Instant payment settlement enables funds to be transferred and received within seconds, significantly improving cash flow efficiency for businesses and consumers. This rapid transaction process reduces delays and enhances financial transparency across payment networks. Explore the article to understand how instant payment settlement can transform your financial operations.
Table of Comparison
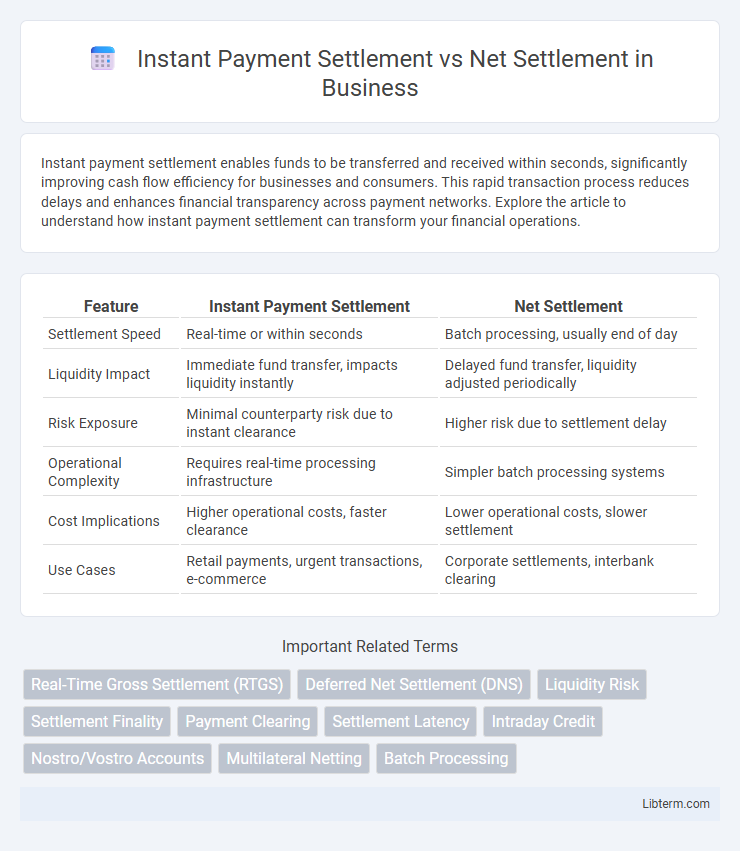
| Feature | Instant Payment Settlement | Net Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement Speed | Real-time or within seconds | Batch processing, usually end of day |
| Liquidity Impact | Immediate fund transfer, impacts liquidity instantly | Delayed fund transfer, liquidity adjusted periodically |
| Risk Exposure | Minimal counterparty risk due to instant clearance | Higher risk due to settlement delay |
| Operational Complexity | Requires real-time processing infrastructure | Simpler batch processing systems |
| Cost Implications | Higher operational costs, faster clearance | Lower operational costs, slower settlement |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, urgent transactions, e-commerce | Corporate settlements, interbank clearing |
Introduction to Payment Settlements
Instant Payment Settlement processes transactions in real-time, ensuring immediate transfer of funds between parties, which enhances liquidity and reduces credit risk. Net Settlement consolidates multiple transactions over a period, settling the net amount at designated intervals, optimizing transaction costs but potentially increasing exposure to settlement risk. Payment settlement methods thus balance speed, efficiency, and risk management depending on operational and financial priorities.
What is Instant Payment Settlement?
Instant Payment Settlement refers to the process where funds are transferred and made available to the recipient immediately after the transaction is initiated. Unlike Net Settlement, which aggregates multiple transactions and settles them at scheduled intervals, Instant Payment Settlement ensures real-time finality and reduces settlement risk. This system is increasingly adopted by financial institutions to enhance liquidity, improve cash flow, and support faster transaction processing in retail and business payments.
What is Net Settlement?
Net settlement is a payment processing method where multiple transactions between parties are aggregated over a specific period, and only the net amount--the difference between credits and debits--is transferred at the end. This system reduces the number of individual payments, lowering transaction costs and easing liquidity management for financial institutions. Compared to instant payment settlement, net settlement introduces a delay in fund availability but enhances operational efficiency for bulk payment scenarios.
Key Differences Between Instant and Net Settlement
Instant Payment Settlement processes transactions individually in real-time, ensuring immediate fund transfer and confirmation between parties, which boosts cash flow efficiency and reduces credit risk. Net Settlement aggregates multiple transactions over a set period and settles the net amount collectively, lowering operational costs but introducing settlement delay and potential exposure to credit risk. The fundamental difference lies in timing and risk: Instant Settlement offers prompt finality with higher infrastructure demands, while Net Settlement prioritizes cost-effectiveness at the expense of immediacy and increased settlement risk.
Advantages of Instant Payment Settlement
Instant Payment Settlement offers immediate fund availability, reducing counterparty risk and improving cash flow management for businesses and consumers. It enhances transaction transparency and supports real-time reconciliation, which increases operational efficiency for financial institutions. This system also enables faster fraud detection and response, strengthening payment security compared to traditional Net Settlement methods.
Benefits of Net Settlement Systems
Net settlement systems reduce the volume of individual transactions by aggregating multiple payments into a single net amount, significantly lowering transaction costs and processing times for banks. These systems enhance liquidity management and risk mitigation by limiting the total funds that must be transferred at any given time, optimizing resource allocation. Net settlement also promotes operational efficiency through batch processing, leading to improved scalability in high-volume payment environments compared to instant payment settlement methods.
Use Cases for Instant Payment Settlement
Instant Payment Settlement enables real-time transfer of funds, making it ideal for retail transactions, emergency payments, and peer-to-peer transfers where immediate fund availability is crucial. Use cases include e-commerce purchases requiring instant confirmation, bill payments to avoid late fees, and cross-border remittances for timely support. This contrasts with Net Settlement, which aggregates payments over a period, suitable for bulk corporate settlements but unsuitable for time-sensitive transfers.
Use Cases for Net Settlement
Net settlement proves advantageous for high-volume, low-value transaction environments such as retail and utility bill payments, where aggregating payments reduces processing costs and operational complexity. It suits financial institutions managing interbank transactions at the end of the day, improving liquidity management and reducing the need for immediate fund transfers. Businesses benefit from net settlement by minimizing transaction fees and enhancing reconciliation efficiency in bulk payment processing scenarios.
Challenges and Risks in Both Settlement Methods
Instant payment settlement faces challenges such as higher fraud risk, requiring robust real-time fraud detection systems and increased liquidity demands for continuous fund availability. Net settlement involves risks like settlement delays and systemic risk exposure since transactions are aggregated and settled later, potentially causing liquidity shortfalls and cascading failures. Both methods encounter operational risks, but instant settlements demand infrastructure for 24/7 processing, while net settlements require strong credit risk management and reliable interbank clearing mechanisms.
Future Trends in Payment Settlements
Instant Payment Settlement is rapidly adopted worldwide due to its ability to process transactions in real-time, supporting the growing demand for immediate fund availability and enhancing liquidity management. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid models that combine the efficiency of net settlement with the speed and transparency of instant settlement systems, driven by advancements in blockchain technology and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). Enhanced security protocols and regulatory frameworks will further enable seamless cross-border instant settlements, reducing operational risks and fostering global financial inclusion.
Instant Payment Settlement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com