Quantitative analysis involves the use of mathematical and statistical methods to evaluate numerical data and identify patterns or trends. It is essential for making data-driven decisions in finance, marketing, and operations. Explore the article to discover how quantitative analysis can enhance your strategic planning and business outcomes.
Table of Comparison
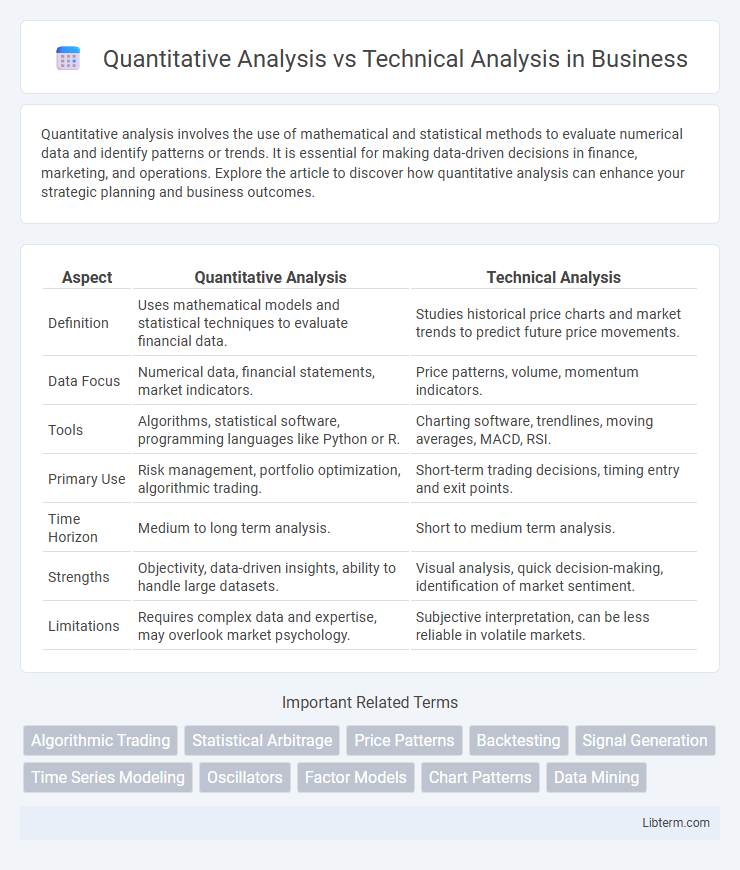
| Aspect | Quantitative Analysis | Technical Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses mathematical models and statistical techniques to evaluate financial data. | Studies historical price charts and market trends to predict future price movements. |
| Data Focus | Numerical data, financial statements, market indicators. | Price patterns, volume, momentum indicators. |
| Tools | Algorithms, statistical software, programming languages like Python or R. | Charting software, trendlines, moving averages, MACD, RSI. |
| Primary Use | Risk management, portfolio optimization, algorithmic trading. | Short-term trading decisions, timing entry and exit points. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term analysis. | Short to medium term analysis. |
| Strengths | Objectivity, data-driven insights, ability to handle large datasets. | Visual analysis, quick decision-making, identification of market sentiment. |
| Limitations | Requires complex data and expertise, may overlook market psychology. | Subjective interpretation, can be less reliable in volatile markets. |
Introduction to Quantitative and Technical Analysis
Quantitative analysis leverages mathematical models, statistical techniques, and algorithmic trading strategies to evaluate financial data and predict market trends with high precision. Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts, trading volumes, and various indicators like moving averages and Relative Strength Index (RSI) to identify patterns and forecast future price movements. Both methods provide critical tools for investors and traders to make informed decisions, with quantitative analysis emphasizing data-driven algorithms while technical analysis focuses on market psychology and trend recognition.
Defining Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves the use of mathematical models, statistical techniques, and algorithms to evaluate financial data and identify investment opportunities. It relies on numerical data, historical price patterns, and financial metrics to forecast market trends and optimize portfolio performance. This method contrasts with technical analysis, which primarily uses chart patterns and market sentiment to make trading decisions.
Understanding Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on analyzing historical price data and trading volumes using chart patterns, trend lines, and technical indicators like moving averages and relative strength index (RSI) to predict future market movements. This method relies on market psychology and price action to identify entry and exit points, emphasizing short-term price fluctuations over fundamental factors. Traders use tools such as candlestick charts and Bollinger Bands to gauge momentum, volatility, and potential reversal points within financial markets.
Key Differences Between Quantitative and Technical Analysis
Quantitative analysis relies on mathematical models, statistical techniques, and algorithms to evaluate financial data and predict market trends, emphasizing data-driven decision-making. Technical analysis focuses on price charts, patterns, and trading indicators to identify market sentiment and potential entry or exit points, primarily based on historical price action. Key differences include the use of quantitative analysis for systematic strategy development and risk management, whereas technical analysis is more subjective and relies on visual interpretation of market behavior.
Data Sources and Tools Used
Quantitative analysis relies heavily on structured numerical data such as historical price series, financial statements, economic indicators, and market sentiment metrics, utilizing advanced statistical methods, algorithms, and programming languages like Python, R, and MATLAB for backtesting and predictive modeling. Technical analysis primarily depends on price and volume data derived from market charts, employing tools such as moving averages, trendlines, oscillators (e.g., RSI, MACD), and chart patterns to identify trading signals and market trends. Both approaches harness proprietary databases, real-time feeds, and specialized software platforms like Bloomberg Terminal, MetaTrader, and QuantConnect to enhance decision-making accuracy.
Applications in Financial Markets
Quantitative analysis employs mathematical models and statistical techniques to evaluate financial data, enabling algorithmic trading, risk management, and portfolio optimization. Technical analysis focuses on price patterns, volume, and historical market data to predict future price movements, widely used in day trading and market timing strategies. Both methods complement each other, with quantitative analysis offering data-driven insights and technical analysis providing behavioral market context in financial decision-making.
Pros and Cons of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis relies on mathematical models and statistical techniques to evaluate financial data, offering objective and data-driven investment decisions with reduced emotional bias. It excels in processing vast datasets and identifying patterns but may struggle with unexpected market events or qualitative factors such as management changes or geopolitical risks. The complexity of model development and the risk of overfitting also present significant challenges for quantitative analysts.
Pros and Cons of Technical Analysis
Technical Analysis offers the advantage of identifying market trends and price patterns through charting tools and indicators, enabling traders to make timely decisions based on historical price movements. However, it relies heavily on past data, which may not always predict future market behavior accurately, and can be influenced by subjective interpretation of charts. This approach may also overlook fundamental market factors such as economic indicators and company performance, potentially leading to incomplete analysis.
Integrating Both Approaches
Integrating both quantitative analysis and technical analysis enhances trading strategies by combining robust statistical models with price action and chart pattern insights. Quantitative analysis leverages algorithms, historical data, and mathematical techniques to identify trends and optimize portfolio performance, while technical analysis focuses on market sentiment, momentum indicators, and support-resistance levels. Combining these approaches enables traders to validate signals, improve risk management, and achieve more consistent, data-driven decision-making in volatile markets.
Choosing the Right Analysis for Your Investment Strategy
Quantitative analysis leverages mathematical models and statistical techniques to evaluate investments, emphasizing objective data and algorithm-driven decision-making. Technical analysis relies on historical price patterns and trading volume trends to forecast future market behavior, appealing to investors focused on timing trades. Selecting the right analysis depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and whether you prioritize data-driven precision or market sentiment insights.
Quantitative Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com