The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) holds the highest-ranking position within a company, responsible for setting strategic direction and making critical decisions that impact overall business performance. Effective CEOs drive company growth by aligning resources, fostering innovation, and building strong leadership teams. Discover how a CEO's role shapes your organization's success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
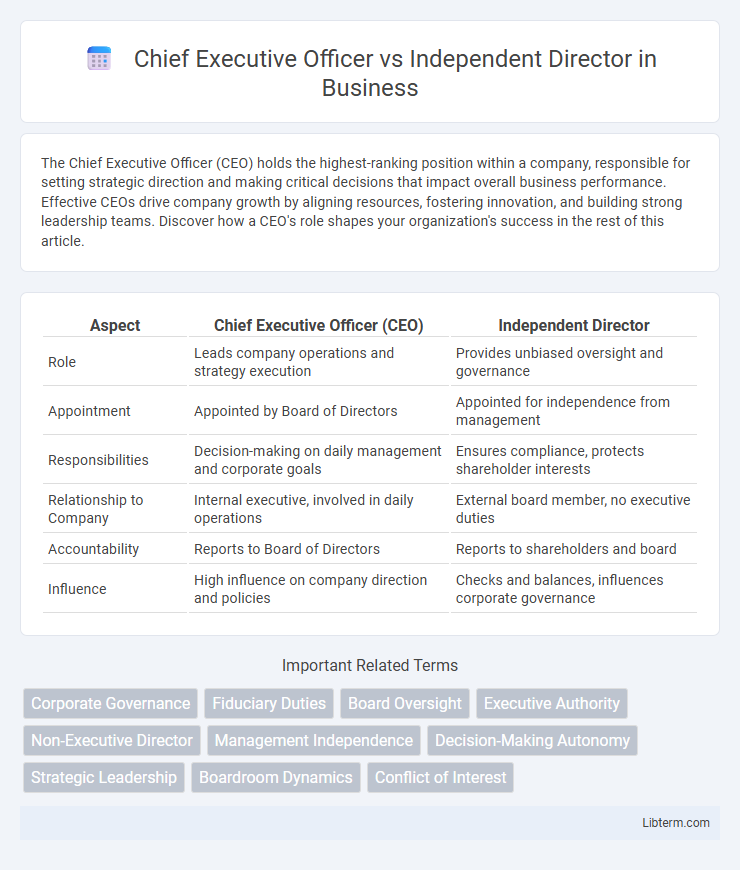
| Aspect | Chief Executive Officer (CEO) | Independent Director |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Leads company operations and strategy execution | Provides unbiased oversight and governance |
| Appointment | Appointed by Board of Directors | Appointed for independence from management |
| Responsibilities | Decision-making on daily management and corporate goals | Ensures compliance, protects shareholder interests |
| Relationship to Company | Internal executive, involved in daily operations | External board member, no executive duties |
| Accountability | Reports to Board of Directors | Reports to shareholders and board |
| Influence | High influence on company direction and policies | Checks and balances, influences corporate governance |
Chief Executive Officer vs Independent Director: Key Differences
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is responsible for the day-to-day management and operational decisions of a company, while the Independent Director provides unbiased oversight and governance on the board, ensuring accountability and protecting shareholder interests. CEOs are typically full-time executives involved in strategic planning and company leadership, whereas Independent Directors serve part-time, offering objective judgment without executive responsibilities. The key differences lie in their roles, responsibilities, and the level of involvement in company operations versus governance.
Roles and Responsibilities of a CEO
A Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is responsible for the overall management, strategic direction, and operational decisions of a company, ensuring that business goals and objectives are met effectively. In contrast, an Independent Director provides unbiased oversight, governance, and accountability, safeguarding shareholders' interests without direct involvement in daily operations. The CEO leads executive teams, drives growth initiatives, manages resources, and reports to the board of directors, which includes Independent Directors tasked with monitoring the CEO's performance and compliance.
Duties and Functions of an Independent Director
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is responsible for the day-to-day management and operational decisions of a company, driving strategy execution and achieving business objectives. An Independent Director, however, primarily serves to provide unbiased oversight and governance, ensuring the company adheres to legal and ethical standards while protecting shareholders' interests. Key duties of an Independent Director include monitoring managerial performance, safeguarding stakeholder rights, contributing to risk management, and ensuring transparency in financial reporting.
Decision-Making Authority: CEO vs Independent Director
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) holds primary decision-making authority, responsible for daily operations, strategic planning, and executing company policies. In contrast, Independent Directors provide oversight and guidance, ensuring decisions align with shareholder interests and corporate governance standards without engaging in everyday management. Their authority is limited to board-level approval and monitoring, serving as a check on executive power rather than direct operational control.
Governance and Oversight: Board’s Role Explained
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) manages day-to-day operations and implements the board's strategic direction, directly influencing company performance. Independent Directors provide unbiased governance and oversight, ensuring the board acts in shareholders' best interests by challenging management decisions and mitigating conflicts of interest. This balance between executive management and independent oversight is essential for effective corporate governance and accountability.
Accountability and Reporting Structures
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) holds primary accountability for the company's operational performance and strategic execution, reporting directly to the board of directors. Independent Directors, meanwhile, provide oversight and hold the CEO accountable by monitoring management decisions without conflicts of interest, reporting their findings and concerns to the full board or shareholders. This dual structure ensures balanced governance, with the CEO driving business results while Independent Directors enforce transparency and accountability.
Criteria for Appointment: CEO and Independent Director
The criteria for appointing a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) typically emphasize extensive leadership experience, strategic vision, and proven operational expertise within the industry, ensuring the individual can drive company performance and growth. In contrast, the appointment of an Independent Director requires strict adherence to regulatory independence standards, absence of material relationships with the company, and a diverse skill set that enhances board oversight and governance. Both roles demand a robust understanding of corporate governance, but the CEO focuses on executive management while Independent Directors prioritize impartial judgment and stakeholder protection.
Impact on Corporate Strategy and Policy
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) directly shapes corporate strategy and policy through daily operational decisions and leadership, driving company vision and growth initiatives. Independent Directors influence corporate strategy by providing unbiased oversight, challenging management decisions, and ensuring alignment with shareholder interests and regulatory compliance. Their combined impact ensures balanced strategic direction, blending executive expertise with objective governance to enhance long-term corporate performance.
Conflict of Interest: Managing Roles Effectively
Chief Executive Officers (CEOs) and Independent Directors often face conflicts of interest due to their differing responsibilities, with CEOs focused on day-to-day management and Independent Directors tasked with unbiased oversight. Effective conflict of interest management requires establishing clear governance frameworks that separate operational control from board supervision, ensuring Independent Directors can objectively challenge executive decisions. Implementing strict disclosure policies and regular audits enhances transparency, promoting balanced decision-making that aligns with shareholder interests and corporate accountability.
CEO vs Independent Director: Importance in Corporate Success
Chief Executive Officers drive corporate success through strategic leadership, operational management, and decision-making authority, directly influencing company performance and shareholder value. Independent Directors provide unbiased oversight, ensuring governance integrity, mitigating risks, and protecting stakeholder interests by challenging executive decisions objectively. The dynamic between CEO leadership and Independent Director oversight is crucial for balanced corporate governance, fostering sustainable growth and accountability.
Chief Executive Officer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com