Gross margin measures the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold, reflecting a company's efficiency in producing and selling its products. A higher gross margin indicates better profitability and operational control, essential for sustaining business growth. Explore the article to understand how improving your gross margin can boost overall financial health.
Table of Comparison
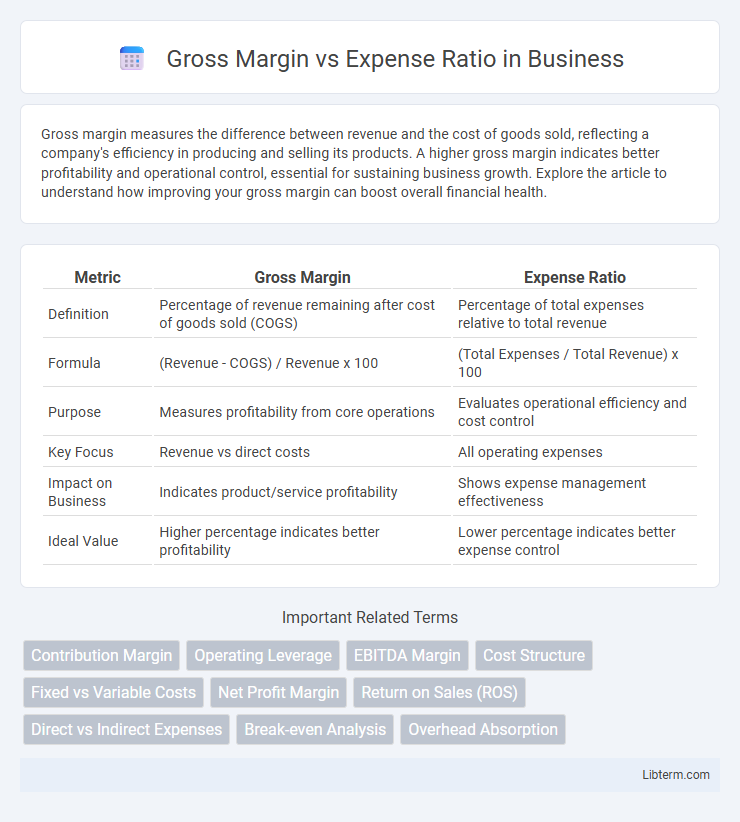
| Metric | Gross Margin | Expense Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of revenue remaining after cost of goods sold (COGS) | Percentage of total expenses relative to total revenue |
| Formula | (Revenue - COGS) / Revenue x 100 | (Total Expenses / Total Revenue) x 100 |
| Purpose | Measures profitability from core operations | Evaluates operational efficiency and cost control |
| Key Focus | Revenue vs direct costs | All operating expenses |
| Impact on Business | Indicates product/service profitability | Shows expense management effectiveness |
| Ideal Value | Higher percentage indicates better profitability | Lower percentage indicates better expense control |
Introduction to Gross Margin and Expense Ratio
Gross margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold, highlighting a company's production efficiency and profitability. Expense ratio measures operating expenses as a percentage of total revenue, indicating how well a company controls its overhead costs relative to income. Comparing gross margin with expense ratio offers insight into overall financial health and operational effectiveness.
Defining Gross Margin
Gross margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS), highlighting the profitability generated from core operations. It is calculated by subtracting COGS from total revenue and dividing the result by total revenue, reflecting how efficiently a company produces and sells its products. A higher gross margin indicates better control over production costs and stronger pricing power relative to the expense ratio, which measures operating expenses against revenue.
Understanding Expense Ratio
The Expense Ratio represents the percentage of a company's revenue consumed by operating expenses, offering insight into cost efficiency and management effectiveness. Unlike Gross Margin, which measures profitability by subtracting direct costs from revenue, the Expense Ratio includes all operating expenses, such as administrative and sales costs. Monitoring the Expense Ratio helps investors and managers assess how well a company controls overhead relative to its total revenue.
Key Differences Between Gross Margin and Expense Ratio
Gross Margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS), highlighting a company's production efficiency and profitability. Expense Ratio measures operating expenses as a percentage of revenue, focusing on management's ability to control overhead costs. Key differences include Gross Margin's emphasis on direct production costs versus Expense Ratio's focus on overall operational expense management.
Importance of Gross Margin in Business Analysis
Gross margin reflects the profitability of core business operations by measuring the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting cost of goods sold (COGS), providing critical insight into operational efficiency and pricing strategy effectiveness. Expense ratio highlights operating costs relative to revenue, but gross margin remains a more direct indicator of a company's ability to generate profit from sales before overhead expenses. Analyzing gross margin enables businesses to identify pricing issues, control production costs, and drive sustainable growth, making it essential in financial performance evaluation and strategic decision-making.
Role of Expense Ratio in Financial Performance
The expense ratio plays a critical role in financial performance by directly impacting net profitability through the management of operating costs relative to revenues. A lower expense ratio indicates efficient cost control, enhancing gross margin retention and contributing to higher net margins. Monitoring the expense ratio helps companies identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize resource allocation to sustain competitive advantage.
How to Calculate Gross Margin and Expense Ratio
Gross margin is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, then dividing the result by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. Expense ratio is determined by dividing total operating expenses by total revenue, also expressed as a percentage to evaluate efficiency in managing costs. Understanding these calculations helps businesses assess profitability by comparing the proportion of revenue retained after production costs versus the proportion spent on operating expenses.
Common Mistakes When Comparing the Two Metrics
Confusing gross margin and expense ratio by treating them as interchangeable metrics leads to misinterpretation of a company's financial health. Gross margin measures the percentage of revenue remaining after direct costs, while expense ratio reflects operating expenses relative to revenue, making direct comparisons misleading. Ignoring the distinct components each metric analyzes often results in flawed decisions regarding profitability and operational efficiency.
Industry Benchmarks for Gross Margin and Expense Ratio
Industry benchmarks for gross margin typically vary by sector, with manufacturing firms averaging around 25%-35%, retail businesses ranging from 20%-50%, and software companies often exceeding 70%. Expense ratios also fluctuate widely, with financial services maintaining lower expense ratios near 1%-2%, while healthcare providers may experience ratios between 15%-25% due to higher operational costs. Comparing gross margin and expense ratio benchmarks helps businesses identify efficiency strengths and cost management opportunities relative to their industry peers.
Choosing the Right Metric for Your Business Strategy
Gross margin reveals the profitability of core operations by showing the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting cost of goods sold, making it essential for pricing and production decisions. Expense ratio measures operating expenses relative to total revenue, providing insight into cost management efficiency and operational control. Selecting between gross margin and expense ratio depends on whether your business strategy prioritizes optimizing product profitability or controlling operational costs to maximize overall financial performance.
Gross Margin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com