Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total economic output produced by a country's residents, both domestically and abroad, within a specific time period. This metric helps assess the overall economic health and the income generated by your nation's citizens and businesses, regardless of where the production occurs. Explore the rest of this article to understand how GNP differs from GDP and why it matters for economic analysis.
Table of Comparison
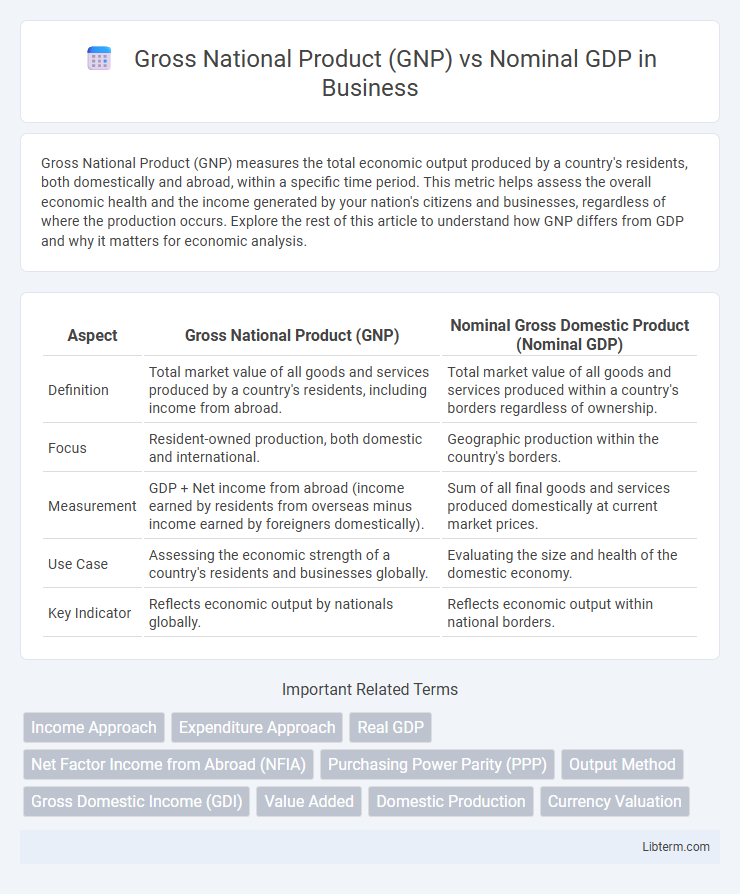
| Aspect | Gross National Product (GNP) | Nominal Gross Domestic Product (Nominal GDP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total market value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad. | Total market value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders regardless of ownership. |
| Focus | Resident-owned production, both domestic and international. | Geographic production within the country's borders. |
| Measurement | GDP + Net income from abroad (income earned by residents from overseas minus income earned by foreigners domestically). | Sum of all final goods and services produced domestically at current market prices. |
| Use Case | Assessing the economic strength of a country's residents and businesses globally. | Evaluating the size and health of the domestic economy. |
| Key Indicator | Reflects economic output by nationals globally. | Reflects economic output within national borders. |
Introduction to GNP and Nominal GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of the production location, over a specified period. Nominal GDP calculates the market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders, valued at current prices without adjusting for inflation. Understanding the distinction between GNP and nominal GDP is essential for analyzing economic performance, as GNP accounts for income from abroad while nominal GDP focuses solely on domestic production.
Defining Gross National Product (GNP)
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of the location of production, during a specific time period. It includes income earned by nationals abroad and excludes income generated by foreign residents within the country, distinguishing it from nominal GDP. GNP reflects the economic output attributed to ownership and citizenship, providing insight into the overall economic performance of a nation's residents.
Understanding Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific period using current prices, without adjusting for inflation. Unlike Gross National Product (GNP), which includes income earned by residents from abroad and excludes income earned by foreigners domestically, nominal GDP focuses solely on domestic production. This distinction is crucial for analyzing economic activity based on current market prices and understanding the scale of a nation's economy in a given time frame.
Key Differences Between GNP and Nominal GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad, while Nominal GDP represents the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders regardless of ownership. GNP accounts for net income earned from foreign investments, distinguishing it from Nominal GDP, which is confined to domestic production. The key difference lies in the scope of production versus ownership, with GNP emphasizing resident-based economic activity and Nominal GDP focusing on geographic location.
Calculation Methods: GNP vs Nominal GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the residents of a country, including income earned abroad, calculated by adding net income from foreign investments to Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Nominal GDP represents the total market value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, calculated using current market prices without adjusting for inflation. The key difference in calculation lies in GNP incorporating net foreign income, while Nominal GDP is strictly domestic output valued at current prices.
Economic Significance of GNP and Nominal GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total economic output produced by a country's residents, including income earned abroad, highlighting the economic strength and global income generation of a nation. Nominal GDP calculates the market value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders without adjusting for inflation, reflecting the current economic activity level. Understanding the distinction between GNP and nominal GDP aids policymakers in assessing domestic economic performance versus international income flows, shaping fiscal and monetary strategies.
GNP vs Nominal GDP: Global Comparisons
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total economic output produced by the residents of a country, including income from abroad, while Nominal GDP accounts for the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders without adjusting for inflation. In global comparisons, countries with significant income from overseas investments like the Philippines or Ireland often report higher GNP than Nominal GDP, reflecting their residents' international earnings. Conversely, resource-rich nations with substantial foreign investments, such as Saudi Arabia, may have Nominal GDP exceeding GNP due to income generated by foreign entities within their borders.
Impact of Exchange Rates and Inflation
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total economic output produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad, while Nominal GDP calculates the market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders without adjustment for inflation. Exchange rate fluctuations significantly affect GNP by altering the value of income earned overseas when converted to the domestic currency, causing variability in international comparisons. Nominal GDP is impacted primarily by inflation, as rising price levels increase the nominal value of goods and services, making it less reliable for measuring real economic growth without inflation adjustments.
Practical Applications: Policy and Analysis
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total income earned by a country's residents, including overseas earnings, providing insight into the economic strength of a nation's citizens and their international activities. Nominal GDP calculates the market value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, reflecting domestic economic performance without adjusting for inflation. Policymakers use GNP to assess national income and inform decisions on foreign investment and remittances, while Nominal GDP guides fiscal and monetary policy by capturing real-time economic output and growth trends.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Economic Indicator
Selecting the appropriate economic indicator depends on the analytical focus: Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total value of goods and services produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad, while Nominal GDP captures the market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders without adjusting for inflation. GNP is more relevant for assessing national income and residents' economic well-being, whereas Nominal GDP provides a snapshot of domestic economic activity. Therefore, understanding differences in scope and purpose ensures accurate economic analysis and policy decisions.
Gross National Product (GNP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com