Revenue represents the total income generated by a business from its core operations, often serving as a key indicator of financial performance and market demand. Understanding how revenue streams work can help you optimize business strategies and identify opportunities for growth. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective ways to increase your revenue and strengthen your financial position.
Table of Comparison
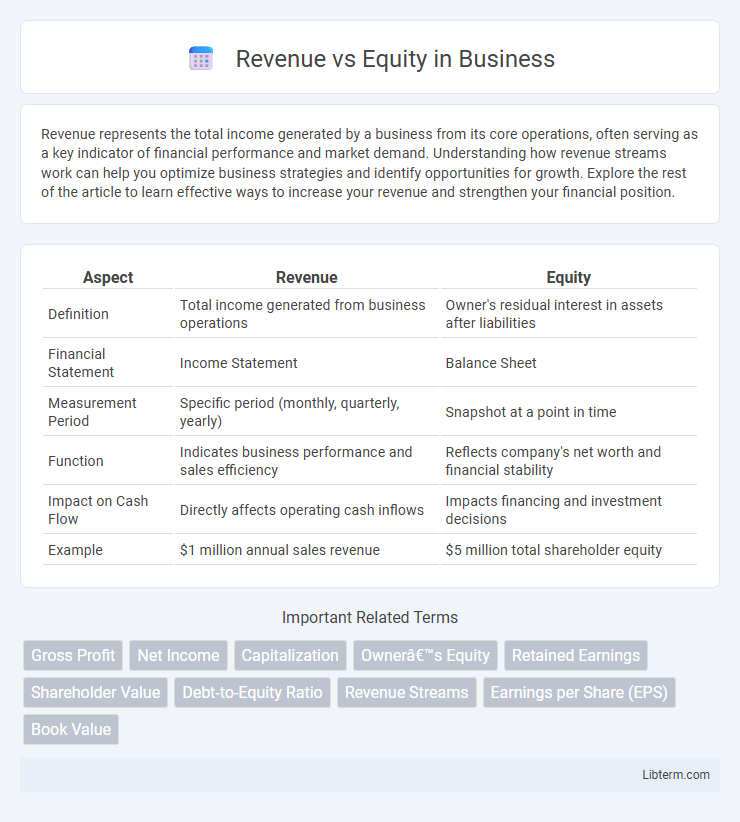
| Aspect | Revenue | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income generated from business operations | Owner's residual interest in assets after liabilities |
| Financial Statement | Income Statement | Balance Sheet |
| Measurement Period | Specific period (monthly, quarterly, yearly) | Snapshot at a point in time |
| Function | Indicates business performance and sales efficiency | Reflects company's net worth and financial stability |
| Impact on Cash Flow | Directly affects operating cash inflows | Impacts financing and investment decisions |
| Example | $1 million annual sales revenue | $5 million total shareholder equity |
Introduction to Revenue and Equity
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company from its core business activities, such as sales of goods or services, during a specific period. Equity refers to the owners' residual interest in the company's assets after liabilities are deducted, commonly represented by shareholders' equity on the balance sheet. Understanding the distinction between revenue, a flow measurement of income, and equity, a stock measurement of ownership value, is essential for assessing a company's financial health.
Defining Revenue: Key Concepts
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company from its core business activities, such as sales of goods or services, before any expenses are deducted. It serves as a critical indicator of business performance and market demand, directly impacting profitability and cash flow management. Understanding revenue involves recognizing its components including gross revenue, net revenue, and recurring revenue, each essential for accurate financial analysis and forecasting.
Understanding Equity: An Overview
Equity represents the ownership value in a company, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities. It reflects shareholders' residual interest after all debts are paid, serving as a crucial indicator of financial health and stability. Understanding equity helps investors assess the company's net worth and potential for growth.
Revenue vs Equity: Core Differences
Revenue represents the total income generated from a company's primary business operations, reflecting its ability to sell goods or services within a specific period. Equity, on the other hand, signifies the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities, indicating ownership value held by shareholders. The core difference lies in revenue measuring operational performance, while equity assesses financial health and ownership structure.
Importance of Revenue in Business Growth
Revenue is a critical indicator of business growth, reflecting a company's ability to generate income from its core operations and sustain day-to-day activities. Unlike equity, which represents ownership value, revenue directly impacts cash flow, enabling reinvestment in innovation, marketing, and expansion strategies. Consistently increasing revenue signals market demand and operational effectiveness, making it essential for long-term business success and competitive advantage.
Role of Equity in Financial Health
Equity represents the ownership value in a company and serves as a critical indicator of financial stability and long-term solvency. Unlike revenue, which measures the income generated from operations, equity reflects the residual assets available to shareholders after liabilities are deducted, providing a buffer against losses. Strong equity positions enhance creditworthiness, support investment capacity, and sustain growth even during periods of fluctuating revenue.
Impact of Revenue on Shareholder Value
Revenue growth directly influences shareholder value by driving higher earnings and increasing cash flows available for dividends and reinvestment. Consistent revenue expansion strengthens market position and enhances investor confidence, leading to stock price appreciation. Effective revenue management also improves return on equity, signaling efficient use of shareholders' capital and maximizing overall company valuation.
How Equity Influences Business Decisions
Equity represents ownership interest in a company and directly impacts business decisions by defining the level of control shareholders have over strategic choices, including dividend policies and capital expenditures. Higher equity often provides greater financial stability and access to funding, influencing decisions on growth investments and risk management. Firms with strong equity positions tend to prioritize long-term value creation, balancing revenue generation with sustainable financial health.
Revenue and Equity in Financial Reporting
Revenue represents the total income generated from primary business activities, serving as a key indicator of a company's operational performance in financial reporting. Equity, reflected as shareholders' equity or owner's equity, denotes the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities, providing insight into the company's net worth and financial stability. Accurate reporting of both revenue and equity is essential for stakeholders to assess profitability, solvency, and long-term viability within financial statements.
Choosing Between Revenue Focus and Equity Growth
Selecting between revenue focus and equity growth depends on a company's long-term strategic goals and market positioning. Prioritizing revenue maximization often suits businesses aiming for immediate cash flow, operational scale, and market penetration, while an equity growth approach emphasizes increasing shareholder value through asset appreciation, dividends, and sustainable profitability. Companies balancing both metrics leverage revenue as a foundation for equity expansion, aligning financial performance with investor expectations.
Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com