Vertical integration streamlines your supply chain by consolidating multiple stages of production and distribution within a single company, reducing costs and improving efficiency. This strategic approach enhances control over quality, timing, and inventory, driving competitive advantage in the market. Discover how vertical integration can transform your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
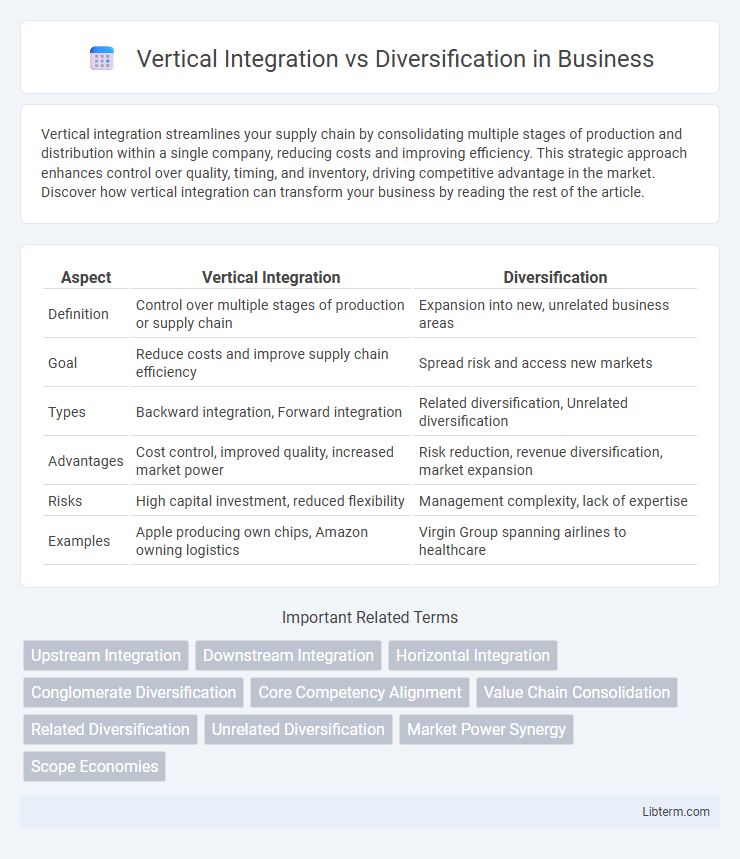
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over multiple stages of production or supply chain | Expansion into new, unrelated business areas |
| Goal | Reduce costs and improve supply chain efficiency | Spread risk and access new markets |
| Types | Backward integration, Forward integration | Related diversification, Unrelated diversification |
| Advantages | Cost control, improved quality, increased market power | Risk reduction, revenue diversification, market expansion |
| Risks | High capital investment, reduced flexibility | Management complexity, lack of expertise |
| Examples | Apple producing own chips, Amazon owning logistics | Virgin Group spanning airlines to healthcare |
Introduction to Vertical Integration and Diversification
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations by taking control over multiple stages of production or supply chain, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Diversification refers to a business strategy where a company enters into new markets or industries to spread risk and capitalize on growth opportunities. Both strategies aim to strengthen competitive advantage but focus on different aspects of business growth and risk management.
Defining Vertical Integration: Concepts and Types
Vertical integration involves a company controlling multiple stages of its supply chain, from production to distribution, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. There are two main types: backward integration, where a company acquires or merges with suppliers, and forward integration, which entails expanding into distribution or retail functions. This strategy boosts market control, improves supply chain coordination, and strengthens competitive advantage by minimizing reliance on external parties.
Understanding Diversification: Strategies and Approaches
Diversification involves expanding a company's operations into new markets or products to reduce risk and enhance growth potential. Common strategies include related diversification, which leverages existing capabilities in similar industries, and unrelated diversification, which ventures into entirely different sectors for portfolio stability. Effective diversification requires thorough market analysis and strategic alignment to optimize resource allocation and maximize competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Vertical Integration and Diversification
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its control over multiple stages of production or distribution within the same industry, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Diversification refers to a business strategy where a company expands into new markets or product lines to spread risk and increase growth opportunities. Key differences include vertical integration's focus on depth within an industry versus diversification's breadth across different industries or sectors.
Advantages of Vertical Integration in Modern Business
Vertical integration allows modern businesses to enhance control over their supply chains, reducing costs and increasing efficiency by eliminating intermediaries. It improves product quality consistency and accelerates innovation by fostering closer collaboration between production stages. Companies adopting vertical integration can achieve greater market power and competitive advantage by securing critical resources and enhancing their responsiveness to market changes.
Advantages and Risks of Diversification Strategies
Diversification strategies offer advantages such as spreading risk across various markets, enhancing revenue streams, and leveraging existing capabilities to enter new industries. However, risks include potential management complexity, dilution of core competencies, and challenges in achieving synergy between diverse business units. Effective diversification requires thorough market analysis and strategic alignment to avoid inefficiencies and resource misallocation.
Case Studies: Successful Vertical Integration Examples
Apple Inc. exemplifies successful vertical integration by controlling its hardware, software, and retail channels, enabling seamless product innovation and customer experience. Tesla vertically integrates battery production, vehicle assembly, and software development, reducing dependency on suppliers and accelerating EV advancements. Ikea's control over design, manufacturing, and distribution reduces costs and ensures quality, illustrating effective vertical integration in the retail furniture industry.
Case Studies: Notable Diversification Success Stories
General Electric's diversification strategy expanded its portfolio across industries such as aviation, healthcare, and energy, driving sustained growth and resilience against sector-specific downturns. Samsung's shift from purely electronics manufacturing to include construction, shipbuilding, and financial services exemplifies successful diversification enhancing global market presence and risk management. Tata Group diversified from textile manufacturing into steel, automotive, and information technology, showcasing how strategic diversification fosters innovation and long-term stability in emerging markets.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between vertical integration and diversification depends on factors such as industry dynamics, resource availability, and competitive advantage. Vertical integration is ideal for controlling supply chains and reducing costs in stable markets, while diversification suits companies seeking risk reduction and growth in varied markets. Assessing market conditions, core competencies, and long-term goals is critical to optimizing strategic outcomes.
Future Trends in Vertical Integration and Diversification
Future trends in vertical integration emphasize increasing use of advanced technologies like AI and blockchain to enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency, enabling companies to tightly control operations from production to distribution. Diversification is expected to leverage data analytics and digital platforms to identify emerging markets and consumer segments rapidly, fostering agile expansion and risk mitigation. Both strategies increasingly prioritize sustainability and resilience, with vertical integration focusing on eco-friendly supply chains and diversification targeting sectors aligned with global green initiatives.
Vertical Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com