A joint venture combines the strengths and resources of two or more businesses to achieve a specific goal or project, fostering shared risks and profits. This strategic alliance allows companies to enter new markets, access new technologies, and enhance competitive advantage efficiently. Discover how forming a joint venture can accelerate Your business growth and open new opportunities by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
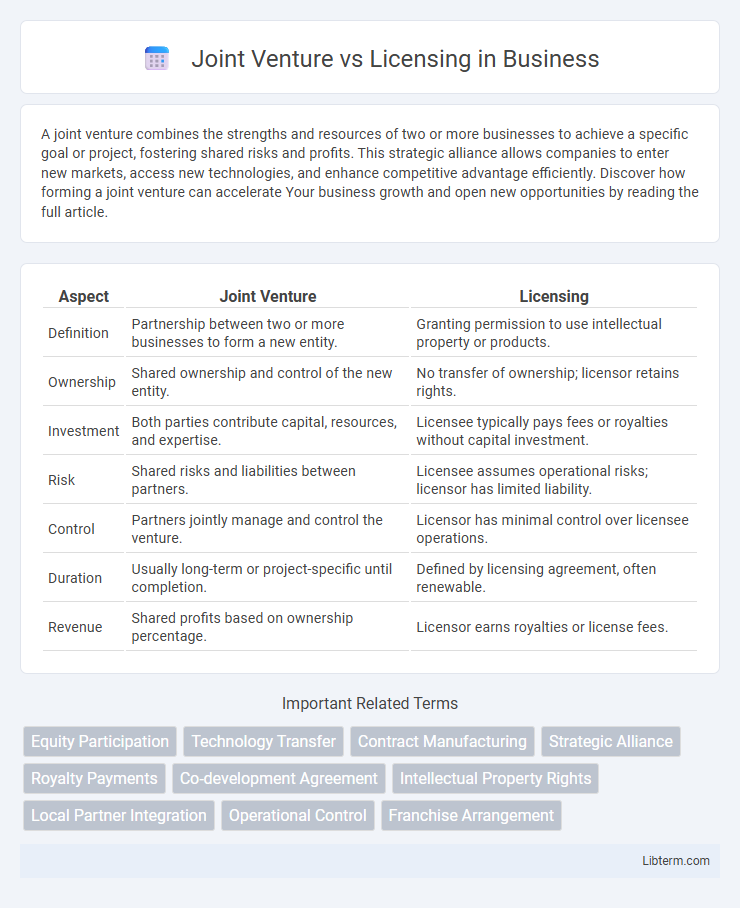
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Licensing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more businesses to form a new entity. | Granting permission to use intellectual property or products. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership and control of the new entity. | No transfer of ownership; licensor retains rights. |
| Investment | Both parties contribute capital, resources, and expertise. | Licensee typically pays fees or royalties without capital investment. |
| Risk | Shared risks and liabilities between partners. | Licensee assumes operational risks; licensor has limited liability. |
| Control | Partners jointly manage and control the venture. | Licensor has minimal control over licensee operations. |
| Duration | Usually long-term or project-specific until completion. | Defined by licensing agreement, often renewable. |
| Revenue | Shared profits based on ownership percentage. | Licensor earns royalties or license fees. |
Introduction to Joint Ventures and Licensing
Joint ventures involve two or more parties collaborating to create a new business entity, sharing resources, risks, and profits while maintaining joint control. Licensing grants one company the legal right to use another's intellectual property, technology, or brand under defined terms without transferring ownership. Both strategies offer pathways for market expansion, with joint ventures focused on partnership integration and licensing emphasizing asset utilization.
Definition and Key Concepts
A joint venture is a strategic alliance where two or more parties create a new legal entity to share resources, risks, and profits, often combining expertise and capital for mutual benefit. Licensing is a business arrangement in which the licensor grants the licensee rights to use intellectual property, technology, or brand name under defined terms without sharing ownership or control. Key concepts in joint ventures include shared decision-making, joint ownership, and profit sharing, whereas licensing centers on contractual permissions, royalty payments, and limited control over operations.
Legal Structure and Control
Joint ventures involve creating a separate legal entity with shared ownership, responsibilities, and profits, providing partners joint control and decision-making authority. Licensing agreements grant one party rights to use intellectual property without sharing ownership or control, maintaining clear legal separation and control by the licensor. The choice impacts liability, governance, and profit distribution based on the desired level of partnership and operational control.
Financial Investment and Risk Sharing
Joint ventures require significant financial investment from all partners, spreading both capital contributions and operational costs, which facilitates shared financial risk across the entities involved. Licensing involves lower initial investment, as the licensee pays fees or royalties to use the licensor's intellectual property, transferring most financial risk to the licensee while the licensor maintains limited exposure. The joint venture model promotes equitable risk sharing through mutual investments and shared liabilities, whereas licensing limits risk primarily to market and performance uncertainties borne by the licensee.
Intellectual Property Considerations
Joint ventures involve shared ownership and control over intellectual property (IP) created or contributed during the partnership, requiring clear agreements on IP rights, usage, and profit sharing to prevent disputes. Licensing agreements grant one party the right to use IP owned by another under specific terms, often including limitations on scope, duration, and exclusivity while preserving the licensor's ownership. Careful IP management in joint ventures ensures protection of proprietary assets, whereas licensing focuses on monetizing IP without transferring ownership, necessitating precise contract terms to safeguard innovations.
Market Entry Strategies
Joint ventures enable companies to share resources, risks, and local market knowledge, facilitating faster and more effective market entry, especially in complex or regulated environments. Licensing allows firms to enter foreign markets with lower investment and operational control by granting local partners the rights to produce and sell products. Both strategies offer scalable market access, but joint ventures provide deeper integration, while licensing emphasizes quick expansion with reduced financial exposure.
Operational Flexibility and Management
Joint ventures offer greater operational flexibility by enabling shared decision-making and resource pooling between partners, facilitating adaptive management strategies in dynamic markets. Licensing grants limited control, as licensees operate independently under predefined contractual terms, restricting the licensor's influence over daily operations and strategic adjustments. Effective management in joint ventures demands collaborative governance structures, whereas licensing relies on compliance monitoring and royalty administration.
Advantages of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures enable companies to combine resources and expertise, facilitating market entry with shared risks and capital investment. They provide strategic advantages such as local market knowledge, enhanced innovation through collaboration, and access to established distribution networks. This structure often results in stronger competitive positioning and faster growth compared to licensing agreements.
Advantages of Licensing
Licensing offers companies a low-risk entry into new markets by granting rights to local firms, reducing capital investment and operational expenses. It enables rapid revenue generation through royalties while maintaining control over intellectual property. Licensing also facilitates access to established distribution networks and local market expertise, accelerating market penetration and brand recognition.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Joint Venture vs Licensing
Choosing between a joint venture and licensing depends on control, risk tolerance, and resource commitment; joint ventures require shared ownership and active involvement, offering greater market integration but higher complexity. Licensing allows faster market entry with lower investment and reduced risk, as the licensor grants rights to use intellectual property in exchange for royalties. Evaluating factors such as desired level of control, financial capacity, and long-term strategic goals is essential to select the optimal approach for international expansion or product commercialization.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com