Dynamic pricing adjusts the cost of products or services based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to maximize revenue. This strategy enables businesses to respond swiftly to changing conditions and optimize profits in real-time. Discover how dynamic price models can transform Your pricing strategy by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
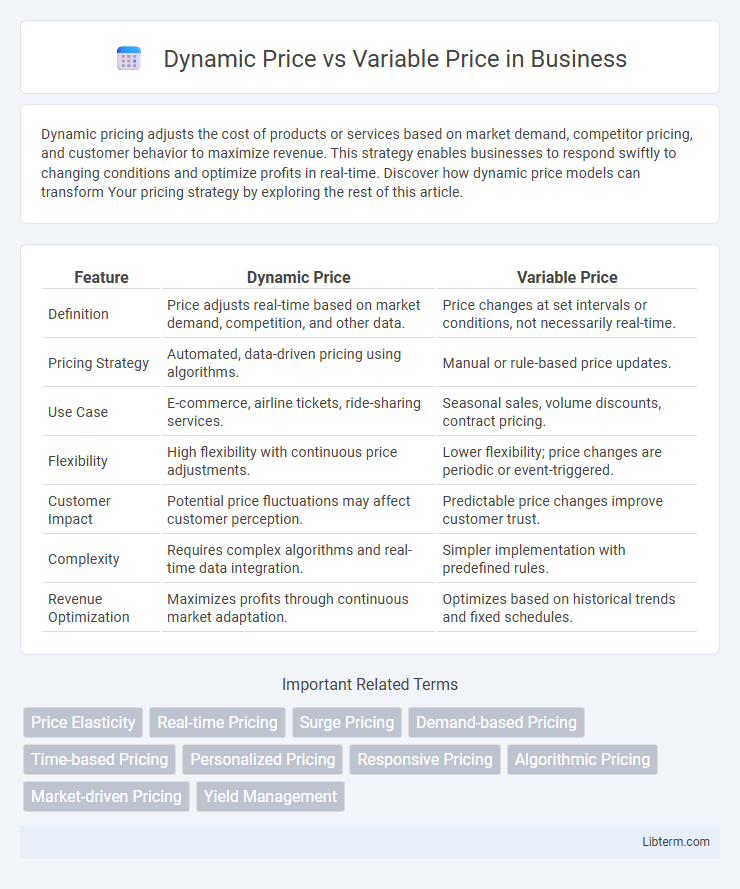
| Feature | Dynamic Price | Variable Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price adjusts real-time based on market demand, competition, and other data. | Price changes at set intervals or conditions, not necessarily real-time. |
| Pricing Strategy | Automated, data-driven pricing using algorithms. | Manual or rule-based price updates. |
| Use Case | E-commerce, airline tickets, ride-sharing services. | Seasonal sales, volume discounts, contract pricing. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with continuous price adjustments. | Lower flexibility; price changes are periodic or event-triggered. |
| Customer Impact | Potential price fluctuations may affect customer perception. | Predictable price changes improve customer trust. |
| Complexity | Requires complex algorithms and real-time data integration. | Simpler implementation with predefined rules. |
| Revenue Optimization | Maximizes profits through continuous market adaptation. | Optimizes based on historical trends and fixed schedules. |
Understanding Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor rates, and customer behavior, maximizing revenue through data-driven algorithms. Variable pricing, by contrast, sets different prices for distinct customer segments or time periods but is less responsive to immediate market fluctuations. Understanding dynamic pricing involves recognizing its reliance on continuous data analysis to optimize pricing strategies dynamically.
What is Variable Pricing?
Variable pricing refers to a strategy where the price of a product or service fluctuates based on predefined factors such as demand, time, or customer segmentation, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to market conditions. Unlike dynamic pricing, which continuously changes prices in real-time using algorithms, variable pricing typically involves set price tiers or adjustments applied periodically. This approach enables companies to optimize revenue by targeting different customer groups or market situations with tailored pricing.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Variable Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts product costs in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior, optimizing revenue through immediate responsiveness. Variable pricing offers predefined price variations depending on specific factors such as customer segments, purchase volume, or geographic location, allowing tailored pricing strategies without continuous fluctuations. The key difference lies in dynamic pricing's continuous, automatic change mechanism versus variable pricing's structured, rule-based adjustments.
How Dynamic Pricing Works
Dynamic pricing adjusts product prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior using advanced algorithms and AI-driven data analysis. This approach enables businesses to maximize revenue by increasing prices during high demand periods and lowering them when demand wanes. Unlike variable pricing, which sets prices based on fixed criteria or time intervals, dynamic pricing continuously updates prices to reflect fluctuating market conditions.
How Variable Pricing Is Implemented
Variable pricing is implemented by adjusting prices based on predetermined factors such as demand, time, and customer segments, often using algorithms to apply discounts or surcharges in real-time within set limits. This method relies on data analytics and market trends to fine-tune prices without constant manual intervention. Unlike dynamic pricing, variable pricing typically operates within fixed price tiers or ranges to maintain predictability while still allowing flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, inventory levels, and competitor pricing, maximizing revenue potential and improving inventory turnover. It allows businesses to capitalize on peak demand but may lead to customer dissatisfaction due to price fluctuations and perceived unfairness. Implementing dynamic pricing requires sophisticated data analytics and can increase operational complexity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Variable Pricing
Variable pricing allows businesses to adjust prices based on specific factors such as time, demand, or customer segments, enabling targeted promotions and increased revenue potential. However, this approach may lead to customer confusion or dissatisfaction if price fluctuations seem unpredictable or unfair. Effective implementation requires transparent communication and robust data analysis to balance pricing flexibility with customer trust.
Industries Using Dynamic vs Variable Pricing
Industries utilizing dynamic pricing include airlines, hospitality, and ride-sharing, where prices fluctuate frequently based on real-time demand, supply, and competitor actions. Variable pricing is common in retail and manufacturing, involving set price tiers or discounts tied to volume or customer segmentation rather than continuous price changes. Dynamic pricing leverages algorithms and data analytics for rapid price adjustments, while variable pricing relies on predefined pricing structures tailored to specific market conditions.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior, maximizing revenue during peak times and minimizing losses when demand falls. Variable pricing sets different fixed prices for various customer segments, product versions, or purchase conditions, focusing on segment-specific value capture. Choosing the right pricing strategy depends on factors like market volatility, customer sensitivity, and operational flexibility to ensure optimal profitability and customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data and AI algorithms to adjust prices based on consumer behavior, demand fluctuations, and competitor pricing, enabling highly personalized markdowns. Variable pricing offers predefined pricing tiers reflecting factors like customer segments or purchase quantities, but lacks the responsiveness of dynamic models. Future trends indicate a shift toward more sophisticated dynamic pricing integrated with machine learning and predictive analytics, driving adaptive, transparent prices that enhance customer experience and maximize revenue.
Dynamic Price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com