Royalties are payments made to individuals or entities for the ongoing use of their intellectual property, such as copyrights, patents, or trademarks. They serve as a crucial revenue stream for creators, inventors, and businesses by compensating them for the commercial exploitation of their original work. Discover how royalties impact your earnings and intellectual property rights throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
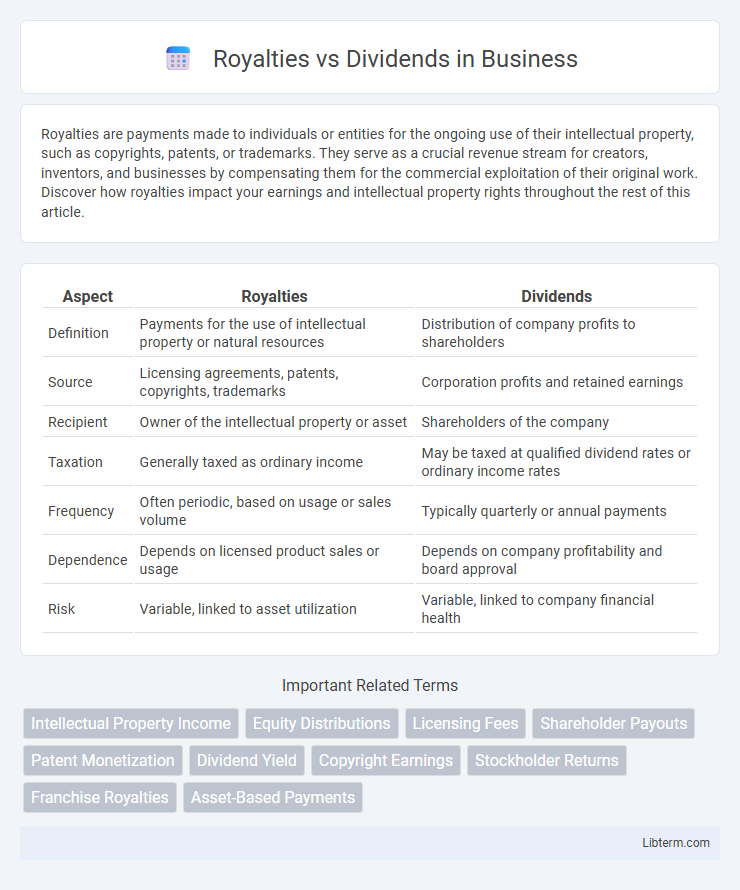
| Aspect | Royalties | Dividends |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payments for the use of intellectual property or natural resources | Distribution of company profits to shareholders |
| Source | Licensing agreements, patents, copyrights, trademarks | Corporation profits and retained earnings |
| Recipient | Owner of the intellectual property or asset | Shareholders of the company |
| Taxation | Generally taxed as ordinary income | May be taxed at qualified dividend rates or ordinary income rates |
| Frequency | Often periodic, based on usage or sales volume | Typically quarterly or annual payments |
| Dependence | Depends on licensed product sales or usage | Depends on company profitability and board approval |
| Risk | Variable, linked to asset utilization | Variable, linked to company financial health |
Introduction: Understanding Royalties and Dividends
Royalties are payments made to content creators or patent holders for the ongoing use of their intellectual property, such as music, books, or inventions. Dividends represent the portion of a company's earnings distributed to shareholders as a return on their investment. Understanding the differences between royalties and dividends is crucial for investors and creators seeking passive income streams aligned with their assets.
Defining Royalties: Key Concepts and Examples
Royalties are payments made to owners of intellectual property or natural resources for the right to use their assets, often calculated as a percentage of revenue or fixed amount per unit sold. Key examples include authors receiving royalties from book sales, musicians earning from song plays, and landowners collecting royalties from oil or mineral extraction. These payments incentivize creators and owners by providing ongoing income linked directly to the commercial success of their property.
What Are Dividends? Structure and Types
Dividends are distributions of a company's earnings to its shareholders, typically paid in cash or additional shares of stock. The structure of dividends includes regular dividends, which are consistent payments, and special dividends, which are one-time distributions often reflecting extraordinary profits. Types of dividends also encompass stock dividends and property dividends, offering diverse ways for companies to reward investors and influence share value.
Sources of Income: Royalties vs Dividends
Royalties generate income from intellectual property rights such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, or natural resources, typically providing ongoing revenue streams based on usage or sales. Dividends represent profit distributions from a corporation's earnings paid to shareholders, reflecting their ownership stake and usually issued on a regular schedule. Both serve as passive income sources, but royalties hinge on asset exploitation, while dividends depend on corporate profitability and board decisions.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Royalties are governed by intellectual property laws, licensing agreements, and specific contractual terms that define usage rights, payment structures, and enforcement mechanisms under statutes such as the Copyright Act, Patent Act, or trademark laws. Dividends fall under corporate law regulations, including securities laws and company bylaws, with oversight from entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to ensure shareholder rights, dividend declarations, and payment processes comply with legal standards. Legal frameworks for royalties often involve international treaties like the Berne Convention, while dividend regulation centers on financial disclosure and anti-fraud provisions to protect investors.
Tax Implications for Royalties and Dividends
Royalties are taxed as ordinary income and subject to self-employment taxes if earned by individuals, while dividends benefit from lower tax rates, often categorized as qualified dividends taxed at capital gains rates. Companies paying dividends may face double taxation, where earnings are taxed at the corporate level first, then as individual dividend income. Understanding these tax implications is crucial for investors to optimize after-tax returns from royalties and dividends.
Pros and Cons of Royalties
Royalties provide a steady income stream from intellectual property or natural resources without sacrificing ownership, allowing for passive earnings while maintaining control. However, they can fluctuate based on market demand, usage rates, or the success of the underlying asset, introducing income variability. Unlike dividends, royalties are not guaranteed and may require ongoing management to optimize revenue and enforce agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dividends
Dividends provide shareholders with a regular income stream, enhancing investment appeal and signaling company profitability, which can attract more investors. However, dividends reduce the company's retained earnings, potentially limiting funds available for growth and reinvestment. Shareholders also face tax liabilities on dividends, which may be higher than capital gains taxes, affecting the overall return on investment.
Choosing Between Royalties and Dividends: Key Considerations
Choosing between royalties and dividends depends on the nature of the asset and desired income stability. Royalties provide ongoing payments tied to the usage or sales of intellectual property, offering potentially higher returns but with variable income. Dividends, typically paid by corporations to shareholders, offer more predictable, regular income streams based on company profits and dividend policies.
Conclusion: Which Income Stream Suits Your Goals?
Royalties provide a passive income stream tied to intellectual property, making them ideal for creators seeking ongoing revenue without active management. Dividends offer shareholders regular income from company profits, attracting investors focused on capital growth and financial stability. Choosing between royalties and dividends depends on your goals for income consistency, risk tolerance, and involvement in the asset generating that income.
Royalties Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com