Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to a stock's current price, providing investors with insight into potential income from their investments. High dividend yields can indicate steady income streams but may also signal underlying company risks, so it's important to analyze the yield in context. Explore the rest of the article to understand how dividend yield impacts your investment decisions and portfolio strategy.
Table of Comparison
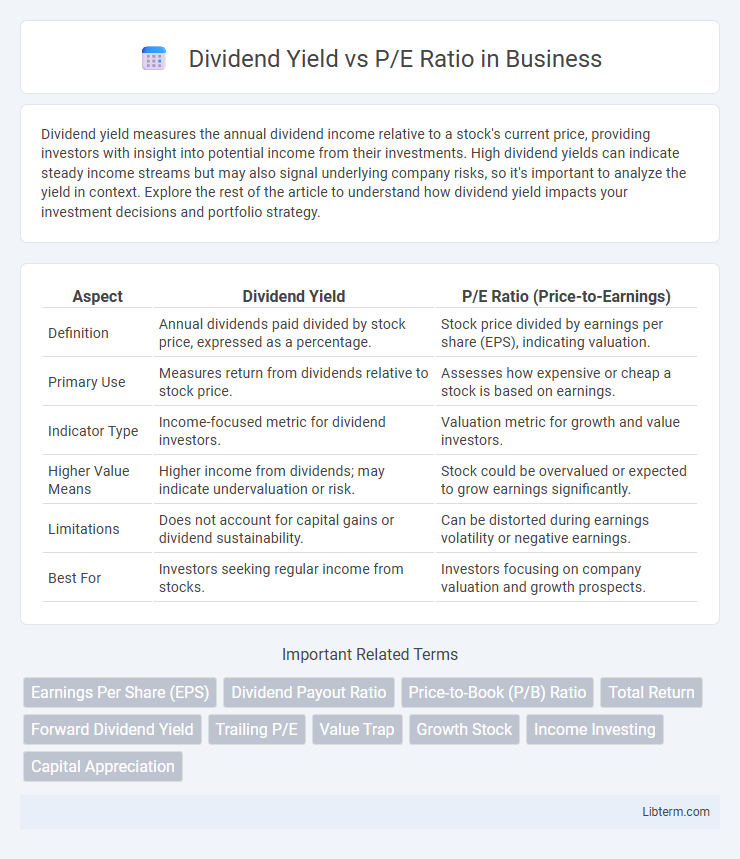
| Aspect | Dividend Yield | P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Annual dividends paid divided by stock price, expressed as a percentage. | Stock price divided by earnings per share (EPS), indicating valuation. |
| Primary Use | Measures return from dividends relative to stock price. | Assesses how expensive or cheap a stock is based on earnings. |
| Indicator Type | Income-focused metric for dividend investors. | Valuation metric for growth and value investors. |
| Higher Value Means | Higher income from dividends; may indicate undervaluation or risk. | Stock could be overvalued or expected to grow earnings significantly. |
| Limitations | Does not account for capital gains or dividend sustainability. | Can be distorted during earnings volatility or negative earnings. |
| Best For | Investors seeking regular income from stocks. | Investors focusing on company valuation and growth prospects. |
Introduction to Dividend Yield and P/E Ratio
Dividend yield measures the annual dividends paid by a company relative to its stock price, expressed as a percentage and indicating potential income from an investment. The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio compares a company's current share price to its per-share earnings, reflecting market expectations about growth and valuation. Both metrics provide critical insights for investors assessing stock attractiveness and income potential.
Understanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend payment relative to the stock price, providing investors with insight into income potential from equity investment. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividends per share by the current stock price, expressed as a percentage. Understanding dividend yield helps investors assess the cash flow they can expect from holding a stock, especially compared to growth metrics like the P/E ratio, which evaluates company earnings relative to price.
Understanding P/E Ratio
The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio measures a company's current share price relative to its earnings per share (EPS), reflecting investor expectations about future growth and profitability. A high P/E ratio can indicate overvaluation or strong growth prospects, while a low P/E may suggest undervaluation or potential risks. Understanding the P/E ratio provides insight into market sentiment and helps investors compare valuation across companies and sectors.
How Dividend Yield Reflects Investor Returns
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend payment relative to a stock's current price, directly reflecting the cash income investors earn from their shares. Unlike the P/E ratio, which indicates how much investors pay for each dollar of earnings, dividend yield captures the tangible return through dividends. High dividend yields often signify steady income streams, appealing to investors seeking consistent cash flow rather than capital appreciation.
P/E Ratio as a Measure of Valuation
The P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, serves as a critical measure of a stock's valuation by comparing its current price to its earnings per share, providing insight into investor expectations for future growth. A high P/E ratio often indicates that the market anticipates strong earnings growth, while a low P/E may suggest undervaluation or potential financial distress. Investors use the P/E ratio alongside dividend yield to balance growth prospects with income generation, optimizing portfolio strategy based on valuation metrics.
Key Differences Between Dividend Yield and P/E Ratio
Dividend yield measures the annual dividend income relative to a stock's price, indicating income generation, while the P/E ratio compares a company's current share price to its earnings per share, reflecting valuation and growth expectations. Dividend yield is expressed as a percentage focusing on cash returns to shareholders, whereas the P/E ratio is a multiple used to assess how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings. Investors use dividend yield to evaluate income potential, and the P/E ratio to analyze profitability and future growth prospects.
Factors Influencing Dividend Yield and P/E Ratio
Dividend yield is primarily influenced by a company's dividend payout policy, earnings stability, and market stock price fluctuations, reflecting the income return on investment. The P/E ratio is affected by earnings growth expectations, risk perceptions, interest rates, and overall market sentiment, indicating how much investors are willing to pay per dollar of earnings. Both metrics are also shaped by macroeconomic factors such as inflation rates and economic cycles, which impact investor behavior and corporate profitability.
When to Prioritize Dividend Yield Over P/E Ratio
Prioritize dividend yield over P/E ratio when seeking steady income from investments, especially in mature, stable companies with consistent dividend payments. High dividend yield indicates reliable cash flow potential, useful for retirees or income-focused investors prioritizing immediate returns over growth. In contrast, P/E ratio suits growth-oriented analysis, but dividend yield remains crucial for assessing income stability during market volatility.
Combining Dividend Yield and P/E Ratio in Investment Strategies
Combining dividend yield and P/E ratio enhances investment strategies by balancing income generation with valuation metrics. High dividend yields often indicate strong cash flow, while a low P/E ratio suggests undervaluation, enabling investors to identify stocks with both attractive income and growth potential. Integrating these indicators supports more informed decisions, optimizing portfolio returns and risk management.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metric for Your Portfolio
Dividend yield offers insight into current income generation from investments, appealing to income-focused investors seeking steady cash flow. The P/E ratio emphasizes growth potential by evaluating stock price relative to earnings, attracting growth-oriented portfolios prioritizing capital appreciation. Balancing these metrics based on investment objectives, risk tolerance, and market conditions ensures a strategic approach for optimizing portfolio performance.
Dividend Yield Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com