One-time revenue refers to income generated from a single transaction or event rather than ongoing sales or subscriptions. This type of revenue can significantly impact your financial statements but may not provide long-term stability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how one-time revenue influences business growth and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
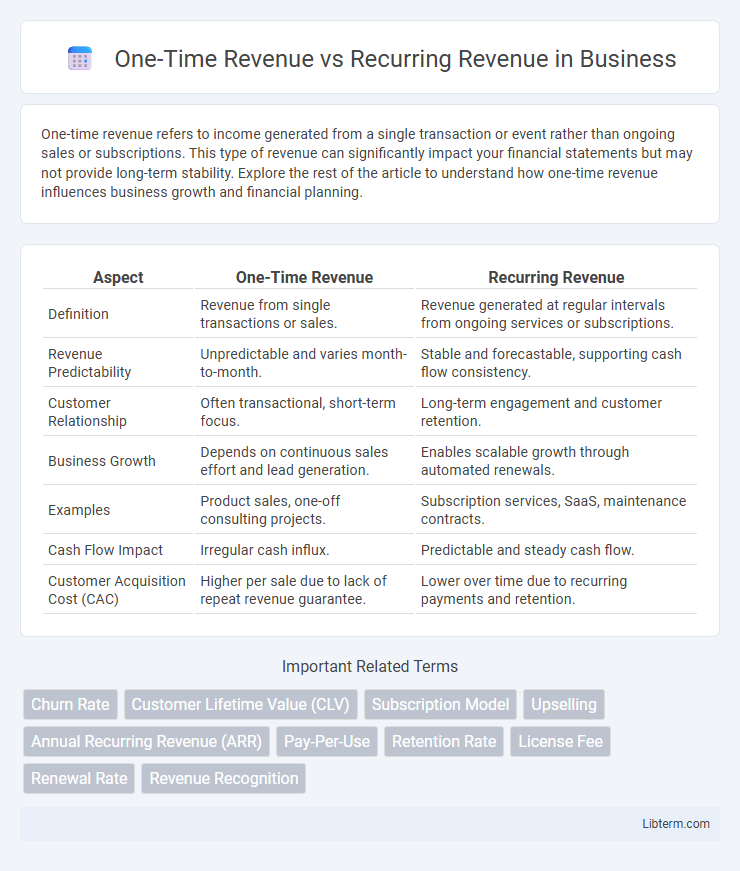
| Aspect | One-Time Revenue | Recurring Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revenue from single transactions or sales. | Revenue generated at regular intervals from ongoing services or subscriptions. |
| Revenue Predictability | Unpredictable and varies month-to-month. | Stable and forecastable, supporting cash flow consistency. |
| Customer Relationship | Often transactional, short-term focus. | Long-term engagement and customer retention. |
| Business Growth | Depends on continuous sales effort and lead generation. | Enables scalable growth through automated renewals. |
| Examples | Product sales, one-off consulting projects. | Subscription services, SaaS, maintenance contracts. |
| Cash Flow Impact | Irregular cash influx. | Predictable and steady cash flow. |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Higher per sale due to lack of repeat revenue guarantee. | Lower over time due to recurring payments and retention. |
Understanding One-Time Revenue
One-time revenue refers to income generated from single, non-repetitive transactions such as a product sale or a one-off service fee, providing immediate but unreliable cash flow. This type of revenue lacks predictability and long-term customer commitment, making financial forecasting challenging. Companies relying heavily on one-time revenue often face volatility, as each transaction requires new customer acquisition without guaranteed follow-up sales.
Defining Recurring Revenue
Recurring revenue is the predictable, consistent income generated from ongoing customer subscriptions or services, such as SaaS products, memberships, or maintenance contracts. Unlike one-time revenue, which comes from single sales, recurring revenue ensures steady cash flow and long-term business stability by fostering customer retention and continuous engagement. This revenue model is critical for scalable growth and accurate financial forecasting in subscription-based industries.
Key Differences Between One-Time and Recurring Revenue
One-time revenue generates income from single sales events, such as product purchases or one-off services, whereas recurring revenue involves consistent, predictable income streams from subscriptions or ongoing contracts. One-time revenue lacks predictability and scalability, making cash flow management more challenging, while recurring revenue supports long-term growth and financial stability. Businesses utilizing recurring revenue models benefit from higher customer lifetime value and easier forecasting compared to those relying on one-time transactions.
Advantages of One-Time Revenue
One-time revenue provides immediate cash flow that can improve a company's short-term liquidity and reduce reliance on external financing. This type of revenue is simpler to manage, with fewer ongoing obligations and reduced customer retention efforts compared to recurring revenue models. Businesses leveraging one-time revenue can quickly capitalize on product launches or seasonal demand spikes without long-term contractual commitments.
Benefits of Recurring Revenue Models
Recurring revenue models provide predictable cash flow that enhances financial stability and supports long-term business planning. These models foster stronger customer relationships through continuous engagement and increased lifetime value. Predictable income streams enable better resource allocation and scalable growth opportunities compared to one-time revenue sources.
Challenges of One-Time Revenue Streams
One-time revenue streams face significant challenges such as unpredictability and lack of sustained cash flow, which impede long-term financial planning and growth. Businesses relying heavily on one-time sales struggle with customer retention and face increased marketing costs to continuously acquire new buyers. This revenue model also limits scalability, making it difficult to invest in innovation or respond to market fluctuations effectively.
Obstacles in Managing Recurring Revenue
Managing recurring revenue faces obstacles such as customer churn, unpredictable subscription cancellations, and the complexity of billing systems that require constant updates and maintenance. Companies must invest in robust analytics to monitor customer behavior and retention rates, addressing these challenges to sustain steady cash flow. Ensuring high-quality customer support and streamlined payment processes is critical to minimize revenue leakage and improve long-term financial stability.
Impact on Business Valuation
One-time revenue generates immediate cash flow but lacks predictability, often resulting in lower business valuation due to inconsistent income streams. Recurring revenue models, such as subscriptions or service retainers, enhance valuation by providing steady, predictable cash flow and increasing customer lifetime value. Investors typically favor businesses with high recurring revenue because they demonstrate stability, scalability, and long-term growth potential.
Strategies to Transition from One-Time to Recurring Revenue
Developing a subscription-based model is a key strategy to transition from one-time sales to recurring revenue by providing customers with ongoing value and consistent service. Implementing tiered pricing plans and personalized offerings encourages long-term customer engagement and increases lifetime value. Leveraging data analytics to understand customer behavior helps optimize retention strategies and identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling subscription services.
Choosing the Best Revenue Model for Your Business
One-time revenue provides immediate cash flow from single sales, ideal for businesses with sporadic customer purchases or project-based services, while recurring revenue ensures consistent, predictable income streams through subscriptions or memberships, beneficial for long-term client retention. Evaluating your target market, product type, and cash flow needs helps determine which model aligns best with your business goals and scalability plans. Prioritize recurring revenue models for sustainable growth and invest in customer relationship management to maximize lifetime value.
One-Time Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com