Acquisition is a crucial strategy for business growth, involving the purchase of one company by another to enhance market share, diversify offerings, or gain competitive advantages. Understanding the key factors behind successful acquisitions can help your company avoid common pitfalls and maximize value. Explore the rest of the article to learn how strategic acquisition decisions can transform your business landscape.
Table of Comparison
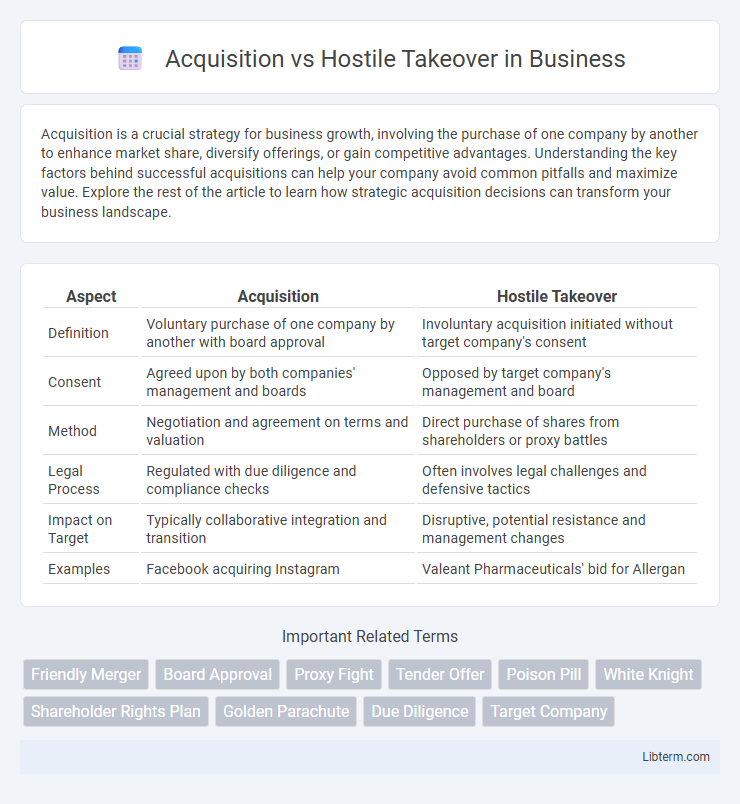
| Aspect | Acquisition | Hostile Takeover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary purchase of one company by another with board approval | Involuntary acquisition initiated without target company's consent |
| Consent | Agreed upon by both companies' management and boards | Opposed by target company's management and board |
| Method | Negotiation and agreement on terms and valuation | Direct purchase of shares from shareholders or proxy battles |
| Legal Process | Regulated with due diligence and compliance checks | Often involves legal challenges and defensive tactics |
| Impact on Target | Typically collaborative integration and transition | Disruptive, potential resistance and management changes |
| Examples | Facebook acquiring Instagram | Valeant Pharmaceuticals' bid for Allergan |
Introduction to Acquisition and Hostile Takeover
Acquisition involves one company purchasing another with mutual consent to expand market share, resources, or capabilities. Hostile takeover occurs when the acquiring company attempts to gain control without the target company's approval, often by directly appealing to shareholders or through aggressive tactics. Understanding the strategic, financial, and legal differences between acquisition and hostile takeover is crucial for corporate governance and investment decision-making.
Defining Acquisition
Acquisition refers to the process where one company purchases most or all of another company's shares to gain control, often executed with the target company's agreement. This strategic move enables the acquiring company to expand its market share, diversify products, or enter new markets smoothly. In contrast to hostile takeovers, acquisitions prioritize cooperative negotiation and mutual consent between the involved parties.
What Constitutes a Hostile Takeover?
A hostile takeover occurs when an acquiring company attempts to gain control of a target company without the approval or cooperation of its board of directors, often by directly appealing to shareholders through a tender offer or proxy fight. This aggressive strategy bypasses traditional negotiation channels, creating conflict between the acquiring firm and the target company's management. Key indicators of a hostile takeover include unsolicited bids, attempts to replace board members, and efforts to influence shareholders against management's wishes.
Key Differences Between Acquisition and Hostile Takeover
Acquisition involves a consensual agreement between the acquiring and target companies, often resulting in mutual benefits and smoother integration processes, while a hostile takeover occurs without the target company's approval, leading to resistance and potential legal battles. Acquisitions typically focus on strategic alignment and synergy creation, whereas hostile takeovers prioritize control acquisition despite opposition. The financial tactics differ significantly, with acquisitions relying on negotiated purchase prices and hostile takeovers using proxy fights or tender offers to seize control.
Common Strategies in Acquisitions
Common strategies in acquisitions include due diligence to assess financial health, strategic fit, and potential synergies between companies. Negotiated transactions are often preferred, involving valuation analysis, offer structuring, and shareholder agreement to ensure smooth integration. Leveraged buyouts and tender offers may also be employed, but the emphasis remains on collaboration to maximize long-term value and minimize disruption.
Tactics Used in Hostile Takeovers
Hostile takeovers employ tactics such as tender offers, where the acquirer directly proposes to purchase shares from shareholders at a premium, bypassing the target company's management. Proxy battles involve persuading shareholders to replace current management with a new board more favorable to the takeover. Another tactic includes a creeping tender offer, which gradually accumulates shares to gain control without immediate detection.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Legal and regulatory considerations in acquisitions involve comprehensive due diligence, compliance with antitrust laws, and adherence to securities regulations to ensure transparent and lawful transactions. Hostile takeovers often trigger regulatory scrutiny, including potential intervention by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and stringent enforcement of tender offer rules under the Williams Act. Both strategies require navigating complex legal frameworks to mitigate risks such as litigation, injunctions, and penalties from agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Department of Justice (DOJ).
Impact on Shareholders and Stakeholders
Acquisitions typically result in a more collaborative process, preserving shareholder value and maintaining stakeholder confidence through negotiated terms and mutual agreements. Hostile takeovers often lead to uncertainty and disruption, risking shareholder value due to potential resistance from management and concerns over strategic direction. Shareholders may benefit from premium offers in hostile takeovers but face increased volatility and possible negative impacts on employee morale and supplier relationships.
Case Studies: Notable Acquisitions and Hostile Takeovers
Notable acquisitions such as Facebook's $19 billion purchase of Instagram highlight strategic growth and market consolidation, while hostile takeovers like Kraft's aggressive $143 billion bid for Cadbury illustrate competitive acquisition tactics often met with resistance. The AOL-Time Warner merger stands as a classic example of a contentious acquisition marked by cultural clashes and integration challenges. These case studies demonstrate how acquisition strategies vary significantly depending on the target company's receptiveness and market conditions.
Best Practices for Navigating Corporate Takeovers
Effective navigation of corporate takeovers requires thorough due diligence to assess financial health, legal obligations, and cultural fit between companies. Clear communication strategies and stakeholder engagement help mitigate resistance and build trust throughout the acquisition or hostile takeover process. Employing experienced legal counsel and financial advisors ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and optimizes deal structuring for maximum value.
Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com