Attrition rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period, providing critical insights into workforce stability and satisfaction. High attrition rates can signal issues such as poor management, lack of growth opportunities, or inadequate compensation, all impacting company productivity and culture. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for reducing attrition and retaining your valuable talent.
Table of Comparison
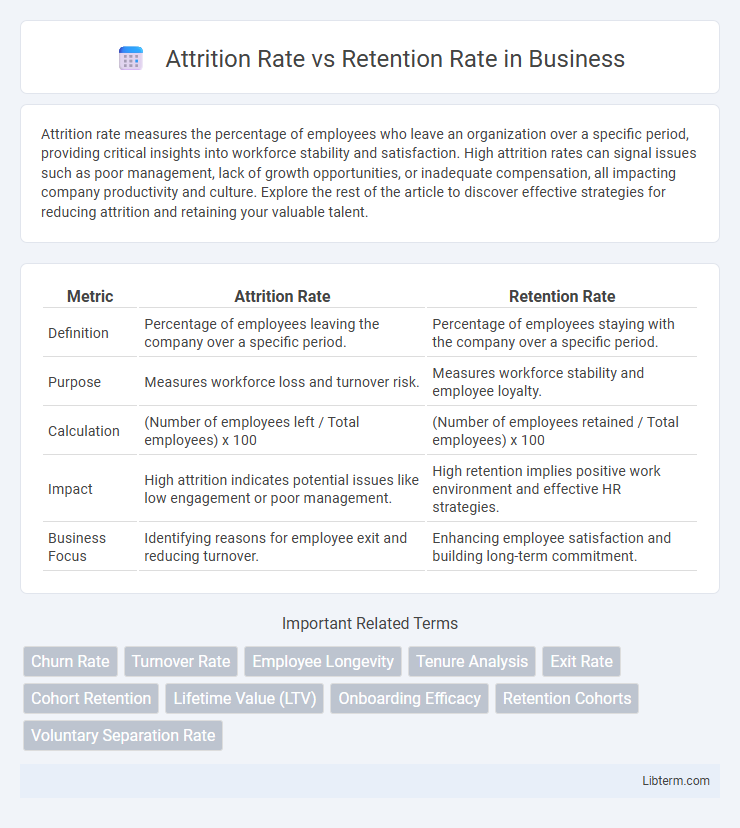
| Metric | Attrition Rate | Retention Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of employees leaving the company over a specific period. | Percentage of employees staying with the company over a specific period. |
| Purpose | Measures workforce loss and turnover risk. | Measures workforce stability and employee loyalty. |
| Calculation | (Number of employees left / Total employees) x 100 | (Number of employees retained / Total employees) x 100 |
| Impact | High attrition indicates potential issues like low engagement or poor management. | High retention implies positive work environment and effective HR strategies. |
| Business Focus | Identifying reasons for employee exit and reducing turnover. | Enhancing employee satisfaction and building long-term commitment. |
Understanding Attrition Rate
Attrition rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization within a specific period, reflecting workforce turnover and potential issues with employee satisfaction or engagement. Tracking attrition rate helps identify patterns in employee departures, enabling companies to address underlying causes such as poor management, lack of growth opportunities, or inadequate compensation. Understanding attrition rate provides critical insights to improve talent management strategies and enhance overall organizational stability.
Defining Retention Rate
Retention Rate measures the percentage of employees who remain with an organization over a specific period, reflecting workforce stability and employee satisfaction. It is calculated by dividing the number of employees retained at the end of the period by the number of employees at the start, then multiplying by 100. High retention rates indicate effective employee engagement and strong company culture, essential for reducing hiring costs and maintaining organizational knowledge.
Key Differences Between Attrition and Retention Rates
Attrition rate measures the percentage of employees leaving an organization over a specific period, indicating workforce losses, while retention rate reflects the percentage of employees who remain, demonstrating stability and satisfaction. Attrition rate highlights turnover challenges, influencing recruitment and training costs, whereas retention rate emphasizes success in employee engagement and organizational commitment. Understanding these key differences supports strategic human resource management for sustaining productivity and reducing operational disruptions.
Why Monitoring Attrition and Retention Matters
Monitoring attrition and retention rates is crucial for understanding workforce stability and predicting future staffing needs. High attrition rates signal potential issues with employee satisfaction, engagement, or organizational culture, leading to increased recruitment and training costs. Conversely, strong retention rates indicate effective talent management strategies, fostering organizational continuity and enhanced productivity.
Calculating Attrition Rate: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating attrition rate involves dividing the number of employees who leave during a specific period by the average number of employees, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. For example, if 10 employees leave in a month and the average workforce is 200, the attrition rate is (10/200) x 100 = 5%. Tracking attrition rate helps organizations identify workforce trends and develop strategies to improve employee retention.
How to Measure Retention Rate
Retention rate is measured by calculating the percentage of employees who remain with an organization over a specific period, typically using the formula: (Number of employees at end of period - Number of new employees during period) / Number of employees at start of period x 100. Accurate retention rate measurement requires tracking employee turnover, tenure, and separation reasons through HR management software or employee databases. Understanding retention rate helps identify workforce stability and informs strategies to reduce attrition and improve employee engagement.
Factors Influencing Attrition and Retention
Attrition rate is influenced by factors such as employee dissatisfaction, poor management, lack of growth opportunities, and inadequate compensation, which drive staff turnover and reduce organizational stability. Retention rate improves through fostering positive workplace culture, offering competitive benefits, providing career development programs, and recognizing employee contributions, thereby enhancing job satisfaction and loyalty. Understanding these dynamics helps organizations implement targeted strategies to minimize attrition and boost retention effectively.
Impact of High Attrition vs High Retention
High attrition rate negatively impacts organizational productivity by increasing recruitment costs, disrupting team dynamics, and causing loss of institutional knowledge. In contrast, a high retention rate fosters employee engagement, enhances customer satisfaction, and strengthens company culture, leading to sustainable business growth. Prioritizing retention strategies can mitigate attrition-related challenges and improve overall operational efficiency.
Strategies to Reduce Attrition and Boost Retention
Effective strategies to reduce attrition and boost retention include implementing comprehensive onboarding programs that align employee expectations with company goals. Offering competitive compensation packages and opportunities for career development significantly enhances employee satisfaction and loyalty. Promoting a positive workplace culture through regular feedback, recognition, and work-life balance initiatives helps maintain high retention rates and lowers turnover costs.
Attrition Rate vs Retention Rate: Which Metric Matters Most?
Attrition rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period, while retention rate tracks the proportion of employees who remain employed. Understanding attrition rate is crucial for identifying turnover causes and mitigating costs, whereas retention rate highlights workforce stability and employee satisfaction. Both metrics are essential, but retention rate often serves as a more proactive indicator for long-term organizational health and talent management strategies.
Attrition Rate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com