An advisory board provides expert guidance and strategic advice to help shape business decisions and drive growth. Your company can benefit from diverse perspectives and industry insights that enhance problem-solving and innovation. Explore the article to learn how establishing an effective advisory board can elevate your organization's success.
Table of Comparison
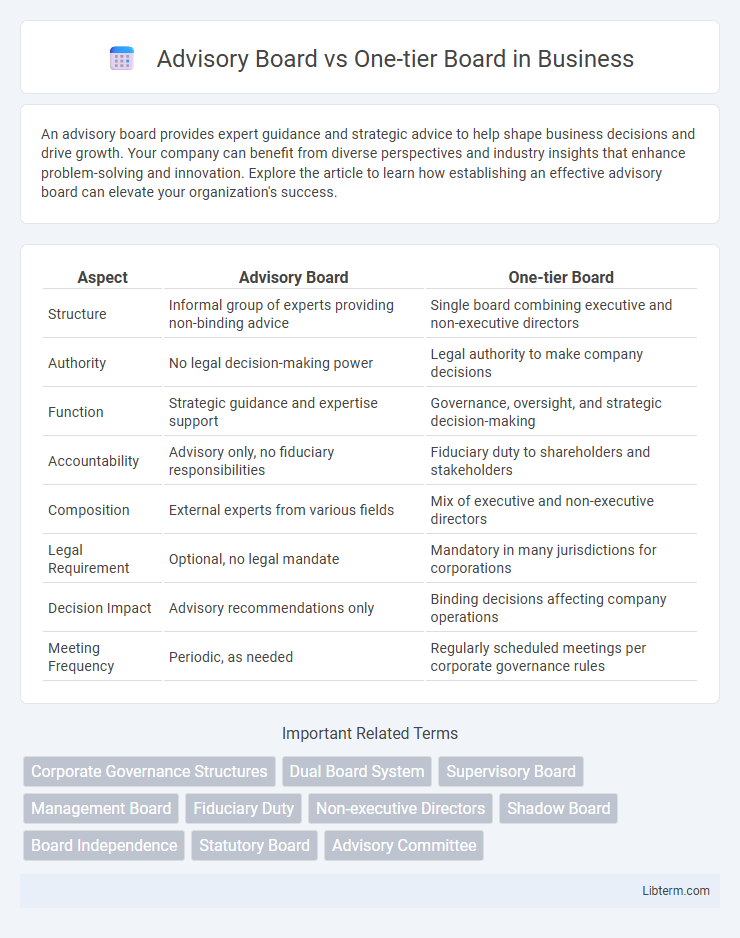
| Aspect | Advisory Board | One-tier Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Informal group of experts providing non-binding advice | Single board combining executive and non-executive directors |
| Authority | No legal decision-making power | Legal authority to make company decisions |
| Function | Strategic guidance and expertise support | Governance, oversight, and strategic decision-making |
| Accountability | Advisory only, no fiduciary responsibilities | Fiduciary duty to shareholders and stakeholders |
| Composition | External experts from various fields | Mix of executive and non-executive directors |
| Legal Requirement | Optional, no legal mandate | Mandatory in many jurisdictions for corporations |
| Decision Impact | Advisory recommendations only | Binding decisions affecting company operations |
| Meeting Frequency | Periodic, as needed | Regularly scheduled meetings per corporate governance rules |
Introduction to Governance Structures
Advisory boards provide non-binding strategic advice without fiduciary responsibilities, allowing companies to benefit from expert insights without formal governance obligations. One-tier boards combine executive directors and non-executive directors in a single board structure, sharing both management oversight and decision-making duties. This governance structure enhances accountability and facilitates seamless communication between management and oversight functions.
Defining the Advisory Board
An Advisory Board is a group of external experts who provide non-binding strategic advice and industry insights to a company's executives, without holding formal decision-making authority or legal responsibilities. Unlike One-tier Boards, which combine executive directors and non-executive directors in a single governing body responsible for both management and oversight, Advisory Boards focus solely on offering guidance to improve business performance. Their role enhances corporate governance by leveraging specialized knowledge and supporting the executive team's strategic decisions.
What is a One-tier Board?
A One-tier Board is a corporate governance structure where executive and non-executive directors sit together on a single board, sharing responsibility for strategic decisions and oversight. This integrated model contrasts with an Advisory Board, which solely provides non-binding advice without formal decision-making authority. One-tier Boards promote unified leadership and streamlined communication between management and oversight functions.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
The Advisory Board provides non-binding strategic advice and expertise without decision-making authority, primarily supporting the company's management with specialized knowledge and industry insights. The One-tier Board combines executive and non-executive directors in a single body responsible for both managerial oversight and strategic decision-making, ensuring direct accountability and integrated governance. Key responsibilities of the One-tier Board include approving major policies, monitoring executive performance, and safeguarding shareholder interests, while the Advisory Board focuses on mentoring, networking, and guiding innovation.
Structural Differences: Advisory vs One-tier
An Advisory Board functions as a non-binding body offering strategic advice without decision-making authority, while a One-tier Board combines executive and non-executive directors in a single board responsible for both management oversight and operational decisions. The One-tier Board structure centralizes governance, facilitating direct accountability and quicker decision-making compared to the Advisory Board's consultative role. Unlike the Advisory Board, the One-tier Board legally directs company affairs, creating a clear hierarchy and integrated control.
Decision-making Authority and Influence
A One-tier Board consolidates decision-making authority within a single group of executive and non-executive directors, enabling swift and unified corporate governance. In contrast, an Advisory Board holds no formal decision-making power but serves as a consultative body, providing strategic guidance and influencing decisions indirectly. The One-tier structure centralizes authority, whereas the Advisory Board enhances influence through expert recommendations without binding control.
Legal Liabilities and Regulatory Implications
An Advisory Board holds no legal liabilities as its role is purely consultative without decision-making authority, distinguishing it from a One-tier Board which carries full fiduciary responsibilities and regulatory obligations under corporate governance laws. Members of a One-tier Board face direct legal consequences for breaches of duty, including negligence and misconduct, which can result in personal liability and penalties mandated by regulatory bodies. Regulatory implications for One-tier Boards include stringent compliance with financial reporting, transparency, and conflict of interest rules, whereas Advisory Boards operate without such regulatory burdens since they lack formal governance powers.
Strategic Benefits and Limitations
An Advisory Board offers strategic benefits such as diverse expertise and flexible guidance without legal obligations, allowing rapid adaptation to business challenges, but lacks formal decision-making authority which can limit its influence on governance. A One-tier Board integrates executive and non-executive directors, enhancing oversight and streamlined decision-making with clear accountability, yet may face conflicts of interest and reduced independence in strategic deliberations. Balancing these structures depends on organizational needs for agility versus formal control and regulatory compliance.
Choosing the Right Board Structure
Choosing the right board structure depends on company size, governance needs, and regulatory requirements, with Advisory Boards providing non-binding strategic advice without fiduciary duties, while One-tier Boards combine supervisory and management roles in a single entity responsible for decision-making and oversight. Companies seeking flexibility and external expertise often prefer Advisory Boards for their informal guidance, whereas firms requiring clear accountability and integrated governance favor One-tier Boards for streamlined leadership and compliance. Evaluating factors such as company complexity, stakeholder interests, and legal environment is crucial to selecting the optimal board structure that supports effective corporate governance and strategic goals.
Conclusion: Advisory Board or One-tier Board?
Choosing between an Advisory Board and a One-tier Board depends on the organization's governance needs and decision-making structure. A One-tier Board combines executive and non-executive directors, providing unified control and clearer accountability, ideal for companies seeking strong oversight and legal compliance. An Advisory Board offers flexible, non-binding guidance without formal governance authority, suited for startups or firms prioritizing expert advice without altering board composition.
Advisory Board Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com