Strategic alliances enhance business growth by combining complementary strengths and resources between companies, creating competitive advantages that are difficult to replicate. These partnerships can accelerate innovation, broaden market reach, and optimize operational efficiencies without the complexities of mergers or acquisitions. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your business can leverage strategic alliances for sustainable success.
Table of Comparison
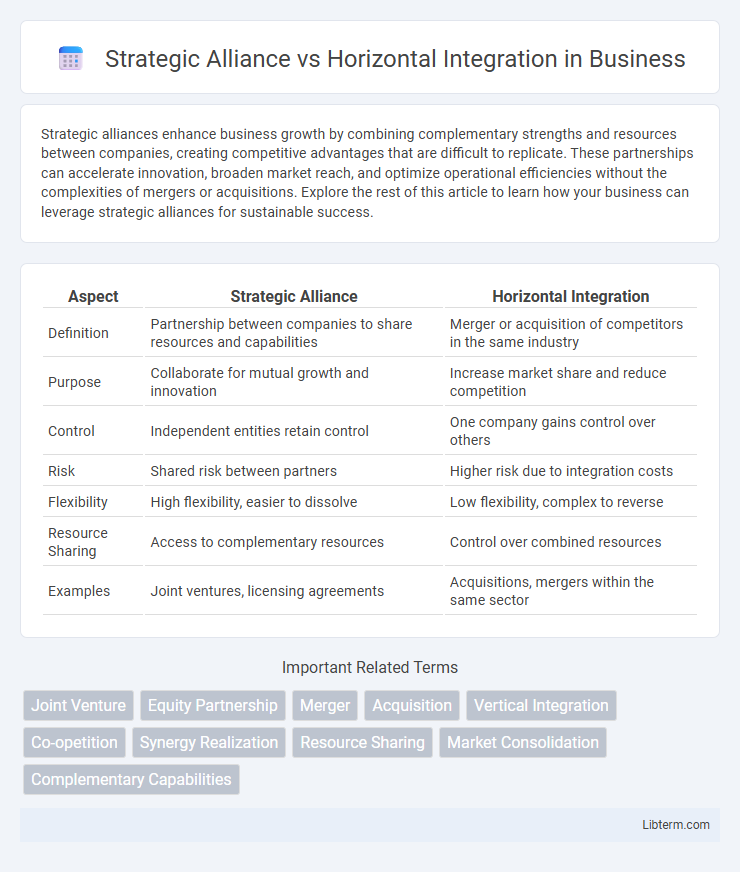
| Aspect | Strategic Alliance | Horizontal Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between companies to share resources and capabilities | Merger or acquisition of competitors in the same industry |
| Purpose | Collaborate for mutual growth and innovation | Increase market share and reduce competition |
| Control | Independent entities retain control | One company gains control over others |
| Risk | Shared risk between partners | Higher risk due to integration costs |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, easier to dissolve | Low flexibility, complex to reverse |
| Resource Sharing | Access to complementary resources | Control over combined resources |
| Examples | Joint ventures, licensing agreements | Acquisitions, mergers within the same sector |
Introduction to Strategic Alliance and Horizontal Integration
Strategic alliances involve partnerships between independent companies aiming to leverage complementary resources and capabilities without merging ownership, promoting innovation, market expansion, and risk-sharing. Horizontal integration refers to the consolidation of firms operating at the same level of the supply chain, often through mergers or acquisitions, to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. Both strategies are pivotal in corporate growth but differ fundamentally in control, resource pooling, and degree of organizational integration.
Definition and Key Features of Strategic Alliance
A strategic alliance is a cooperative agreement between two or more independent companies to achieve shared objectives while remaining separate entities. Key features include resource sharing, complementary strengths, mutual benefits, and flexibility without full ownership or merger. Unlike horizontal integration, which involves full acquisition or merger of competitors to consolidate market share, strategic alliances emphasize collaboration without sacrificing autonomy.
Understanding Horizontal Integration: Overview and Examples
Horizontal integration involves a company expanding its market share by acquiring or merging with competitors operating at the same level of the supply chain, thereby increasing economies of scale and reducing competition. Prominent examples include Facebook's acquisition of Instagram and Disney's purchase of 21st Century Fox, both of which enhanced market dominance within their respective industries. This strategic approach helps firms consolidate resources, streamline operations, and access larger customer bases in highly competitive sectors.
Main Objectives: Strategic Alliance vs Horizontal Integration
The main objective of a strategic alliance is to leverage complementary strengths, share resources, and access new markets or technologies without full ownership, fostering collaboration and innovation while minimizing risks. In contrast, horizontal integration aims to increase market share, reduce competition, achieve economies of scale, and enhance bargaining power by acquiring or merging with competitors operating in the same industry level. Both strategies seek growth but differ fundamentally in structure, control, and risk distribution.
Advantages of Strategic Alliances for Businesses
Strategic alliances enable businesses to access new markets, share resources, and leverage complementary strengths without the financial commitment or risks associated with mergers typical in horizontal integration. These partnerships foster innovation through collaborative efforts, accelerate product development, and enhance competitive advantage by combining unique capabilities from each firm. Furthermore, strategic alliances offer flexibility, allowing companies to adapt quickly to changing market conditions while maintaining operational independence.
Benefits and Challenges of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enables companies to expand market share, achieve economies of scale, and reduce competition by acquiring or merging with firms in the same industry. The benefits include increased operational efficiency, enhanced product offerings, and greater bargaining power with suppliers and customers. Challenges involve regulatory scrutiny due to antitrust concerns, potential culture clashes, and risks of overextension leading to reduced innovation and flexibility.
Key Differences between Strategic Alliance and Horizontal Integration
Strategic alliances involve collaboration between independent firms to achieve mutual goals while maintaining their autonomy, whereas horizontal integration entails the direct acquisition or merger of companies operating at the same level within an industry to consolidate market share. Key differences include the level of control, with horizontal integration resulting in unified management and ownership, contrasted with strategic alliances where control remains separate. Furthermore, strategic alliances typically offer greater flexibility and lower capital investment compared to the full resource commitment and regulatory scrutiny often required in horizontal integration.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between the Two Strategies
Choosing between strategic alliance and horizontal integration involves analyzing company goals, resource capabilities, and market conditions. Strategic alliances suit businesses seeking flexibility and shared expertise without full control, while horizontal integration offers complete control and potential economies of scale but requires significant investment and regulatory scrutiny. Assessing competitive environment, cultural compatibility, and long-term objectives helps determine the optimal approach.
Real-World Case Studies: Success and Failure Stories
Strategic alliances, such as the partnership between Starbucks and PepsiCo, have leveraged complementary strengths to expand market reach and drive innovation without full mergers, demonstrating agility and risk-sharing benefits. In contrast, horizontal integrations like Disney's acquisition of 21st Century Fox illustrate how consolidating competitors can achieve economies of scale and content diversification but may face regulatory hurdles and cultural integration challenges. Failures in horizontal integration, exemplified by AOL and Time Warner's merger, highlight risks of overestimating synergies and misaligned strategic goals, while unsuccessful strategic alliances often result from poor coordination and conflicting interests, as seen in the Daimler-Chrysler joint venture.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Growth Strategy
Selecting the appropriate growth strategy depends on a company's objectives, resources, and market conditions; strategic alliances offer flexibility and shared risk, ideal for entering new markets or leveraging complementary strengths. Horizontal integration provides control and market power through the acquisition or merger with competitors, enhancing economies of scale and competitive positioning. Assessing industry dynamics, financial capacity, and long-term goals guides businesses in deciding between collaboration through alliances or consolidation via horizontal integration.
Strategic Alliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com