Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a fundamental inventory management formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering and holding expenses. By calculating EOQ, businesses can efficiently balance stock levels to avoid overstocking and stockouts, enhancing operational efficiency and cash flow. Discover how applying EOQ principles can optimize Your inventory strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
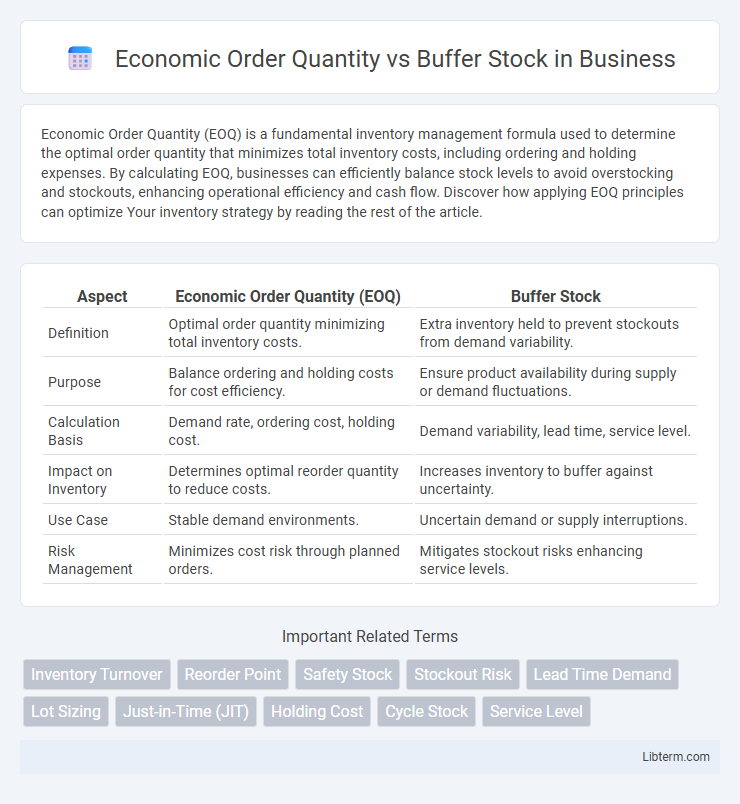
| Aspect | Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) | Buffer Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimal order quantity minimizing total inventory costs. | Extra inventory held to prevent stockouts from demand variability. |
| Purpose | Balance ordering and holding costs for cost efficiency. | Ensure product availability during supply or demand fluctuations. |
| Calculation Basis | Demand rate, ordering cost, holding cost. | Demand variability, lead time, service level. |
| Impact on Inventory | Determines optimal reorder quantity to reduce costs. | Increases inventory to buffer against uncertainty. |
| Use Case | Stable demand environments. | Uncertain demand or supply interruptions. |
| Risk Management | Minimizes cost risk through planned orders. | Mitigates stockout risks enhancing service levels. |
Introduction to Economic Order Quantity and Buffer Stock
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a fundamental inventory management technique that determines the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs, balancing ordering costs and holding costs. Buffer stock, also known as safety stock, refers to the extra inventory maintained to prevent stockouts caused by demand variability or supply delays. Understanding the trade-offs between EOQ's cost-efficiency and buffer stock's risk mitigation is key to optimizing inventory control and ensuring supply chain resilience.
Definition and Core Principles of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a fundamental inventory management model that determines the optimal order quantity minimizing total inventory costs, including ordering and holding expenses, to achieve efficient stock control. EOQ operates on core principles such as balancing demand rate, ordering cost per order, and carrying cost per unit to optimize replenishment cycles and reduce stockouts or overstock situations. Buffer stock, in contrast, refers to additional inventory held to protect against uncertainties in demand or supply, serving as a safety net rather than a calculation-driven optimal quantity like EOQ.
Understanding Buffer Stock: Purpose and Mechanisms
Buffer stock serves as a critical inventory control mechanism designed to mitigate risks associated with demand variability and supply chain disruptions. By maintaining additional quantities beyond the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), buffer stock ensures continuity in production and customer service during periods of uncertainty. Its primary purpose is to absorb fluctuations in supply and demand, thereby stabilizing operations and preventing stockouts.
Key Differences Between EOQ and Buffer Stock
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) determines the optimal order size to minimize total inventory costs, balancing ordering and holding expenses, whereas Buffer Stock is maintained as a safety reserve to prevent stockouts during demand variability or supply delays. EOQ relies on predictable demand and lead times for cost efficiency, while Buffer Stock emphasizes risk management and service level assurance. The key difference lies in EOQ's focus on cost optimization versus Buffer Stock's role in enhancing inventory resilience.
Situations Where EOQ is Most Effective
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is most effective in situations with stable demand and consistent lead times, enabling precise calculation of optimal order sizes to minimize total inventory costs. EOQ excels when carrying costs, ordering costs, and demand rates are predictable, allowing businesses to balance order frequency and storage expenses efficiently. In contrast, buffer stock is more vital in scenarios with high demand variability or supply disruptions, where EOQ parameters alone cannot ensure service level stability.
Scenarios Favoring Buffer Stock Implementation
Buffer stock implementation is favored in scenarios with high demand variability and uncertain supply lead times, ensuring continuous production and customer service levels. Industries facing frequent disruptions, such as perishable goods or seasonal products, benefit from maintaining buffer stock to prevent stockouts. This strategy also supports companies dealing with long supplier lead times or unpredictable market conditions by providing a safety net beyond the Economic Order Quantity model.
Impact on Inventory Costs: EOQ vs Buffer Stock
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) optimizes order size to minimize total inventory costs, balancing ordering costs and holding costs for efficient stock management. Buffer stock increases safety inventory levels to prevent stockouts, which raises holding costs but reduces the risk of lost sales and production delays. EOQ focuses on cost-efficiency by reducing excess inventory, while buffer stock prioritizes service level and operational continuity, impacting inventory costs through higher carrying expenses.
Risk Management in EOQ and Buffer Stock Strategies
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) minimizes total inventory costs by optimizing order size, but it is sensitive to demand variability and lead time fluctuations, posing risks of stockouts. Buffer stock acts as a risk mitigation strategy by holding extra inventory to absorb demand spikes and supply delays, enhancing supply chain resilience. Combining EOQ with strategic buffer stock balances cost efficiency and risk management, ensuring smoother operations under uncertainty.
Integrating EOQ and Buffer Stock for Optimal Inventory Control
Integrating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) with buffer stock strategies optimizes inventory control by balancing order size and safety stock to minimize total costs and prevent stockouts. EOQ determines the ideal order quantity based on demand, ordering, and holding costs, while buffer stock accounts for demand variability and supply chain uncertainties. Combining these approaches enhances service levels and inventory turnover, ensuring efficient stock availability without excessive capital tied in inventory.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Selecting between Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and Buffer Stock hinges on the specific operational needs and demand variability of your business. EOQ optimizes order size to minimize total inventory costs and is ideal for stable demand patterns, while Buffer Stock provides a safety net against supply chain disruptions and demand fluctuations, ensuring service level consistency. Businesses with predictable sales and low risk of stockouts benefit from EOQ, whereas those facing uncertain demand and lead times may find Buffer Stock crucial for maintaining continuous operations and customer satisfaction.
Economic Order Quantity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com