Advisory fee refers to the charge clients pay for professional financial advice and portfolio management services. This fee is typically calculated as a percentage of the assets under management, aligning the advisor's interests with your financial growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand how advisory fees impact your investments and what to consider when choosing a financial advisor.
Table of Comparison
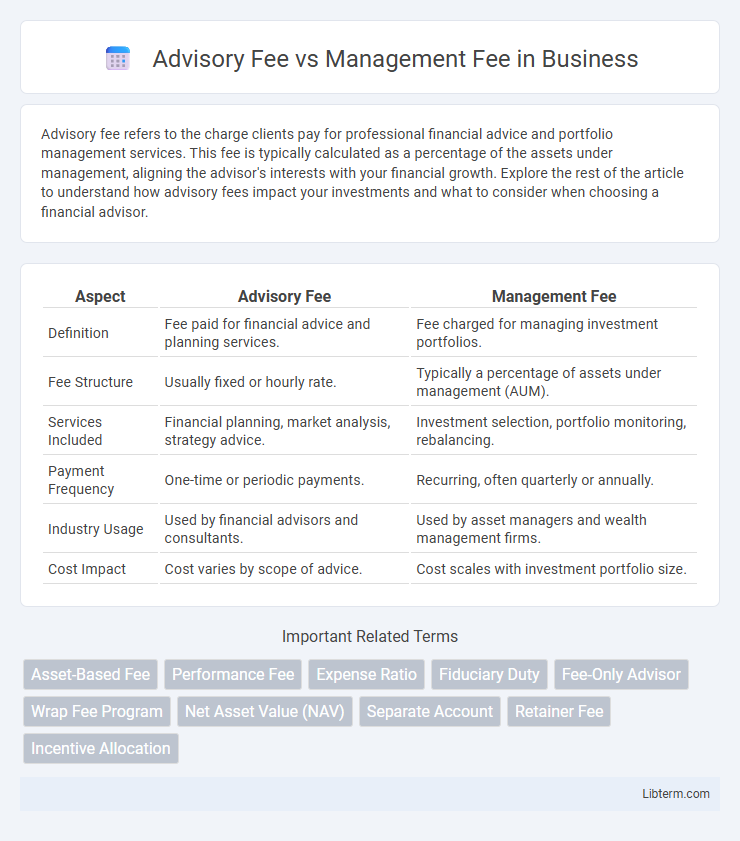
| Aspect | Advisory Fee | Management Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fee paid for financial advice and planning services. | Fee charged for managing investment portfolios. |
| Fee Structure | Usually fixed or hourly rate. | Typically a percentage of assets under management (AUM). |
| Services Included | Financial planning, market analysis, strategy advice. | Investment selection, portfolio monitoring, rebalancing. |
| Payment Frequency | One-time or periodic payments. | Recurring, often quarterly or annually. |
| Industry Usage | Used by financial advisors and consultants. | Used by asset managers and wealth management firms. |
| Cost Impact | Cost varies by scope of advice. | Cost scales with investment portfolio size. |
Understanding Advisory Fees
Advisory fees are charges by financial advisors for personalized investment guidance and strategic planning, typically calculated as a percentage of assets under management or a flat rate. These fees cover tailored services such as portfolio analysis, risk assessment, and ongoing financial advice, separate from management fees that specifically pay for the day-to-day investment management. Understanding advisory fees helps investors evaluate the cost-to-value ratio of comprehensive financial planning versus simple asset management.
What Are Management Fees?
Management fees are charges imposed by investment managers or funds to cover the costs of managing an investment portfolio, typically calculated as a percentage of assets under management (AUM). These fees compensate portfolio managers for their expertise, research, and active decision-making aimed at optimizing investment returns. Management fees differ from advisory fees, which often cover personalized financial advice and planning services rather than direct portfolio management.
Key Differences Between Advisory and Management Fees
Advisory fees are charged for personalized investment advice, financial planning, and portfolio strategy consultations, reflecting the value of expert guidance. Management fees pertain to the ongoing oversight, administration, and execution of investment portfolios, typically expressed as a percentage of assets under management (AUM). Key differences include the advisory fee's emphasis on consultation and tailored advice, while management fees cover continuous asset management and operational costs.
How Advisory Fees Are Calculated
Advisory fees are typically calculated as a percentage of assets under management (AUM), often ranging from 0.5% to 2% annually, depending on the complexity and size of the portfolio. These fees might be tiered, decreasing as AUM increases, and are usually charged quarterly or annually. Unlike flat management fees, advisory fees can also incorporate performance-based components tied to investment returns or specific financial goals.
Management Fee Structures Explained
Management fee structures typically involve a fixed percentage of assets under management (AUM), often ranging from 0.5% to 2% annually, designed to cover portfolio management and administrative services. Some structures incorporate tiered percentages, decreasing as AUM increases, to incentivize larger investments and align interests between clients and managers. These fees differ from advisory fees, which may be flat-rate or hourly charges focused on financial planning and consulting rather than ongoing asset management.
Pros and Cons of Advisory Fees
Advisory fees typically charge a percentage of assets under management, aligning advisors' incentives with clients' portfolio growth and providing ongoing personalized financial guidance. However, these fees can be higher than flat-rate management fees, potentially reducing net investment returns over time. Some clients may find advisory fees more transparent and value-added, while others see them as costly, especially if the advisory service does not significantly enhance investment performance.
Pros and Cons of Management Fees
Management fees provide consistent revenue streams for investment firms and cover operational costs, enhancing portfolio management quality. However, high management fees can reduce investor returns and may not correlate directly with fund performance, potentially discouraging investors. Transparent fee structures and competitive rates are essential to balance profitability and client satisfaction in investment management.
Factors Influencing Fee Selection
Advisory fee selection depends on factors such as the complexity of financial advice, the advisor's expertise, and the scope of services offered, often reflecting personalized investment strategies or comprehensive financial planning. Management fees are influenced by portfolio size, asset class, and the level of active portfolio management, with larger portfolios or specialized investments typically incurring higher costs. Market conditions and regulatory standards also play a role in determining the competitive fee structures between advisory and management services.
Impact on Investment Returns
Advisory fees typically range from 0.25% to 1% of assets under management and directly reduce net investment returns by lowering the capital available for growth. Management fees, often higher and associated with mutual funds or ETFs, can significantly erode returns over time due to compounding effects, with average rates around 0.5% to 2%. Minimizing these fees is crucial for investors aiming to maximize long-term portfolio performance and achieve better net outcomes.
Choosing the Right Fee Structure for You
Advisory fees typically involve a flat or percentage-based charge for personalized financial advice, while management fees are ongoing expenses covering asset management services. Choosing the right fee structure depends on your investment goals, level of desired service, and budget, with advisory fees often suited for tailored guidance and management fees for continuous portfolio oversight. Evaluating fee transparency, service scope, and potential impact on returns helps ensure the chosen structure aligns with your financial priorities.
Advisory Fee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com