Efficient supply chain management ensures seamless coordination of resources, inventory, and distribution, driving cost reduction and customer satisfaction. Leveraging advanced technologies like AI and IoT boosts transparency and predictive capabilities, optimizing every link in the chain. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies that can transform your supply chain operations.
Table of Comparison
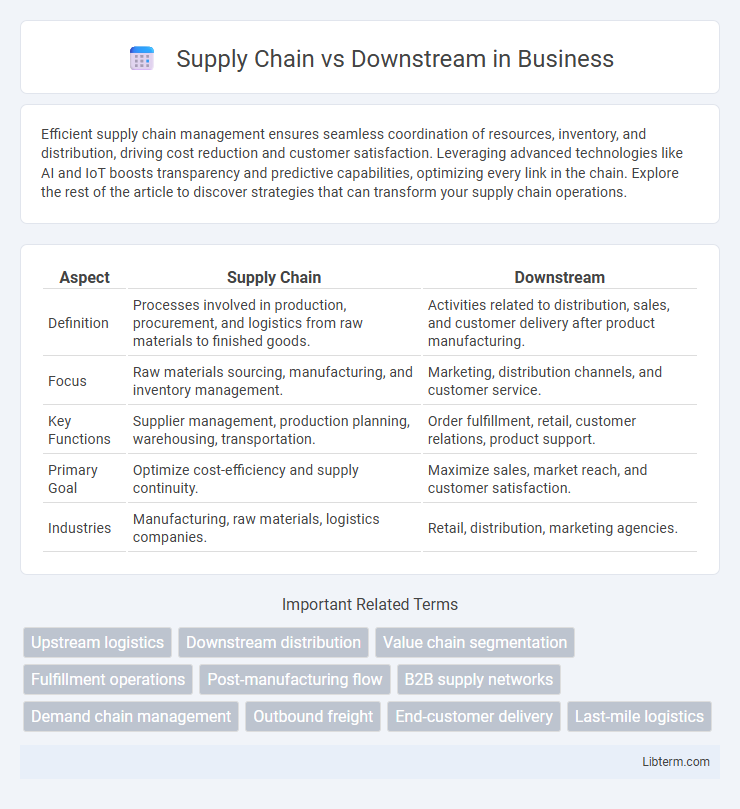
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Downstream |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes involved in production, procurement, and logistics from raw materials to finished goods. | Activities related to distribution, sales, and customer delivery after product manufacturing. |
| Focus | Raw materials sourcing, manufacturing, and inventory management. | Marketing, distribution channels, and customer service. |
| Key Functions | Supplier management, production planning, warehousing, transportation. | Order fulfillment, retail, customer relations, product support. |
| Primary Goal | Optimize cost-efficiency and supply continuity. | Maximize sales, market reach, and customer satisfaction. |
| Industries | Manufacturing, raw materials, logistics companies. | Retail, distribution, marketing agencies. |
Introduction to Supply Chain and Downstream
Supply chain encompasses the entire network of entities involved in producing and delivering a product, from raw material suppliers to manufacturing, logistics, and distribution channels. Downstream specifically refers to the final stages of this process, including distribution, sales, and customer service activities that ensure product delivery to end-users. Understanding the distinction between supply chain and downstream operations is critical for optimizing overall business efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Definitions: Supply Chain vs Downstream
Supply Chain encompasses the entire process of sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and delivering finished products to consumers, involving suppliers, production, distribution, and logistics. Downstream refers specifically to the latter stages of this process, focusing on distribution, marketing, sales, and customer service activities that deliver products to end users. Understanding these distinctions clarifies operational responsibilities and optimizes efficiency across production and distribution networks.
Components of the Supply Chain
The supply chain encompasses all stages involved in producing and delivering a product, including sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. Components of the supply chain consist of suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, wholesalers, and retailers, whereas downstream primarily refers to the activities from the manufacturer to the end consumer. Efficient management of components such as procurement, inventory control, transportation, and customer service is crucial for optimizing supply chain performance and meeting downstream demand.
Understanding Downstream Processes
Downstream processes in supply chain management refer to activities involved in distributing finished products from manufacturers to end consumers, including warehousing, transportation, and retail. Optimizing downstream supply chain operations enhances customer satisfaction through timely delivery and efficient inventory management. Understanding these processes is crucial for reducing costs, improving demand forecasting, and ensuring seamless product availability across multiple distribution channels.
Major Differences Between Supply Chain and Downstream
The supply chain encompasses the entire process of sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and delivering products to the end consumer, involving multiple stages such as procurement, production, and logistics. Downstream specifically refers to activities related to refining, marketing, distribution, and sales of finished goods to customers, primarily focusing on the latter part of the supply chain. The major difference lies in scope: supply chain covers end-to-end operations from raw materials to consumer delivery, while downstream targets the final processes after production, emphasizing customer engagement and product distribution.
Roles and Responsibilities in Supply Chain and Downstream
Supply Chain management encompasses the planning, sourcing, manufacturing, and logistics of products to ensure efficient production and delivery, managing supplier relationships and inventory control. Downstream roles focus on refining, marketing, distribution, and sales, handling product delivery to end customers and optimizing customer satisfaction. Both functions require coordination for demand forecasting, cost management, and ensuring product availability across the entire value chain.
Impact on Business Efficiency
Supply chain management directly influences business efficiency by optimizing procurement, production, and distribution processes, reducing costs, and minimizing delays. Downstream activities, including marketing, sales, and customer service, enhance customer satisfaction and drive revenue growth by ensuring timely product availability and effective market response. Efficient coordination between supply chain and downstream operations leads to improved resource utilization and agile adaptation to market demands.
Challenges in Supply Chain and Downstream Management
Supply chain management faces challenges such as demand forecasting inaccuracies, supplier disruptions, and inventory mismanagement, which can lead to increased costs and delays. Downstream management struggles with distribution complexities, real-time tracking inefficiencies, and fluctuating customer preferences impacting delivery speed and service quality. Both require integrated solutions to enhance visibility, streamline operations, and improve responsiveness across the value chain.
Trends Shaping Supply Chain and Downstream Operations
Emerging trends in supply chain management include increased adoption of advanced analytics, automation technologies, and sustainable practices to enhance efficiency and resilience. In downstream operations, digital transformation and real-time data integration are driving improvements in demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and customer experience. Both sectors are increasingly leveraging AI and IoT to create more agile, transparent, and responsive networks that adapt to market volatility and regulatory changes.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Supply Chain or Downstream Focus
Choosing the right strategy between supply chain management and downstream focus hinges on prioritizing either production efficiency or customer-centric distribution. Emphasizing supply chain optimization enhances inventory control, supplier coordination, and cost reduction, while a downstream strategy targets personalized marketing, sales channel expansion, and improved customer service. Businesses that align their strategic focus with market demands and operational strengths can maximize profitability and streamline product delivery.
Supply Chain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com