Payroll count directly impacts your business's financial management by determining the exact number of employees to be compensated during each pay period. Accurate payroll counts ensure compliance with tax regulations and prevent costly errors in salary disbursement. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective methods for maintaining precise payroll counts and optimizing your payroll process.
Table of Comparison
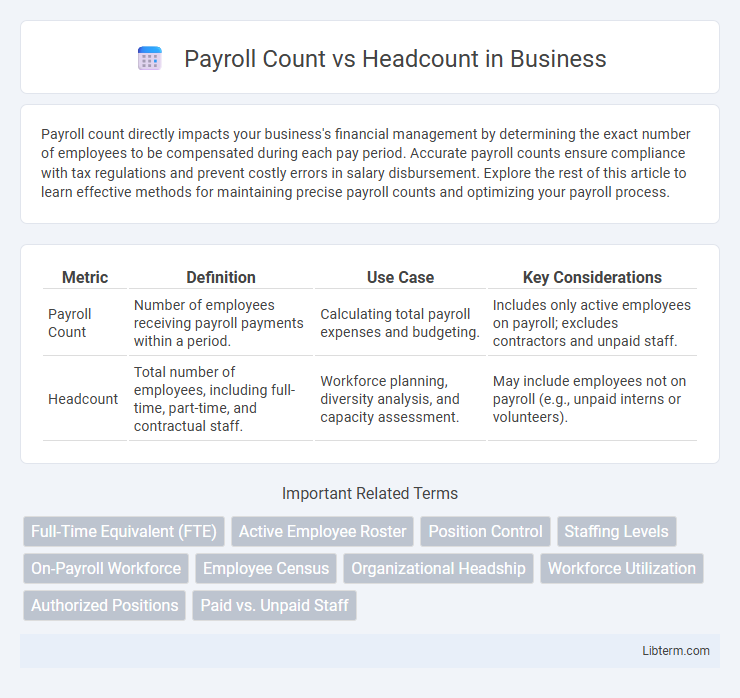
| Metric | Definition | Use Case | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payroll Count | Number of employees receiving payroll payments within a period. | Calculating total payroll expenses and budgeting. | Includes only active employees on payroll; excludes contractors and unpaid staff. |
| Headcount | Total number of employees, including full-time, part-time, and contractual staff. | Workforce planning, diversity analysis, and capacity assessment. | May include employees not on payroll (e.g., unpaid interns or volunteers). |
Understanding Payroll Count and Headcount
Payroll count represents the total number of employees receiving salary or wages within an organization, including full-time, part-time, and contractual workers actively on the payroll during a specific period. Headcount refers to the total number of individuals employed, regardless of their payment status or hours worked, encompassing active employees, leave, and sometimes temporary personnel. Differentiating between payroll count and headcount is essential for accurate workforce planning, budgeting, and compliance with labor regulations.
Defining Payroll Count
Payroll Count refers to the total number of employees who receive compensation through a company's payroll system within a specific period, encompassing full-time, part-time, temporary, and contract workers. This metric is crucial for calculating labor costs, tax obligations, and compliance with employment regulations. Unlike Headcount, which simply counts employees on the roster, Payroll Count provides a precise measure of individuals actively compensated, reflecting the organization's financial commitments.
What is Headcount?
Headcount refers to the total number of employees within an organization, representing individual personnel regardless of their employment status or hours worked. It includes full-time, part-time, temporary, and contract workers, providing a comprehensive snapshot of the workforce size. Headcount is essential for organizational planning, budgeting, and assessing workforce capacity.
Key Differences Between Payroll Count and Headcount
Payroll count measures the number of employees receiving payment during a specific period, including full-time, part-time, and temporary workers counted based on active payroll records. Headcount represents the total number of employees employed by a company, regardless of payroll status or hours worked, reflecting overall workforce size on a given date. Key differences include payroll count's focus on compensation and pay periods, while headcount emphasizes the total employee roster without weighting for payroll processing or employment status variations.
Why Payroll Count Matters in HR Analytics
Payroll count provides a precise measure of employees actively compensated within a payroll period, reflecting actual workforce costs and financial accuracy in HR analytics. Unlike headcount, which includes all employees regardless of pay status, payroll count offers critical insights into labor expenses, overtime trends, and productivity metrics. This distinction enables organizations to optimize budgeting, forecast labor needs accurately, and enhance decision-making in workforce management.
The Importance of Accurate Headcount
Accurate headcount is essential for effective payroll management, ensuring precise salary disbursements and compliance with labor laws. Discrepancies between payroll count and headcount can lead to financial errors, tax reporting issues, and budget misallocations. Maintaining accurate headcount data supports strategic workforce planning and optimizes human resource allocation.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Payroll Count vs Headcount
Confusing payroll count with headcount often leads to inaccurate labor cost analysis, as payroll count includes only employees receiving compensation while headcount encompasses all employees, including unpaid interns or contractors. Overlooking part-time and seasonal workers can skew payroll calculations, resulting in underreported labor expenses and budgeting errors. Failure to reconcile discrepancies between payroll data and HR records causes compliance risks and misinformed strategic decisions.
Impact on Budgeting and Workforce Planning
Payroll count reflects the number of employees actively receiving compensation, directly influencing labor cost forecasts and budget allocations. Headcount includes all employees, such as those on unpaid leave or inactive status, providing a broader understanding of workforce capacity and future staffing needs. Accurate differentiation between payroll count and headcount ensures precise budgeting and effective workforce planning by aligning financial resources with actual payroll obligations and strategic talent management goals.
Payroll Count vs Headcount: Which Metric to Use?
Payroll count measures the number of employees actively receiving paychecks during a specific period, while headcount includes all individuals on the organization's roster regardless of pay status. Companies should use payroll count to assess labor costs and budgeting, as it reflects actual workforce expenses. Headcount remains essential for understanding total workforce size and planning resources but can overstate active employee numbers when including leave or inactive employees.
Best Practices for Tracking Payroll Count and Headcount
Payroll count and headcount represent distinct metrics; payroll count tracks employees receiving compensation within a pay period, while headcount reflects the total number of active employees regardless of pay status. Best practices for tracking include integrating HRIS and payroll systems to maintain data accuracy, regularly auditing records to reconcile discrepancies, and using real-time dashboards for timely insights. Ensuring clear definitions and consistent updates supports compliance, budgeting, and workforce planning across organizational levels.
Payroll Count Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com