Net income represents the profit a company retains after deducting all expenses, including taxes and operating costs, from its total revenue. It serves as a key indicator of a business's financial health and profitability, influencing investment decisions and growth strategies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how net income impacts your financial planning and business success.
Table of Comparison
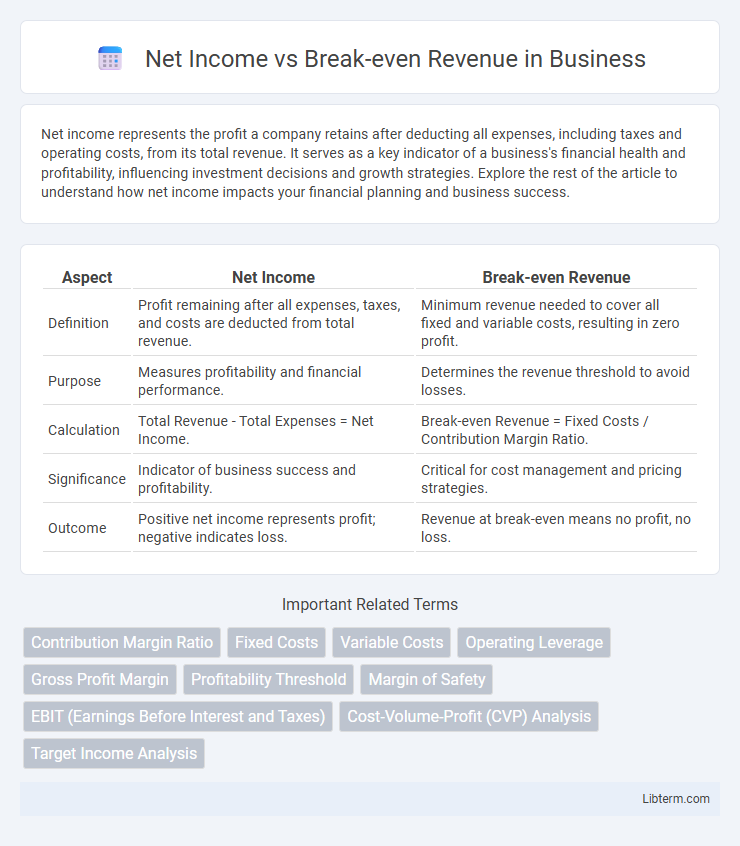
| Aspect | Net Income | Break-even Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted from total revenue. | Minimum revenue needed to cover all fixed and variable costs, resulting in zero profit. |
| Purpose | Measures profitability and financial performance. | Determines the revenue threshold to avoid losses. |
| Calculation | Total Revenue - Total Expenses = Net Income. | Break-even Revenue = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin Ratio. |
| Significance | Indicator of business success and profitability. | Critical for cost management and pricing strategies. |
| Outcome | Positive net income represents profit; negative indicates loss. | Revenue at break-even means no profit, no loss. |
Understanding Net Income: Definition and Importance
Net income represents the total profit a company earns after subtracting all expenses, taxes, and costs from total revenue, indicating overall financial health. Understanding net income is crucial for assessing business profitability, guiding investment decisions, and planning for sustainable growth. This metric highlights the efficiency of operations and the ability to generate surplus revenue beyond the break-even point.
What is Break-even Revenue? Key Concepts Explained
Break-even revenue is the total sales amount a business needs to cover all its fixed and variable costs, resulting in zero net income or profit. This critical financial metric helps companies determine the minimum revenue required to avoid losses and serves as a benchmark for setting sales targets. Understanding break-even revenue enables better pricing strategies, cost management, and financial forecasting.
Core Differences Between Net Income and Break-even Revenue
Net income represents the profit remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted from total revenue, indicating a company's financial health and profitability. Break-even revenue is the minimum amount of sales needed to cover all fixed and variable costs, showing the point where total revenue equals total expenses without profit or loss. The core difference lies in net income reflecting actual profit or loss, while break-even revenue identifies the sales threshold necessary to avoid losses.
Calculating Net Income: Methods and Formula
Net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses, including fixed and variable costs, from total revenue, reflecting the company's profitability after covering all operational costs. The formula for net income is Net Income = Total Revenue - Total Expenses, where expenses encompass cost of goods sold, operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments. Understanding the distinction between net income and break-even revenue is crucial; break-even revenue represents the minimum sales required to cover all fixed and variable costs, resulting in zero net income.
Determining Break-even Revenue: Step-by-Step Guide
Determining break-even revenue involves calculating the fixed and variable costs associated with production and sales, then dividing total fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio, which is the difference between sales price per unit and variable cost per unit divided by the sales price per unit. This step-by-step process accurately identifies the minimum revenue required to cover all expenses without generating profit or loss, ensuring precise financial forecasting. Utilizing tools like break-even analysis spreadsheets or software enhances accuracy and facilitates strategic pricing and budgeting decisions.
Impact of Fixed and Variable Costs on Net Income
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of sales volume, directly influencing the break-even revenue needed to avoid losses. Variable costs fluctuate with production levels, affecting the net income as sales increase beyond the break-even point. Efficiently managing both fixed and variable costs enhances net income by lowering the break-even revenue threshold and increasing profitability.
How Break-even Analysis Influences Business Decisions
Break-even analysis identifies the minimum revenue required to cover fixed and variable costs, directly influencing net income projections. By determining the break-even point, businesses can set realistic sales targets and assess the profitability of new products or services. This financial insight guides pricing strategies, cost control measures, and investment decisions to optimize net income and reduce financial risk.
Net Income vs Break-even Revenue: Real-World Examples
Net income represents the profit a company earns after all expenses are deducted from total revenue, whereas break-even revenue is the minimum amount of sales needed to cover all fixed and variable costs without generating profit or loss. For example, a startup may achieve break-even revenue at $500,000 in annual sales, but only start reporting positive net income beyond that point, such as $50,000 net income at $600,000 revenue. Real-world analysis often reveals how surpassing break-even revenue is crucial for profitability, highlighting the gap between covering costs and generating sustainable earnings.
Common Mistakes When Comparing Net Income and Break-even Revenue
Net income and break-even revenue often get confused, but it's critical to understand that net income represents total profit after all expenses, while break-even revenue only covers fixed and variable costs without generating profit. A common mistake is comparing net income directly to break-even revenue without considering that break-even revenue points to the minimum sales needed to avoid losses, not to profitability. Misinterpreting break-even revenue as net income can lead to flawed financial decisions and misleading assessments of business performance.
Best Practices for Monitoring Financial Performance
Tracking net income alongside break-even revenue is essential for accurate financial performance analysis, ensuring businesses identify profitability thresholds and operational efficiency. Employing real-time financial dashboards and variance analysis helps detect deviations from expected revenue and cost patterns, facilitating timely decision-making. Regularly updating break-even calculations to reflect market changes and fixed or variable cost shifts supports strategic planning and sustainable growth.
Net Income Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com