Value-based pricing focuses on setting product or service prices based on the perceived value to the customer rather than on cost or competitor prices. This strategy aligns prices with the benefits and outcomes your offerings deliver, maximizing both customer satisfaction and profitability. Discover how to implement value-based pricing effectively to enhance your business success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
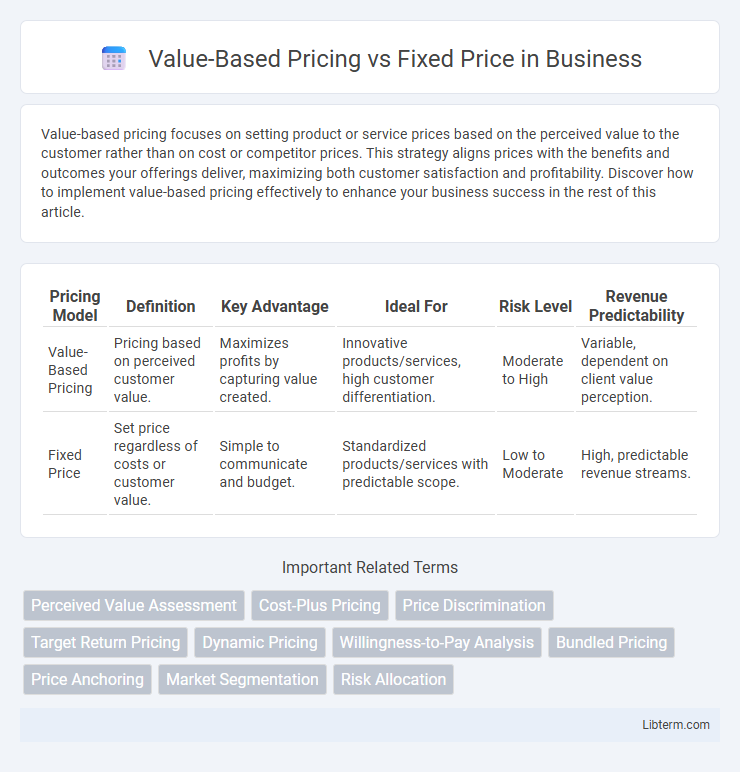
| Pricing Model | Definition | Key Advantage | Ideal For | Risk Level | Revenue Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value-Based Pricing | Pricing based on perceived customer value. | Maximizes profits by capturing value created. | Innovative products/services, high customer differentiation. | Moderate to High | Variable, dependent on client value perception. |
| Fixed Price | Set price regardless of costs or customer value. | Simple to communicate and budget. | Standardized products/services with predictable scope. | Low to Moderate | High, predictable revenue streams. |
Understanding Value-Based Pricing
Value-Based Pricing focuses on setting prices based on the perceived value delivered to the customer rather than the cost of production or a predetermined fixed price. This approach requires a deep understanding of the customer's needs, market conditions, and the unique benefits the product or service provides. By aligning prices with customer value, businesses can maximize profitability and foster stronger customer relationships.
What Is Fixed Price Pricing?
Fixed price pricing is a pricing strategy where a product or service is sold at a set, predetermined price regardless of the costs or customer demand fluctuations. This method provides buyers with clear budget expectations and helps sellers maintain consistent revenue streams by avoiding unforeseen cost overruns. Fixed price contracts are commonly used in construction, software development, and manufacturing industries to ensure project costs remain within agreed limits.
Key Differences Between Value-Based and Fixed Price
Value-based pricing sets product or service costs based on perceived customer value, dynamically adjusting prices to reflect demand and benefits, while fixed price pricing remains constant regardless of market changes or customer preferences. Value-based pricing maximizes profitability by aligning price with customer willingness to pay, enhancing revenue opportunities, whereas fixed price offers predictability and simplicity for budgeting and contracting. The key differences lie in flexibility, customer-centric valuation, and responsiveness to market conditions, making value-based pricing adaptive and profit-driven compared to the stability and uniformity of fixed price models.
Advantages of Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing maximizes profit by aligning prices with the customer's perceived value, leading to higher revenue potential compared to fixed price models. This approach enhances customer satisfaction by reflecting the true benefits and outcomes derived from the product or service. Businesses using value-based pricing can adapt to market changes dynamically, optimizing price points for different customer segments and increasing competitive advantage.
Benefits of Fixed Price Models
Fixed price models offer predictable budgeting and financial control, reducing the risk of cost overruns for projects with clearly defined scopes. This pricing approach enhances transparency and accountability, allowing clients to evaluate project value upfront with a fixed financial commitment. Additionally, fixed price agreements streamline contract negotiations and simplify project management by establishing clear deliverables and deadlines.
Challenges of Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing faces significant challenges such as accurately determining customer perceived value and aligning it with product costs, which requires extensive market research and customer insights. Companies often struggle with fluctuating customer preferences and difficulty in communicating the price justification clearly, leading to potential trust issues. Implementation complexity and the need for continuous pricing adjustments further hinder the consistent application of value-based pricing strategies.
Drawbacks of Fixed Price Strategies
Fixed price strategies often limit flexibility, causing businesses to miss opportunities for higher profits when customer willingness to pay exceeds the set price. They can lead to reduced innovation, as companies may avoid investing in product enhancements that don't align with predetermined costs. Moreover, fixed pricing fails to capture variations in perceived value across different customer segments, resulting in potential revenue loss.
How to Choose the Right Pricing Model
Choosing the right pricing model requires analyzing your product's value proposition, customer willingness to pay, and market demand. Value-based pricing maximizes revenue by aligning prices with perceived customer benefits and unique features, ideal for innovative or differentiated products. Fixed price suits cost-sensitive markets or standardized offerings where predictability and simplicity help streamline purchasing decisions and budgeting.
Industry Applications: Value-Based vs Fixed Price
Value-based pricing is widely applied in technology and consulting industries where product value varies significantly across clients, enabling providers to capture higher returns based on customer-perceived benefits. Fixed price models dominate manufacturing and construction sectors due to their predictability and simpler cost estimation requirements, facilitating budget control and risk management. Selecting between value-based and fixed pricing depends on industry dynamics, with value-based suited for high-innovation markets and fixed pricing preferred in standardized, process-driven environments.
Future Trends in Pricing Strategies
Value-based pricing is increasingly favored over fixed pricing due to its alignment with customer perceived value and willingness to pay, driving revenue optimization. Future trends indicate greater adoption of dynamic pricing models powered by artificial intelligence and big data analytics, enabling real-time adjustments based on market demand and customer behavior. Companies leveraging value-based pricing will benefit from enhanced profitability and competitive differentiation in rapidly evolving markets.
Value-Based Pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com