An Initial Public Offering (IPO) marks the first time a private company offers its shares to the public, unlocking new opportunities for investment and growth. This process can significantly increase your company's capital, improve market visibility, and provide liquidity for shareholders. Explore the rest of the article to learn how IPOs can transform businesses and what steps are essential for a successful listing.
Table of Comparison
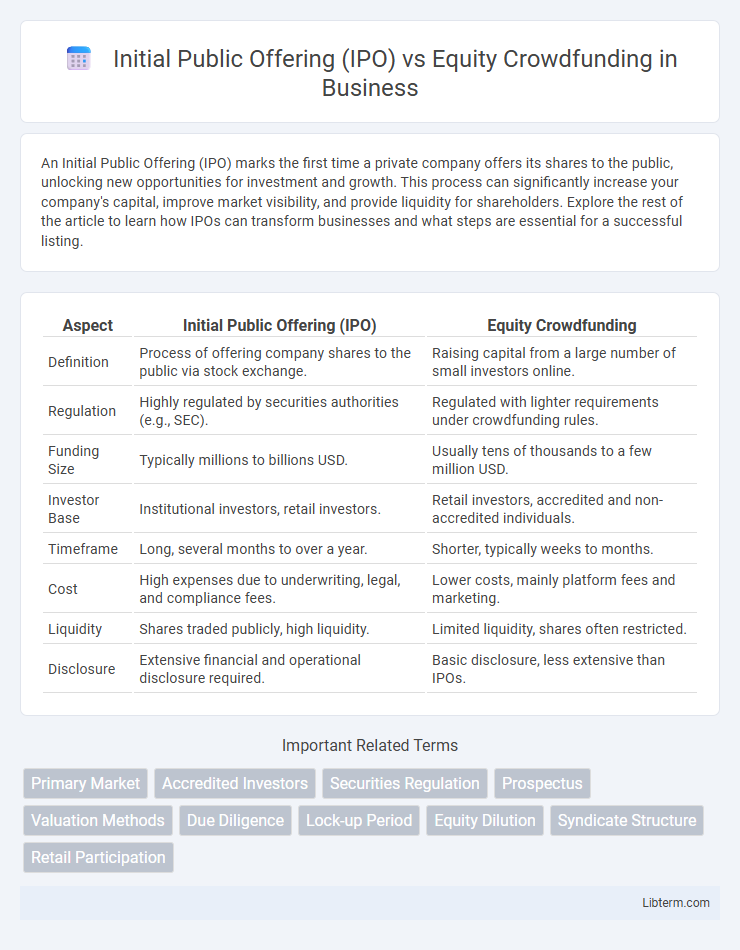
| Aspect | Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Equity Crowdfunding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of offering company shares to the public via stock exchange. | Raising capital from a large number of small investors online. |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by securities authorities (e.g., SEC). | Regulated with lighter requirements under crowdfunding rules. |
| Funding Size | Typically millions to billions USD. | Usually tens of thousands to a few million USD. |
| Investor Base | Institutional investors, retail investors. | Retail investors, accredited and non-accredited individuals. |
| Timeframe | Long, several months to over a year. | Shorter, typically weeks to months. |
| Cost | High expenses due to underwriting, legal, and compliance fees. | Lower costs, mainly platform fees and marketing. |
| Liquidity | Shares traded publicly, high liquidity. | Limited liquidity, shares often restricted. |
| Disclosure | Extensive financial and operational disclosure required. | Basic disclosure, less extensive than IPOs. |
Introduction to IPOs and Equity Crowdfunding
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) involve a private company offering shares to the public for the first time to raise substantial capital, often requiring regulatory approval and significant financial disclosures. Equity crowdfunding allows startups and small businesses to raise funds by selling equity shares to a broad audience through online platforms, enabling access to diverse investors without the complex IPO process. Both methods provide capital influx but differ in scale, regulatory requirements, investor reach, and cost structure.
Key Differences Between IPOs and Equity Crowdfunding
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) involve selling shares to the public through regulated stock exchanges, typically requiring extensive regulatory compliance and substantial capital investment. Equity crowdfunding allows companies to raise smaller amounts from a large pool of investors online, offering more accessible entry points but with limited liquidity and regulatory oversight. IPOs target professional and institutional investors, while equity crowdfunding appeals primarily to retail investors looking for early-stage opportunities.
How Initial Public Offerings Work
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) involve a private company offering shares to the public for the first time through stock exchanges, enabling large-scale capital raising and increased liquidity. The process includes regulatory filings with agencies like the SEC, underwriting by investment banks, and pricing shares based on market demand and company valuation. Equity crowdfunding, in contrast, raises smaller amounts of capital from numerous individual investors online, without the stringent regulatory and financial disclosure requirements characteristic of IPOs.
Understanding Equity Crowdfunding Processes
Equity crowdfunding involves raising capital by selling shares to a large number of investors through online platforms, offering a streamlined process compared to traditional Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). This method allows startups and small businesses to access funds without the extensive regulatory requirements and high costs associated with IPOs, enabling quicker market entry. Understanding equity crowdfunding processes includes navigating investor outreach, complying with securities regulations like the JOBS Act in the U.S., and managing stakeholder communications post-funding.
Advantages of Going Public Through an IPO
Going public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) offers companies significant access to large pools of capital by selling shares to institutional and retail investors on regulated stock exchanges. IPOs provide enhanced liquidity for existing shareholders and establish greater transparency and credibility, which can attract additional investors and business partners. Furthermore, being publicly listed enables companies to use their stock as currency for mergers and acquisitions, driving strategic growth.
Benefits of Raising Capital via Equity Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding offers startups and small businesses access to a diverse pool of investors without the extensive regulatory requirements and high costs associated with Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). This method facilitates faster capital raising, increased market validation, and enhanced community engagement by allowing everyday investors to participate in the company's growth. The lower barriers to entry and retention of greater control make equity crowdfunding an attractive alternative for early-stage companies seeking flexible funding solutions.
Risks and Challenges: IPO vs Equity Crowdfunding
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) carry significant regulatory scrutiny and high costs, creating barriers for smaller companies and exposing them to market volatility and investor pressure for short-term performance. Equity Crowdfunding offers easier access to capital for startups but involves risks such as less regulatory oversight, potential fraud, and difficulty in valuing shares, which can lead to investor losses. Both options face challenges in liquidity, with IPOs offering public market exit opportunities, while crowdfunding investments often remain illiquid for extended periods.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) require extensive regulatory compliance, including filing a detailed prospectus with securities regulators such as the SEC in the United States, adhering to strict disclosure requirements, and undergoing rigorous financial audits. Equity crowdfunding, regulated under frameworks like the JOBS Act Title III in the U.S., involves less stringent compliance, allowing private companies to raise capital from non-accredited investors with limits on fundraising amounts and investor contributions. While IPOs demand ongoing public company reporting standards post-offering, equity crowdfunding platforms must ensure issuer transparency and compliance with investor protection rules but do not require the comprehensive disclosures typical of public market listings.
Suitability for Different Types of Businesses
Initial Public Offering (IPO) suits established companies with substantial revenue, strong financial history, and regulatory compliance readiness seeking significant capital and broad market exposure. Equity Crowdfunding fits startups and small businesses aiming to raise smaller amounts of capital from a diverse group of investors without extensive regulatory burdens. The choice depends on business maturity, fundraising goals, and regulatory capacity, with IPOs often requiring rigorous disclosure and equity crowdfunding offering more accessible entry points.
Choosing the Right Path: IPO or Equity Crowdfunding?
Choosing the right path between an Initial Public Offering (IPO) and equity crowdfunding depends on a company's growth stage, funding needs, and regulatory readiness. IPOs offer access to significant capital and liquidity through public markets but require extensive compliance with securities regulations and higher costs. Equity crowdfunding provides quicker access to capital from a broader base of smaller investors with less regulatory burden, making it ideal for early-stage companies seeking community engagement and incremental funding.
Initial Public Offering (IPO) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com