Fraudulent accounting involves intentional manipulation of financial statements to deceive stakeholders and misrepresent a company's true financial health. Detecting these schemes requires thorough audits, strong internal controls, and a keen understanding of common red flags such as unexplained discrepancies and abnormal transactions. Discover how to protect your business from fraudulent accounting by exploring effective prevention strategies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
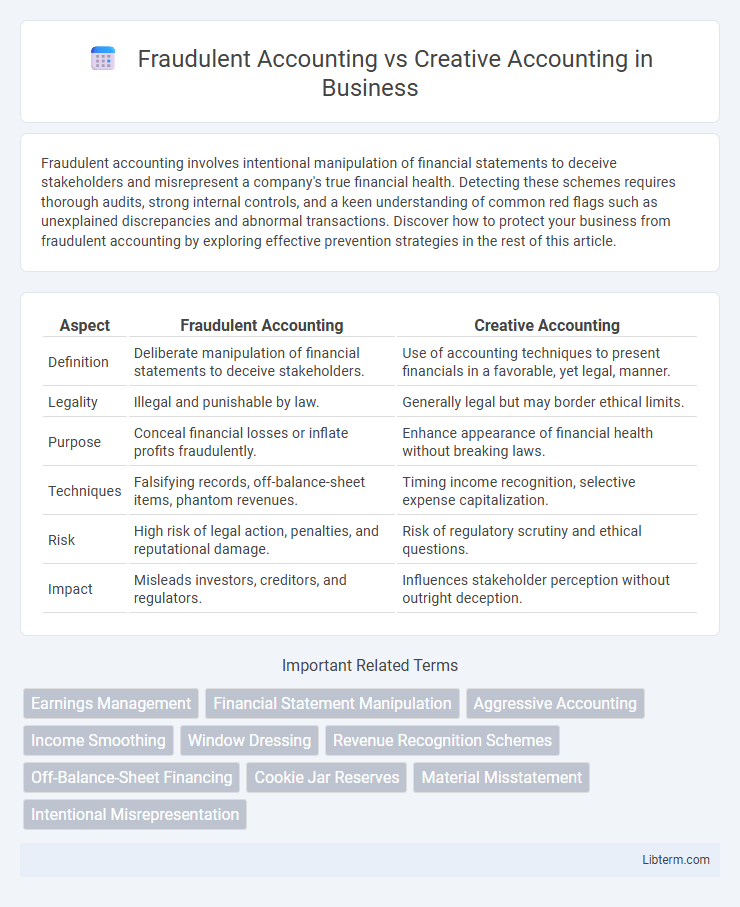
| Aspect | Fraudulent Accounting | Creative Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate manipulation of financial statements to deceive stakeholders. | Use of accounting techniques to present financials in a favorable, yet legal, manner. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Generally legal but may border ethical limits. |
| Purpose | Conceal financial losses or inflate profits fraudulently. | Enhance appearance of financial health without breaking laws. |
| Techniques | Falsifying records, off-balance-sheet items, phantom revenues. | Timing income recognition, selective expense capitalization. |
| Risk | High risk of legal action, penalties, and reputational damage. | Risk of regulatory scrutiny and ethical questions. |
| Impact | Misleads investors, creditors, and regulators. | Influences stakeholder perception without outright deception. |
Introduction to Fraudulent vs Creative Accounting
Fraudulent accounting involves intentionally manipulating financial data to deceive stakeholders and misrepresent a company's true financial health, often violating legal and ethical standards. Creative accounting employs legally permissible methods to present financial statements in a favorable light, exploiting accounting rules and judgments without explicit fraud. Understanding the distinction between fraudulent and creative accounting is crucial for evaluating the reliability and integrity of financial reports.
Defining Fraudulent Accounting
Fraudulent accounting involves intentionally manipulating financial statements to deceive stakeholders by presenting false or misleading information, often for personal gain or to hide poor performance. It includes actions such as fabricating transactions, inflating revenues, or understating liabilities, violating accounting standards and legal regulations. In contrast, creative accounting exploits loopholes within accounting rules to present financial data more favorably without outright illegal conduct.
Understanding Creative Accounting
Creative accounting involves the manipulation of financial statements within legal boundaries to present a more favorable view of a company's financial position, often through aggressive revenue recognition or expense deferral techniques. Unlike fraudulent accounting, which entails intentional misrepresentation of financial data and is illegal, creative accounting exploits loopholes and accounting standards to influence stakeholders' perceptions without breaching laws explicitly. Understanding creative accounting is crucial for investors and regulators to discern genuine financial health from artfully crafted numbers designed to mislead.
Key Differences Between Fraudulent and Creative Accounting
Fraudulent accounting involves deliberately falsifying financial records to deceive stakeholders, violating legal and ethical standards, whereas creative accounting exploits loopholes within accounting regulations to present a more favorable financial position without outright deception. Key differences include intent and legality: fraudulent accounting is illegal and done with intent to mislead, while creative accounting remains within the boundaries of the law, albeit often pushing ethical limits. The impact on financial statements also differs, with fraudulent accounting distorting true financial health and creative accounting enhancing reported results through legitimate but aggressive interpretation of accounting rules.
Motivations Behind Fraudulent and Creative Accounting
Fraudulent accounting is primarily motivated by the intention to deceive stakeholders and manipulate financial outcomes for personal or organizational gain, often involving illegal activities. Creative accounting arises from the desire to present financial statements in a more favorable light within legal boundaries, aiming to attract investors or meet regulatory standards without outright falsification. Both practices reflect underlying pressures such as performance targets, market expectations, and regulatory compliance challenges that drive companies to alter financial reporting strategies.
Common Techniques in Fraudulent Accounting
Fraudulent accounting commonly involves techniques such as intentional revenue recognition manipulation, fictitious asset creation, and liability concealment to distort financial statements. These methods include inflating sales figures through fake invoices, understating expenses by omitting liabilities, and falsifying inventory records to boost profitability. Unlike creative accounting, which operates within legal frameworks, fraudulent accounting violates accounting standards and often results in legal consequences.
Common Techniques in Creative Accounting
Creative accounting often involves techniques such as earnings management, revenue recognition manipulation, and off-balance-sheet financing to present a more favorable financial position. These methods exploit loopholes and flexible accounting standards without outright breaking the law, unlike fraudulent accounting which involves intentional deception or misrepresentation. Common tools in creative accounting include cookie jar reserves, channel stuffing, and aggressive capitalization of expenses, aiming to influence financial outcomes while maintaining legal compliance.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Fraudulent accounting involves intentional manipulation of financial statements to deceive stakeholders, violating legal standards such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and resulting in criminal penalties. Creative accounting, while exploiting loopholes within accounting regulations to present a more favorable financial position, operates in a gray area that can erode ethical trust despite being technically legal. Both practices undermine corporate transparency and investor confidence, but fraudulent accounting carries direct legal consequences, whereas creative accounting raises significant ethical concerns and risks reputational damage.
Impact on Stakeholders and Financial Statements
Fraudulent accounting involves intentional misrepresentation of financial data, leading to false financial statements that mislead investors, creditors, and regulators, causing severe trust erosion and potential legal consequences. Creative accounting manipulates accounting rules within legal boundaries to present a more favorable financial position, which can mislead stakeholders about a company's true performance and risk profile without immediate legal repercussions. Both practices distort the accuracy of financial statements, impacting investment decisions, creditworthiness assessments, and overall market confidence.
Strategies for Detection and Prevention
Fraudulent accounting involves intentional misrepresentation of financial statements to deceive stakeholders, whereas creative accounting uses legal but aggressive techniques to present a desired financial image. Detection strategies include rigorous internal audits, employing forensic accounting methods, and implementing robust whistleblower policies to uncover irregularities. Prevention relies on strong corporate governance, continuous staff training on ethical standards, and adopting advanced data analytics tools for real-time anomaly detection.
Fraudulent Accounting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com