A professional client demands tailored services that prioritize efficiency, expertise, and clear communication to meet their specific business needs. Understanding the nuances of your industry allows providers to deliver solutions that drive growth and ensure long-term success. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to effectively cater to a professional client and elevate your service approach.
Table of Comparison
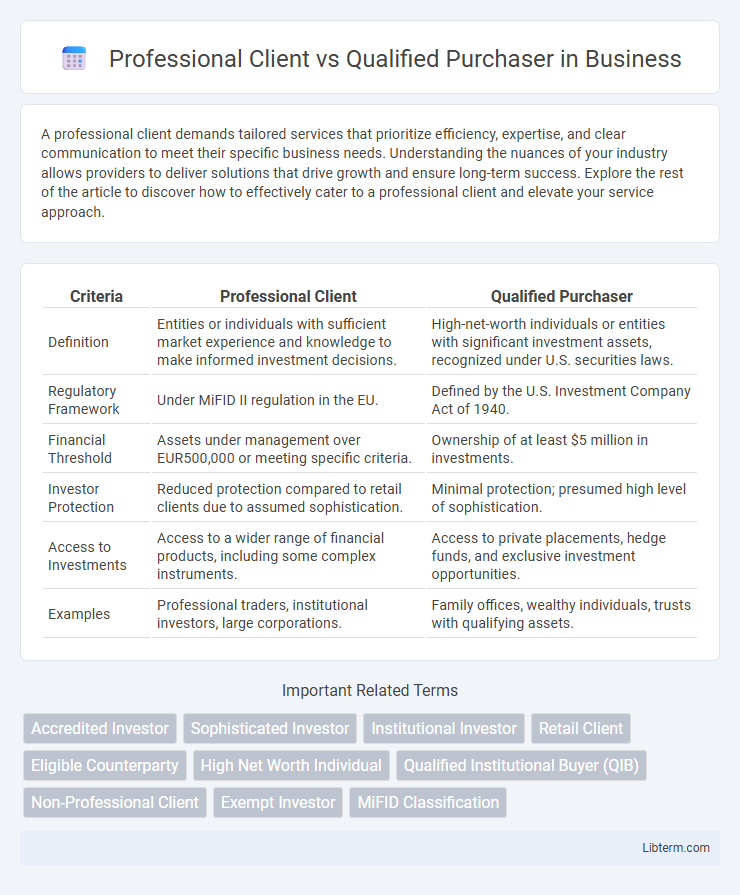
| Criteria | Professional Client | Qualified Purchaser |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entities or individuals with sufficient market experience and knowledge to make informed investment decisions. | High-net-worth individuals or entities with significant investment assets, recognized under U.S. securities laws. |
| Regulatory Framework | Under MiFID II regulation in the EU. | Defined by the U.S. Investment Company Act of 1940. |
| Financial Threshold | Assets under management over EUR500,000 or meeting specific criteria. | Ownership of at least $5 million in investments. |
| Investor Protection | Reduced protection compared to retail clients due to assumed sophistication. | Minimal protection; presumed high level of sophistication. |
| Access to Investments | Access to a wider range of financial products, including some complex instruments. | Access to private placements, hedge funds, and exclusive investment opportunities. |
| Examples | Professional traders, institutional investors, large corporations. | Family offices, wealthy individuals, trusts with qualifying assets. |
Introduction to Professional Clients and Qualified Purchasers
Professional Clients encompass financial institutions, large corporations, and high-net-worth individuals meeting specific regulatory criteria, granting them access to a broader range of investment products with reduced protections compared to retail clients. Qualified Purchasers represent an elite category defined primarily by the U.S. Investment Company Act of 1940, including individuals or entities owning at least $5 million in investments, allowing them to invest in private funds exempt from certain registration requirements. Understanding the distinctions between Professional Clients and Qualified Purchasers is essential for navigating investment opportunities and regulatory frameworks in global financial markets.
Defining a Professional Client
A Professional Client is defined under financial regulations as an entity or individual possessing the expertise, experience, and knowledge necessary to make informed investment decisions and properly assess risks involved. This classification typically includes financial institutions, large corporations, and government bodies that meet specific criteria related to size, market activity, or portfolio value. Being recognized as a Professional Client grants access to a broader range of investment services and exemptions from certain investor protections applicable to retail clients.
Who Qualifies as a Qualified Purchaser?
Qualified Purchasers include individuals or family-owned businesses owning at least $5 million in investments, as well as entities such as trusts and corporations holding $25 million or more in investments. These criteria surpass the thresholds for Professional Clients, who typically meet the regulation standards set for financial sophistication but may not reach the higher asset requirements of Qualified Purchasers. Qualification as a Qualified Purchaser grants access to exclusive investment opportunities under the Investment Company Act of 1940, often reserved for the wealthiest investors.
Regulatory Framework: Key Differences
Professional Clients are defined under MiFID II regulations, requiring firms to provide a lower level of investor protection compared to retail clients, while Qualified Purchasers fall under the U.S. Investment Company Act of 1940, enabling access to private funds and exempt securities offerings. The regulatory framework for Professional Clients emphasizes categorization based on experience, assets, and knowledge within the European Union, whereas Qualified Purchasers require meeting stringent asset thresholds, generally $5 million in investments, to qualify in the U.S. market. These distinctions impact disclosure obligations, suitability assessments, and the range of financial instruments accessible to each entity, reflecting differing investor protection standards and market scopes.
Eligibility Criteria Comparison
Professional Client eligibility requires entities or individuals to demonstrate sufficient financial sophistication and size, such as meeting thresholds for assets under management exceeding EUR500,000 or having relevant professional experience in financial markets. Qualified Purchaser status demands higher financial thresholds, including owning at least $5 million in investments or being an entity managing $25 million or more in investments, often limiting eligibility to institutional investors or affluent individuals. The key distinction lies in the Qualified Purchaser category's emphasis on significant asset levels and control over investments, surpassing the Professional Client's focus on expertise and moderate financial capacity.
Rights and Protections for Each Category
Professional Clients have access to a wide range of financial services with fewer regulatory protections due to their presumed expertise and ability to assess risks independently. Qualified Purchasers, typically high-net-worth individuals or entities with at least $5 million in investments, benefit from fewer investment restrictions but possess robust rights under the Investment Company Act of 1940, allowing greater flexibility in private fund participation. Both categories receive tailored rights and protections that balance regulatory oversight with their sophisticated investor status, ensuring appropriate disclosures and risk management relative to their financial acumen.
Investment Opportunities and Restrictions
Professional Clients benefit from broader investment opportunities due to lighter regulatory restrictions compared to Retail Clients, but they do not have access to all private investment vehicles reserved for Qualified Purchasers. Qualified Purchasers, defined by owning at least $5 million in investments, gain exclusive access to a wider range of private funds, hedge funds, and venture capital opportunities under the Investment Company Act exemptions. Regulatory frameworks impose stricter limitations on Professional Clients than on Qualified Purchasers, restricting their eligibility for certain high-risk, high-return investment options.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Professional Clients face stricter compliance rules under MiFID II, requiring firms to provide clear disclosures and ensure suitability assessments, while Qualified Purchasers under U.S. securities laws benefit from streamlined reporting obligations due to their sophisticated investor status. Compliance for Professional Clients involves detailed record-keeping, ongoing monitoring, and adherence to investor protection measures, whereas Qualified Purchasers are subject to less frequent disclosures but must still meet asset thresholds and certification standards. Firms dealing with both categories must implement tailored compliance frameworks to address jurisdiction-specific regulatory reporting and investor verification processes effectively.
Practical Implications for Financial Institutions
Professional Clients and Qualified Purchasers differ in regulatory criteria, affecting financial institutions' client onboarding and compliance processes. Financial institutions must implement enhanced due diligence for Qualified Purchasers, who typically hold higher net worth or investment thresholds, to align with stricter regulatory protections and disclosure requirements. Managing these distinctions ensures tailored investment opportunities and risk mitigation in portfolio management and advisory services.
Choosing the Right Classification for Your Needs
Choosing the right classification between Professional Client and Qualified Purchaser is essential for aligning investment opportunities with regulatory protections and eligibility criteria. Professional Clients typically benefit from broader access to financial services under MiFID II but face fewer investor protections compared to Qualified Purchasers, who meet higher asset thresholds and gain entry to exclusive private placements and hedge funds. Evaluating factors such as investment capital, risk tolerance, and legal requirements ensures an informed classification that maximizes portfolio growth while maintaining compliance.
Professional Client Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com