A joint venture allows two or more businesses to collaborate by pooling resources, expertise, and market access to achieve common goals and share profits. This strategic partnership can accelerate growth, reduce risks, and enhance competitive advantage in new or existing markets. Discover how forming a joint venture can benefit your business and what steps to follow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
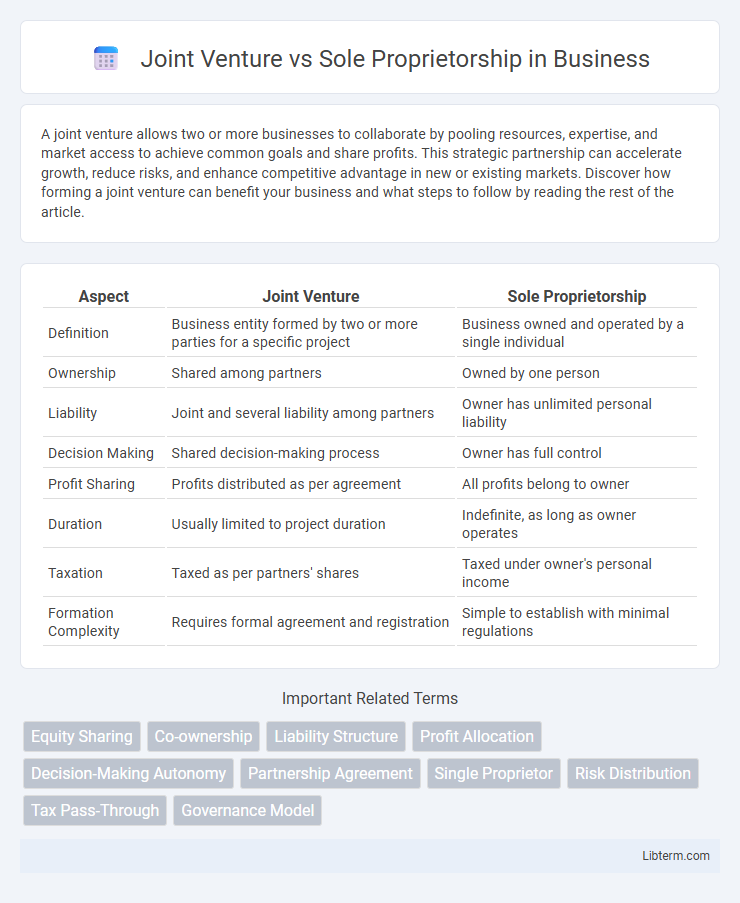
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Sole Proprietorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business entity formed by two or more parties for a specific project | Business owned and operated by a single individual |
| Ownership | Shared among partners | Owned by one person |
| Liability | Joint and several liability among partners | Owner has unlimited personal liability |
| Decision Making | Shared decision-making process | Owner has full control |
| Profit Sharing | Profits distributed as per agreement | All profits belong to owner |
| Duration | Usually limited to project duration | Indefinite, as long as owner operates |
| Taxation | Taxed as per partners' shares | Taxed under owner's personal income |
| Formation Complexity | Requires formal agreement and registration | Simple to establish with minimal regulations |
Understanding Joint Ventures: Definition and Features
A joint venture is a strategic business arrangement where two or more parties collaborate by pooling resources, sharing risks, and combining expertise to achieve a specific project or business goal, distinct from creating a new legal entity like a partnership. Key features of joint ventures include shared ownership, joint control over operations, and a defined timeline or project scope, often outlined in a formal agreement specifying profit and loss distribution. Unlike sole proprietorships, where a single individual owns and manages the entire business with unlimited liability, joint ventures promote collaborative decision-making and resource sharing without dissolving the individual identities of the participating entities.
What is a Sole Proprietorship? Key Characteristics
A sole proprietorship is a business entity owned and operated by a single individual, offering complete control and decision-making authority to the owner. Key characteristics include unlimited personal liability, meaning the owner is personally responsible for all business debts and obligations. This structure is simple to establish, with minimal regulatory requirements and tax benefits as business income is reported on the owner's personal tax return.
Formation Process: Joint Venture vs Sole Proprietorship
The formation process of a joint venture requires a formal agreement between two or more parties outlining shared responsibilities, contributions, and profit distribution, ensuring clear legal and operational frameworks. In contrast, a sole proprietorship is established by a single individual with minimal legal formalities, often requiring only registration with local authorities and obtaining necessary licenses. Joint ventures typically involve more complex documentation and negotiation due to multiple stakeholders, while sole proprietorships offer a straightforward setup ideal for individual entrepreneurs.
Liability and Risk Comparison
Joint ventures distribute liability among participating partners, reducing individual risk exposure compared to sole proprietorships, where the owner bears unlimited personal liability for business debts and obligations. In a sole proprietorship, the proprietor's personal assets are at risk in case of legal claims or financial losses, while in joint ventures, liability is typically shared according to the partnership agreement and can be limited through specific contractual arrangements. Risk management in joint ventures often involves mutual decision-making and resource sharing, whereas sole proprietors assume full responsibility for operational risks and liabilities.
Tax Implications of Joint Ventures and Sole Proprietorships
Joint ventures and sole proprietorships differ significantly in their tax implications; joint ventures are typically treated as pass-through entities where profits and losses are reported on the partners' individual tax returns, avoiding double taxation. Sole proprietorships file taxes using Schedule C on the owner's personal tax return, with income subject to self-employment tax. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective tax planning and compliance in business operations.
Capital and Funding Differences
Joint ventures pool capital from multiple partners, allowing access to diverse funding sources and shared financial risk, which can lead to larger investment opportunities. Sole proprietorships rely solely on the owner's personal funds or loans, limiting capital availability and concentrating financial risk on one individual. The collaborative funding structure of joint ventures often enables more substantial and flexible capital allocation compared to the single-source funding in sole proprietorships.
Management and Decision-Making Structures
Joint ventures involve collaborative management where partners share decision-making authority based on agreed roles and contributions, enabling pooled expertise and risk distribution. Sole proprietorships centralize management and decision-making power solely with the owner, allowing swift actions but exposing the business to individual accountability. These structural differences significantly impact strategic planning, operational control, and liability in each business model.
Flexibility and Control in Operations
A joint venture offers shared control and collaborative decision-making, allowing partners to leverage combined expertise and resources while dividing operational responsibilities. Sole proprietorship provides complete autonomy and flexibility for the owner to make swift decisions without consulting others, enabling rapid adaptation to changing business conditions. However, sole proprietorship carries the risk of limited perspectives, whereas joint ventures benefit from diverse input but may face challenges in aligning interests during operations.
Pros and Cons: Joint Venture vs Sole Proprietorship
Joint ventures provide shared resources, risks, and expertise, facilitating larger projects and market expansion, but require clear agreements to avoid conflicts and often involve profit-sharing. Sole proprietorships offer full control and simplicity with fewer regulatory requirements, allowing for quick decision-making, yet expose owners to unlimited personal liability and limit capital-raising opportunities. Choosing between a joint venture and sole proprietorship depends on factors like risk tolerance, funding needs, and desired level of management autonomy.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Selecting the right business structure depends on factors such as capital requirements, risk tolerance, and management style. A joint venture allows multiple parties to share resources and expertise while limiting individual liability, making it ideal for collaborative projects with defined timelines. In contrast, a sole proprietorship offers full control and simplicity but exposes the owner to unlimited personal liability, suitable for single-person startups with low risk.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com