Green bonds finance projects that have positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or conservation initiatives. Social bonds support projects addressing social issues like affordable housing, education, and healthcare improvement. Explore the article to understand how these bonds can align with Your sustainable investment goals.
Table of Comparison
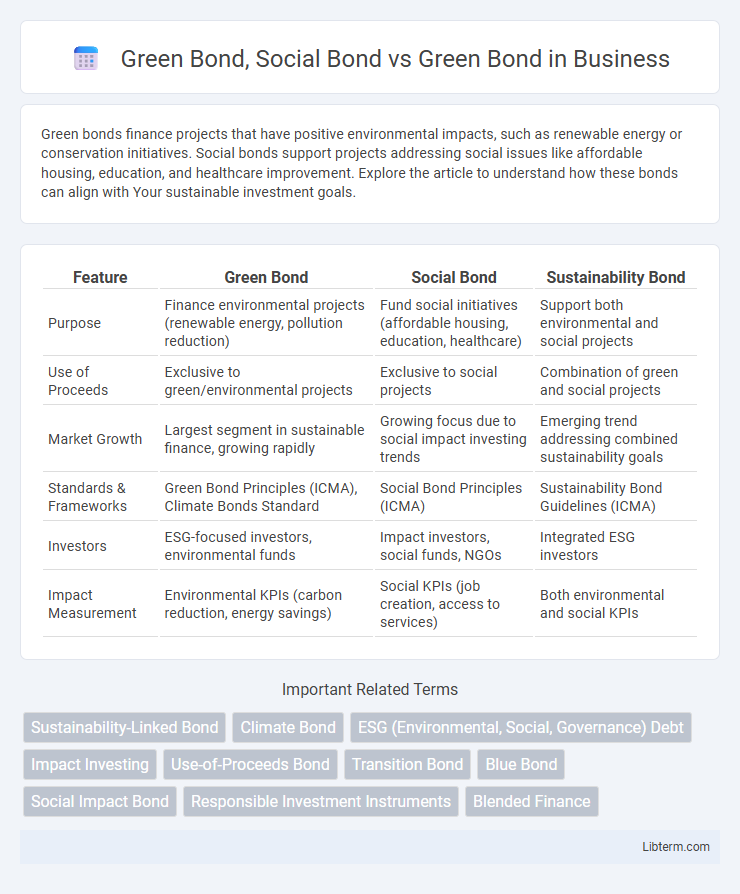
| Feature | Green Bond | Social Bond | Sustainability Bond |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Finance environmental projects (renewable energy, pollution reduction) | Fund social initiatives (affordable housing, education, healthcare) | Support both environmental and social projects |
| Use of Proceeds | Exclusive to green/environmental projects | Exclusive to social projects | Combination of green and social projects |
| Market Growth | Largest segment in sustainable finance, growing rapidly | Growing focus due to social impact investing trends | Emerging trend addressing combined sustainability goals |
| Standards & Frameworks | Green Bond Principles (ICMA), Climate Bonds Standard | Social Bond Principles (ICMA) | Sustainability Bond Guidelines (ICMA) |
| Investors | ESG-focused investors, environmental funds | Impact investors, social funds, NGOs | Integrated ESG investors |
| Impact Measurement | Environmental KPIs (carbon reduction, energy savings) | Social KPIs (job creation, access to services) | Both environmental and social KPIs |
Introduction to Green Bonds
Green Bonds are debt instruments specifically designed to fund projects with environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. Social Bonds, while similar in structure, prioritize financing initiatives that generate positive social outcomes, including affordable housing and healthcare access. Understanding Green Bonds as a subset of Sustainable Bonds highlights their role in driving capital towards climate-friendly projects, thereby promoting environmental sustainability and meeting investor demand for eco-conscious assets.
Overview of Social Bonds
Social bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects that generate positive social outcomes, such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare access, targeting underprivileged communities. Unlike green bonds, which specifically fund environmental initiatives like renewable energy and climate adaptation, social bonds emphasize social impact and community well-being. The global social bond market has seen rapid growth, driven by investor demand for sustainable development aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Key Features of Green Bonds
Green Bonds are debt instruments specifically designed to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution prevention. Key features include transparency through dedicated use of proceeds, independent third-party verification, and alignment with international standards like the Green Bond Principles (GBP). In contrast, Social Bonds focus on funding projects with social benefits such as affordable housing and healthcare, emphasizing social outcomes over environmental impacts.
Key Features of Social Bonds
Social Bonds primarily finance projects that address social issues such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare, ensuring measurable social outcomes. Unlike Green Bonds which focus exclusively on environmental benefits, Social Bonds emphasize social impact by targeting underserved communities and promoting social inclusion. Key features include rigorous eligibility criteria, transparent reporting on social outcomes, and alignment with international social frameworks like the Social Bond Principles (SBP).
Differences Between Green and Social Bonds
Green bonds finance projects with positive environmental impacts such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction. Social bonds allocate capital to initiatives addressing social issues like affordable housing, healthcare, education, and community development. The primary difference lies in their purpose: green bonds target environmental sustainability, while social bonds focus on social welfare and inclusive growth.
Environmental Impact: Green Bonds Focus
Green Bonds are specifically designed to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction, whereas Social Bonds primarily target social outcomes like affordable housing or healthcare. The environmental focus of Green Bonds ensures capital is directed toward initiatives that mitigate climate change and promote sustainability, driving measurable reductions in carbon emissions and resource consumption. By contrast, Social Bonds may include environmental projects but do not prioritize environmental metrics as the core objective, emphasizing social benefits instead.
Social Impact: Social Bonds Focus
Social Bonds prioritize funding projects that generate measurable social benefits, such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare improvements, directly addressing community needs. Unlike Green Bonds which target environmental sustainability through projects like renewable energy and pollution reduction, Social Bonds emphasize social impact and equitable development. Investors seeking to support social inclusion, poverty alleviation, and human welfare often prefer Social Bonds for their targeted social outcomes and transparent impact reporting.
Market Trends and Growth: Green vs Social Bonds
Green bonds have experienced rapid market growth, reaching over $500 billion in cumulative issuance by 2023, driven by increasing investor demand for climate-focused investments. Social bonds, while smaller in scale, have grown significantly, with issuance surpassing $150 billion as investors prioritize social impact amid global challenges such as poverty and healthcare. Market trends indicate that green bonds maintain a larger share of sustainable finance despite rapid expansion in social bonds, reflecting diverging but complementary investor priorities in environmental and social objectives.
Investment Opportunities and Risks
Green bonds, focused on financing environmentally sustainable projects, offer investors opportunities to benefit from the growing green economy and align portfolios with ESG criteria, while social bonds target funding for projects addressing social issues such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare. Green bonds typically present lower risks related to regulatory compliance and reputation due to established environmental standards, whereas social bonds may carry higher risks stemming from less standardized impact measurement and potential social outcome uncertainties. Both bond types attract capital from investors seeking sustainable impact but require careful assessment of project credibility, impact verification, and evolving market regulations to mitigate investment risks.
Future Outlook for Green and Social Bonds
Green bonds are dedicated to financing environmentally sustainable projects, while social bonds focus on addressing social issues such as affordable housing and healthcare access. The future outlook for green and social bonds is promising as global emphasis on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria drives increased investor demand and regulatory support. Market forecasts project substantial growth in issuance volumes, with innovations in reporting standards enhancing transparency and attracting mainstream capital.
Green Bond, Social Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com