Profit sharing aligns employees' interests with company success by distributing a portion of profits as bonuses, boosting motivation and retention. This approach fosters teamwork and drives productivity by making employees feel directly invested in outcomes. Discover how profit sharing can transform your business dynamics and enhance overall performance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
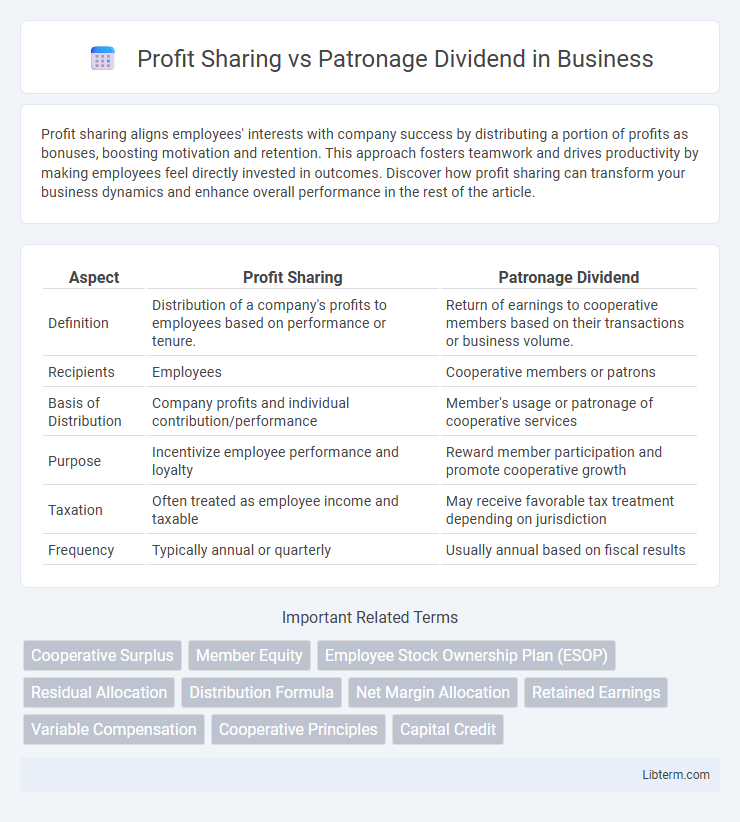
| Aspect | Profit Sharing | Patronage Dividend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distribution of a company's profits to employees based on performance or tenure. | Return of earnings to cooperative members based on their transactions or business volume. |
| Recipients | Employees | Cooperative members or patrons |
| Basis of Distribution | Company profits and individual contribution/performance | Member's usage or patronage of cooperative services |
| Purpose | Incentivize employee performance and loyalty | Reward member participation and promote cooperative growth |
| Taxation | Often treated as employee income and taxable | May receive favorable tax treatment depending on jurisdiction |
| Frequency | Typically annual or quarterly | Usually annual based on fiscal results |
Understanding Profit Sharing and Patronage Dividend
Profit sharing distributes a portion of a company's profits to employees based on predetermined criteria, aligning staff interests with business performance and incentivizing productivity. Patronage dividends are payments made to members of cooperatives, proportionate to their use of the cooperative's services, reflecting their direct contribution to the business. Understanding the distinction lies in profit sharing rewarding employment roles while patronage dividends reward patronage or participation in cooperative business activities.
Key Differences Between Profit Sharing and Patronage Dividend
Profit sharing distributes a portion of a company's profits to employees based on predetermined criteria, aiming to motivate and reward performance directly linked to the business's success. Patronage dividends are payments returned to cooperative members or customers proportional to their transactions or usage, emphasizing equitable benefit distribution rather than individual performance. Key differences lie in their recipients--employees versus cooperative members--and calculation methods--profit percentage versus patronage volume.
How Profit Sharing Works in Organizations
Profit sharing in organizations involves distributing a portion of the company's profits to employees based on predetermined criteria such as salary level or performance metrics. This incentive aligns employees' interests with organizational success, promoting productivity and retention by providing financial rewards linked directly to the company's profitability. Unlike patronage dividends, which return surplus funds to customers or members based on their usage, profit sharing exclusively benefits employees to motivate engagement and contribution to business growth.
The Mechanism of Patronage Dividend in Cooperatives
Patronage dividends in cooperatives are distributed based on each member's level of participation, typically proportional to the amount of business conducted with the cooperative. This mechanism aligns members' interests with the cooperative's success by returning surplus earnings relative to their patronage volume, rather than through fixed profit shares. The approach fosters equitable allocation of financial benefits, reinforcing member engagement and democratic control within the cooperative structure.
Advantages of Profit Sharing for Employees
Profit sharing offers employees a direct financial stake in the company's success, boosting motivation and fostering a sense of ownership. This approach aligns employee interests with corporate goals, often leading to improved productivity and job satisfaction. Furthermore, profit sharing provides immediate cash rewards, enhancing employees' overall compensation without diluting equity.
Benefits of Patronage Dividend for Members
Patronage dividends directly reward members based on their level of participation, aligning profits with individual contributions and fostering a sense of ownership. This system encourages loyalty and consistent engagement, as members receive returns proportional to their use of cooperative services. Unlike profit sharing, which typically distributes earnings equally or based on salary, patronage dividends provide equitable financial benefits tied to actual member activity, promoting fairness and transparency.
Tax Implications: Profit Sharing vs Patronage Dividend
Profit sharing distributions are treated as ordinary income and taxed at the recipient's individual income tax rate, impacting the overall taxable income. Patronage dividends, often issued by cooperatives, may qualify for favorable tax treatment, such as being deductible by the cooperative and potentially taxed at lower rates for members, depending on the patronage agreement. Understanding the specific tax codes and IRS guidelines governing each is crucial for accurate tax reporting and optimizing after-tax returns.
Eligibility Criteria for Profit Sharing and Patronage Dividend
Profit sharing eligibility typically requires employees to meet defined service length or performance benchmarks set by the employer, often linked to company profits and individual contribution. Patronage dividend eligibility is generally based on membership or customer status within a cooperative or mutual organization, with dividends distributed proportionally based on the amount of business conducted with the entity. Both systems emphasize rewarding stakeholders, but profit sharing focuses on employee participation while patronage dividends prioritize cooperative members' engagement.
Real-World Examples of Profit Sharing and Patronage Dividend
Profit sharing is commonly practiced in companies such as Microsoft, where employees receive a portion of the company's profits based on individual or collective performance metrics, enhancing motivation and retention. Patronage dividends are prominent in cooperative businesses like REI Co-op, where members earn dividends proportional to their purchases, reinforcing member loyalty and democratic control. These real-world examples highlight how profit sharing aligns employees' interests with company success, while patronage dividends emphasize member benefits in cooperative models.
Choosing the Right Incentive: Profit Sharing or Patronage Dividend
Selecting the appropriate incentive between profit sharing and patronage dividend depends on organizational structure and stakeholder involvement. Profit sharing distributes earnings based on employee compensation, aligning employee performance with company profitability, while patronage dividends allocate returns proportional to member transactions in cooperatives, emphasizing member participation. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses tailor incentives to motivate employees or reward member engagement effectively.
Profit Sharing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com