Venture capital fuels innovation by providing startups with crucial funding and strategic guidance to scale rapidly in competitive markets. Investors seek high-growth potential companies that can disrupt industries and deliver substantial returns on investment. Discover how venture capital can transform Your business prospects in the full article.
Table of Comparison
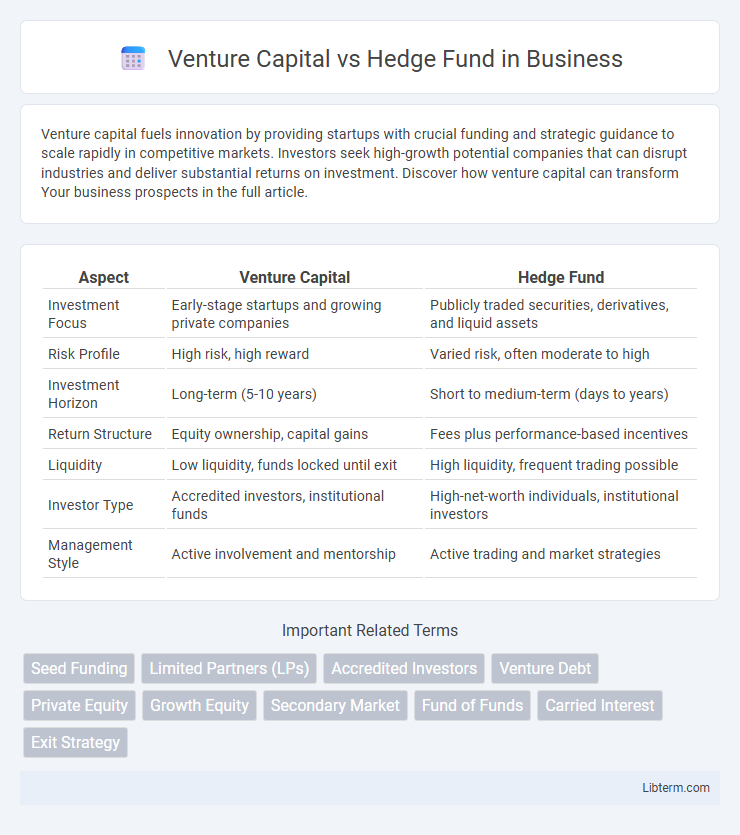
| Aspect | Venture Capital | Hedge Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Focus | Early-stage startups and growing private companies | Publicly traded securities, derivatives, and liquid assets |
| Risk Profile | High risk, high reward | Varied risk, often moderate to high |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term (5-10 years) | Short to medium-term (days to years) |
| Return Structure | Equity ownership, capital gains | Fees plus performance-based incentives |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity, funds locked until exit | High liquidity, frequent trading possible |
| Investor Type | Accredited investors, institutional funds | High-net-worth individuals, institutional investors |
| Management Style | Active involvement and mentorship | Active trading and market strategies |
Introduction to Venture Capital and Hedge Funds
Venture capital involves investing in early-stage startups with high growth potential, providing funding in exchange for equity. Hedge funds employ diverse strategies, including long and short positions, to generate high returns for accredited investors through pooled capital. Both serve distinct roles in the financial ecosystem, targeting different types of assets and investment horizons.
Key Differences Between Venture Capital and Hedge Funds
Venture capital primarily invests in early-stage startups with high growth potential, while hedge funds deploy capital in diverse assets, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives, aiming for short-term returns. Venture capital investments are typically illiquid and involve active management to nurture portfolio companies, whereas hedge funds offer more liquidity and employ various strategies like long-short equity, arbitrage, and leverage. Risk profiles also differ; venture capital faces high failure risk with potentially outsized rewards, while hedge funds manage risk through diversification and hedging techniques.
Investment Strategies: Venture Capital vs Hedge Funds
Venture capital focuses on early-stage investments in startups with high growth potential, emphasizing long-term value creation through equity stakes and active involvement in company development. Hedge funds employ diverse investment strategies, including long/short equity, arbitrage, and derivatives, aiming for high returns with risk management across various asset classes. Venture capital prioritizes illiquid, high-risk ventures, whereas hedge funds target liquid markets with flexible, often short-term positions.
Risk Profiles and Return Expectations
Venture capital typically involves high risk with the potential for substantial long-term returns by investing in early-stage startups, while hedge funds employ diverse strategies aiming for more immediate, moderate returns with varied risk levels. Venture capital investments are illiquid and concentrated in innovative companies, leading to unpredictable outcomes but significant upside potential. Hedge funds diversify assets across equities, derivatives, and other instruments to manage volatility and generate consistent returns regardless of market conditions.
Types of Investors in Each Fund
Venture capital funds primarily attract institutional investors such as pension funds, endowments, and family offices, alongside high-net-worth individuals seeking high-growth opportunities in early-stage startups. Hedge funds tend to draw a broader range of sophisticated investors including accredited individuals, institutional investors, and fund of funds looking for diversified strategies with active risk management. Both fund types demand significant minimum investments and target investors with a strong risk tolerance and long-term capital commitment.
Fund Structure and Regulatory Environment
Venture capital funds typically operate as limited partnerships with general partners managing investments in early-stage startups, facing lighter regulatory scrutiny mainly under the Investment Advisers Act. Hedge funds also use limited partnership structures but invest across diverse asset classes, subject to more stringent regulations including periodic disclosures and compliance with the Securities Act and the Dodd-Frank Act. The distinct regulatory frameworks influence fund strategies, investor eligibility, and reporting requirements, shaping the operational dynamics of venture capital versus hedge funds.
Capital Deployment and Holding Periods
Venture capital typically involves deploying capital into early-stage startups with a holding period ranging from 5 to 10 years, aiming for significant growth and eventual exit through IPO or acquisition. Hedge funds deploy capital across a wide range of liquid assets including equities, derivatives, and fixed income, with holding periods that can vary from seconds to months depending on the trading strategy. Venture capital emphasizes long-term value creation, while hedge funds prioritize liquidity and short- to medium-term returns.
Sectors and Stages of Investment Focus
Venture capital firms primarily invest in early-stage startups within high-growth sectors such as technology, healthcare, and clean energy, focusing on seed to Series C funding rounds to support innovation and scale. Hedge funds target more mature companies across diverse sectors including equities, fixed income, and commodities, employing strategies that range from long-short equity to arbitrage for short-term and diversified returns. The fundamental difference lies in venture capital's emphasis on nurturing emerging enterprises, whereas hedge funds concentrate on maximizing financial gains through flexible, market-driven investments.
How to Choose Between Venture Capital and Hedge Funds
Choosing between venture capital and hedge funds depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Venture capital suits investors seeking high growth through early-stage companies with longer lock-up periods, while hedge funds offer diversified strategies with more liquidity and potentially lower risk. Understanding the differences in fund structure, investment strategy, and expected returns is essential for aligning with your financial objectives.
Future Trends in Venture Capital and Hedge Fund Industries
The venture capital industry is increasingly adopting artificial intelligence and data analytics to identify high-potential startups, driving more informed investment decisions and faster scalability. Hedge funds are focusing on algorithmic trading and sustainable investment strategies, integrating ESG criteria to attract ethical investors while enhancing portfolio performance. Both industries are witnessing a surge in globalization, with emerging markets presenting new opportunities and risks shaped by geopolitical shifts and regulatory changes.
Venture Capital Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com