Franchising offers a proven business model that allows entrepreneurs to leverage established brand recognition and operational support. By investing in a franchise, you gain access to a network of resources, training, and marketing strategies designed to increase your chances of success. Explore the rest of the article to discover how franchising can be the right path for your business ambitions.
Table of Comparison
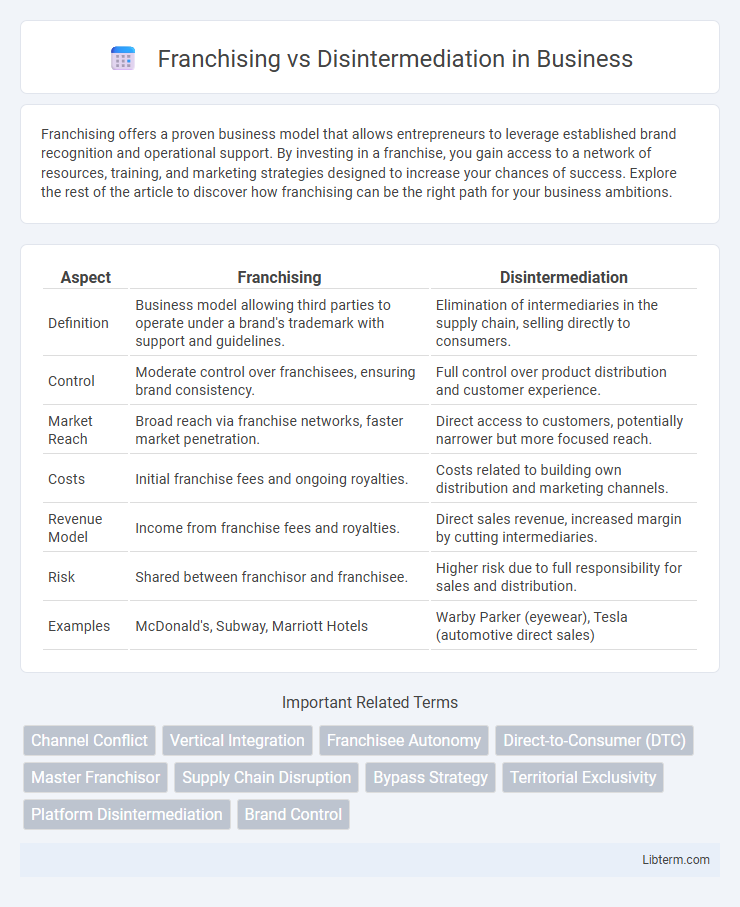
| Aspect | Franchising | Disintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model allowing third parties to operate under a brand's trademark with support and guidelines. | Elimination of intermediaries in the supply chain, selling directly to consumers. |
| Control | Moderate control over franchisees, ensuring brand consistency. | Full control over product distribution and customer experience. |
| Market Reach | Broad reach via franchise networks, faster market penetration. | Direct access to customers, potentially narrower but more focused reach. |
| Costs | Initial franchise fees and ongoing royalties. | Costs related to building own distribution and marketing channels. |
| Revenue Model | Income from franchise fees and royalties. | Direct sales revenue, increased margin by cutting intermediaries. |
| Risk | Shared between franchisor and franchisee. | Higher risk due to full responsibility for sales and distribution. |
| Examples | McDonald's, Subway, Marriott Hotels | Warby Parker (eyewear), Tesla (automotive direct sales) |
Introduction to Franchising and Disintermediation
Franchising is a business model where a franchisor grants the franchisee the right to operate a business using the franchisor's brand, products, and support systems, fostering rapid expansion and brand consistency. Disintermediation involves the removal of intermediaries in the supply chain to allow direct transactions between producers and consumers, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Both strategies impact market dynamics differently, with franchising emphasizing network growth and control, while disintermediation focuses on streamlining distribution and enhancing direct customer relationships.
Defining Franchising: Structure and Models
Franchising is a business model where a franchisor licenses its brand, products, and operational methods to franchisees in exchange for fees or royalties, creating a network of independently owned outlets under a unified brand. The primary structures include product distribution franchising, where the franchisee sells the franchisor's goods, and business format franchising, which offers an entire business system including marketing, training, and support. This model contrasts sharply with disintermediation, where intermediaries are removed to enable direct relationships between producers and consumers.
Understanding Disintermediation in Business
Disintermediation in business removes traditional intermediaries, allowing companies to interact directly with customers, which reduces costs and increases control over the supply chain. Unlike franchising, which relies on a network of authorized partners to distribute goods or services, disintermediation leverages digital platforms and technology to streamline operations and enhance customer experience. This shift enables businesses to improve efficiency, gather direct customer feedback, and adapt quickly to market changes.
Key Differences Between Franchising and Disintermediation
Franchising involves a contractual agreement where a franchisor grants a franchisee the rights to operate under its brand and business model, ensuring brand consistency and support. Disintermediation eliminates intermediaries in the supply chain, enabling manufacturers or service providers to sell directly to consumers, often reducing costs and increasing control over customer relations. Key differences include the relationship structure--franchise vs. direct control--and the presence of a formal business system in franchising versus a streamlined, direct-to-consumer approach in disintermediation.
Benefits of Franchising for Entrepreneurs
Franchising offers entrepreneurs the benefit of a proven business model, reducing the risk associated with startups by leveraging established brand recognition and operational support. Franchisees gain access to comprehensive training, marketing resources, and ongoing assistance, which enhances their chances of success and accelerates business growth. This structured system allows entrepreneurs to focus on management and customer service rather than developing products or marketing strategies from scratch.
Advantages of Disintermediation for Companies
Disintermediation allows companies to eliminate intermediaries, resulting in increased profit margins and more direct control over customer relationships. This approach enhances efficiency by reducing distribution costs and improving supply chain transparency. Companies benefit from faster feedback loops and greater agility in adapting to market changes without relying on franchising restrictions.
Challenges and Risks of Franchising
Franchising faces significant challenges including maintaining brand consistency, managing franchisee compliance, and controlling operational standards across diverse locations. Risks involve potential legal disputes over franchise agreements, dependency on franchisees' performance, and the financial burden of support and training. These factors can hinder growth and undermine the overall brand reputation if not effectively addressed.
Potential Pitfalls of Disintermediation
Disintermediation can lead to significant challenges such as increased operational complexity and the loss of valuable intermediaries who provide market access, customer relationships, and logistical support. Brands may struggle with scaling effectively due to the absence of established franchise networks that offer localized expertise and shared resources. Furthermore, direct-to-consumer models risk alienating traditional partners and encountering legal and regulatory hurdles that franchises typically navigate more efficiently.
Case Studies: Franchising vs Disintermediation Success Stories
Franchising success stories often highlight brands like McDonald's and Subway, where standardized operations and brand consistency drive rapid global expansion and strong consumer trust. Disintermediation case studies emphasize companies such as Tesla and Warby Parker, which bypass traditional retail channels to directly engage customers, reducing costs and enhancing control over the customer experience. Both models demonstrate distinct advantages: franchising leverages local entrepreneurs for scale, while disintermediation fosters innovation and closer customer relationships through direct sales.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right model between franchising and disintermediation depends on factors such as control over brand consistency, scalability potential, and initial investment requirements. Franchising offers a proven operational framework and extensive network support, ideal for rapid expansion with standardized quality. Disintermediation allows direct customer engagement, higher profit margins, and greater flexibility but demands robust infrastructure and marketing capabilities to succeed independently.
Franchising Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com