Efficient logistics management ensures the smooth flow of goods from origin to destination, minimizing delays and reducing costs. Advanced technologies and strategic planning optimize supply chains, enhancing customer satisfaction and business profitability. Discover how improving your logistics can transform operations and boost success by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
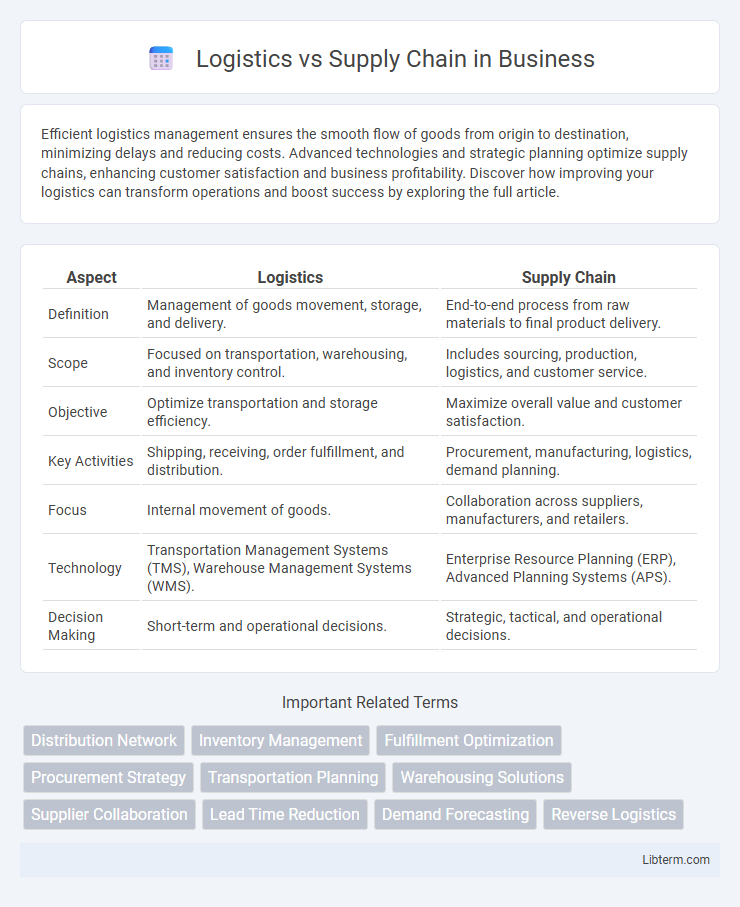
| Aspect | Logistics | Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of goods movement, storage, and delivery. | End-to-end process from raw materials to final product delivery. |
| Scope | Focused on transportation, warehousing, and inventory control. | Includes sourcing, production, logistics, and customer service. |
| Objective | Optimize transportation and storage efficiency. | Maximize overall value and customer satisfaction. |
| Key Activities | Shipping, receiving, order fulfillment, and distribution. | Procurement, manufacturing, logistics, demand planning. |
| Focus | Internal movement of goods. | Collaboration across suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. |
| Technology | Transportation Management Systems (TMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Advanced Planning Systems (APS). |
| Decision Making | Short-term and operational decisions. | Strategic, tactical, and operational decisions. |
Introduction to Logistics and Supply Chain
Logistics involves the efficient management of the movement and storage of goods, services, and information within a specific part of the supply chain. Supply Chain encompasses the entire network of entities, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, involved in producing and delivering a product to the end customer. Understanding the distinction highlights that logistics is a crucial component of the broader supply chain process, focusing on tactical execution, while supply chain management integrates strategic planning and coordination of all activities.
Defining Logistics: Key Functions and Scope
Logistics involves the planning, implementation, and control of the efficient movement and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Key functions include transportation management, warehousing, inventory control, order fulfillment, and distribution. Unlike the broader supply chain, logistics specifically focuses on the internal flow of goods and materials within a company and its immediate network.
Understanding Supply Chain: Broader Perspective
Supply chain encompasses the entire process of producing and delivering a product, including sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, distribution, and retail, while logistics focuses specifically on the transportation and storage of goods within that chain. Understanding supply chain management requires a broader perspective that integrates procurement, production planning, inventory management, and demand forecasting to optimize overall efficiency and customer satisfaction. Effective supply chain strategies align these interconnected activities to reduce costs, improve speed, and enhance flexibility in responding to market changes.
Core Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain
Logistics primarily involves the planning, implementation, and control of the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Supply chain management encompasses a broader scope, integrating logistics with procurement, production, inventory management, and demand forecasting to optimize the entire network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. The core difference lies in logistics focusing on transportation and warehousing, whereas supply chain management coordinates all activities and partners involved in delivering final products.
Roles and Responsibilities in Logistics
Logistics primarily focuses on the efficient management of transportation, warehousing, inventory control, and order fulfillment to ensure timely delivery of goods. Responsibilities include route planning, freight management, and coordinating inbound and outbound shipments to optimize cost and service levels. Supply chain extends beyond logistics, encompassing procurement, production, demand forecasting, and supplier relationship management for end-to-end value creation.
Supply Chain Management: Processes and Strategies
Supply Chain Management (SCM) encompasses the strategic coordination of end-to-end processes including procurement, production, distribution, and inventory management to optimize the flow of goods, information, and finances across the supply network. Effective SCM integrates demand forecasting, supplier relationship management, and logistics planning to reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve operational efficiency. Advanced strategies in SCM, such as just-in-time inventory, lean manufacturing, and digital supply chain analytics, enable businesses to respond dynamically to market fluctuations and sustain competitive advantage.
Technology’s Role in Logistics and Supply Chain
Technology revolutionizes logistics and supply chain operations through advanced tools like IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and blockchain for enhanced transparency and efficiency. Real-time data tracking and automation streamline inventory management, reduce errors, and optimize transportation routes, leading to cost savings and faster delivery times. Integration of cloud-based platforms enables seamless collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, enhancing responsiveness and resilience in supply chain networks.
Integration and Collaboration Across Functions
Logistics involves the efficient management of transportation, warehousing, and inventory control, focusing on the movement of goods within the supply chain. Supply chain management extends beyond logistics by integrating procurement, production, distribution, and information flow to optimize overall value delivery. Effective collaboration across functions such as procurement, manufacturing, and distribution ensures seamless coordination, reduces costs, and enhances responsiveness to market demands.
Challenges in Logistics vs Supply Chain Management
Logistics faces challenges such as real-time inventory tracking, transportation delays, and optimizing last-mile delivery to meet customer expectations. Supply chain management encounters complexities in demand forecasting, coordinating multiple stakeholders, and managing global disruptions like geopolitical risks and pandemics. Both require advanced technology integration and data analytics to enhance visibility and responsiveness across networks.
Future Trends in Logistics and Supply Chain
Future trends in logistics and supply chain emphasize the integration of AI-driven analytics, autonomous delivery vehicles, and blockchain technology to enhance transparency and efficiency. Advanced robotics and IoT sensors enable real-time inventory tracking, predictive maintenance, and dynamic route optimization, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Growing adoption of sustainable practices and digital twins provides companies with the ability to simulate supply chain scenarios, improving resilience against disruptions.
Logistics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com