Efficient supply chain management is crucial for minimizing costs and maximizing customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery of goods and services. Advanced technologies like AI and IoT optimize inventory levels and streamline logistics to adapt to market demands dynamically. Explore the following insights to discover how your business can leverage supply chain strategies for competitive advantage.
Table of Comparison
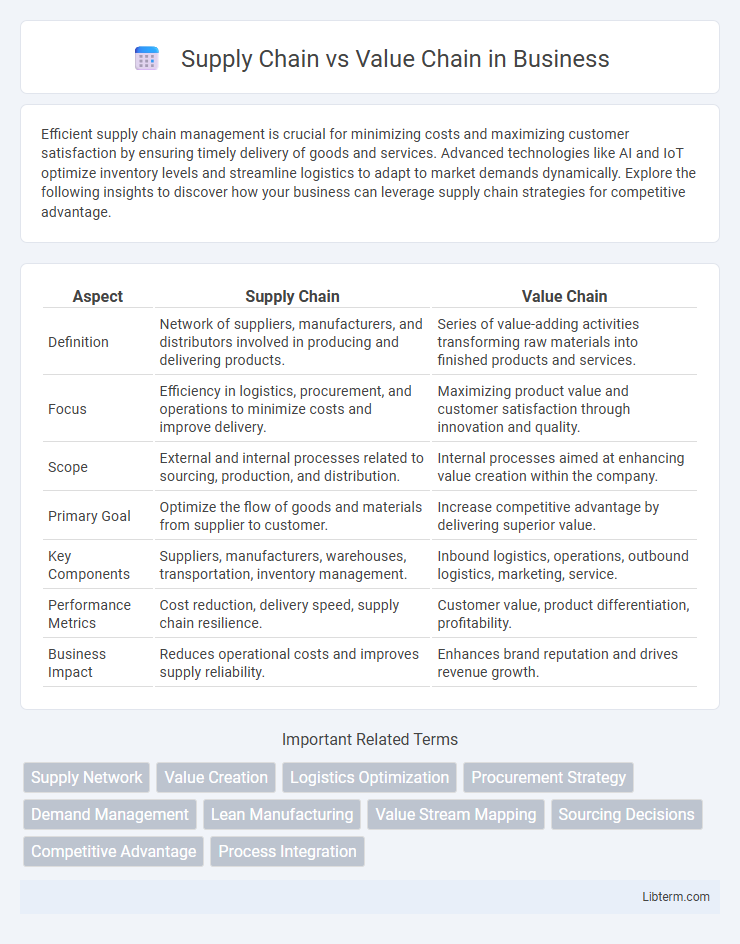
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Value Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors involved in producing and delivering products. | Series of value-adding activities transforming raw materials into finished products and services. |
| Focus | Efficiency in logistics, procurement, and operations to minimize costs and improve delivery. | Maximizing product value and customer satisfaction through innovation and quality. |
| Scope | External and internal processes related to sourcing, production, and distribution. | Internal processes aimed at enhancing value creation within the company. |
| Primary Goal | Optimize the flow of goods and materials from supplier to customer. | Increase competitive advantage by delivering superior value. |
| Key Components | Suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, transportation, inventory management. | Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, service. |
| Performance Metrics | Cost reduction, delivery speed, supply chain resilience. | Customer value, product differentiation, profitability. |
| Business Impact | Reduces operational costs and improves supply reliability. | Enhances brand reputation and drives revenue growth. |
Introduction to Supply Chain and Value Chain
The supply chain encompasses all processes involved in producing and delivering a product, starting from raw material procurement to final customer distribution. The value chain focuses on activities that add value to the product or service, including design, production, marketing, and after-sales support. Understanding both concepts is vital for optimizing operational efficiency and maximizing customer satisfaction within competitive markets.
Defining the Supply Chain
The supply chain encompasses the entire network of entities, resources, activities, and technologies involved in the creation and distribution of a product, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. It emphasizes logistics, procurement, manufacturing, and distribution processes to ensure efficient product flow and cost optimization. Understanding the supply chain is crucial for managing inventory, reducing lead times, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Defining the Value Chain
The value chain encompasses all activities a company undertakes to create products or services that deliver value to customers, extending beyond the supply chain's focus on procurement and logistics. It includes primary activities such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, sales, and service, along with support activities like technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure. Defining the value chain highlights how each step adds value, driving competitive advantage and customer satisfaction throughout the process.
Key Components of a Supply Chain
Key components of a supply chain include procurement of raw materials, manufacturing or production processes, inventory management, warehousing, transportation, and distribution to end customers. Effective supply chain management integrates demand forecasting, supplier relationship management, and logistics coordination to optimize flow and reduce costs. These components work together to ensure timely delivery, quality control, and overall operational efficiency within the supply chain network.
Key Elements of a Value Chain
Key elements of a value chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, all aimed at enhancing product value and customer satisfaction. Each activity adds incremental value by optimizing resource use, improving quality, and facilitating innovation. Effective coordination across these elements drives competitive advantage and maximizes profitability beyond the traditional focus on supply chain efficiency.
Supply Chain vs Value Chain: Core Differences
The supply chain focuses on the logistics and processes involved in sourcing, production, and distribution of goods, emphasizing efficiency and cost reduction. The value chain centers on activities that add value to products or services, from design to marketing and after-sales support, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. Core differences lie in the supply chain's operational scope versus the value chain's strategic focus on creating value beyond the physical flow of goods.
Impact on Business Strategy
Supply chain management focuses on optimizing the flow of goods, information, and resources from suppliers to customers, directly influencing operational efficiencies and cost reductions in business strategy. Value chain analysis emphasizes creating competitive advantage by enhancing activities that add value to products or services, shaping strategic priorities around innovation, differentiation, and customer experience. Integrating both supply chain and value chain perspectives enables businesses to align operational execution with strategic goals, driving sustained profitability and market responsiveness.
Benefits of Optimizing Each Chain
Optimizing the supply chain enhances operational efficiency by reducing costs, improving inventory management, and accelerating product delivery, which leads to increased customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. Streamlining the value chain focuses on maximizing value creation at each stage, driving innovation, improving product quality, and enhancing customer experiences to boost overall profitability. Both optimized supply and value chains contribute to sustainable growth by aligning resources with strategic business goals and adapting to market demands effectively.
Challenges in Supply Chain and Value Chain Management
Challenges in supply chain management include demand forecasting inaccuracies, supplier disruptions, inventory management complexities, and logistics inefficiencies that can lead to increased costs and delays. Value chain management faces difficulties in coordinating cross-functional activities, aligning stakeholders' goals, and integrating technology to enhance customer value and competitive advantage. Both supply chain and value chain management require robust risk mitigation strategies and process optimization to effectively address these challenges and drive business performance.
Future Trends in Supply Chain and Value Chain Integration
Future trends in supply chain and value chain integration emphasize digital transformation powered by AI, blockchain, and IoT to enhance transparency and efficiency. Companies are increasingly adopting real-time data analytics and automation to synchronize supply chain operations with value creation activities. Sustainability and circular economy principles are driving the alignment of supply and value chains to reduce waste and optimize resource utilization.
Supply Chain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com