Sentiment analysis uses advanced algorithms to identify and interpret emotions expressed in text, such as positive, negative, or neutral sentiments. It plays a crucial role in understanding customer feedback, monitoring brand reputation, and enhancing user experience by capturing the true tone behind words. Explore the article to discover how sentiment analysis can transform your approach to data interpretation.
Table of Comparison
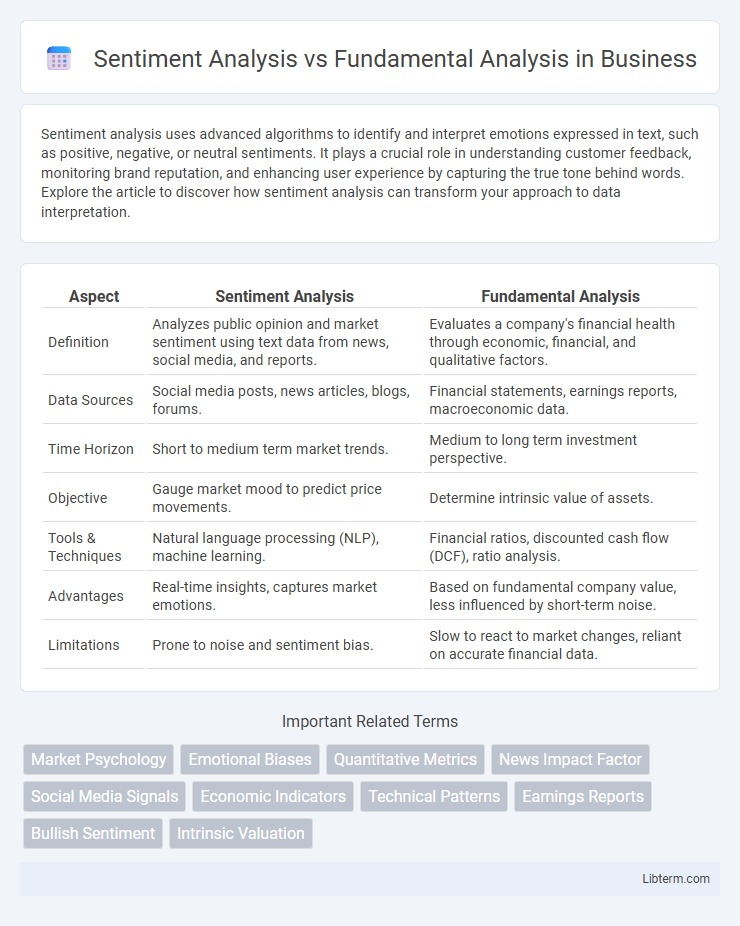
| Aspect | Sentiment Analysis | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes public opinion and market sentiment using text data from news, social media, and reports. | Evaluates a company's financial health through economic, financial, and qualitative factors. |
| Data Sources | Social media posts, news articles, blogs, forums. | Financial statements, earnings reports, macroeconomic data. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term market trends. | Medium to long term investment perspective. |
| Objective | Gauge market mood to predict price movements. | Determine intrinsic value of assets. |
| Tools & Techniques | Natural language processing (NLP), machine learning. | Financial ratios, discounted cash flow (DCF), ratio analysis. |
| Advantages | Real-time insights, captures market emotions. | Based on fundamental company value, less influenced by short-term noise. |
| Limitations | Prone to noise and sentiment bias. | Slow to react to market changes, reliant on accurate financial data. |
Introduction to Sentiment Analysis and Fundamental Analysis
Sentiment analysis interprets public opinions and emotional tones from social media, news, and other textual data to gauge market mood and predict price movements. Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health by examining earnings, revenue, assets, and industry conditions to estimate intrinsic value. Combining both approaches provides a comprehensive view by incorporating quantitative financial metrics and qualitative market sentiment.
Defining Sentiment Analysis in Financial Markets
Sentiment analysis in financial markets involves using natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to evaluate public opinion and emotions expressed in news articles, social media, and financial reports. This approach quantifies market sentiment to predict stock price movements by assessing investor mood and market psychology rather than relying solely on financial metrics. Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines company financial health, earnings, and economic indicators, sentiment analysis provides real-time insights into market trends influenced by behavioral factors.
Understanding Fundamental Analysis: Key Concepts
Fundamental analysis evaluates a company's intrinsic value by examining financial statements, economic indicators, and industry trends to assess its long-term growth potential. Key concepts include earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, revenue growth, profit margins, and cash flow analysis, which help investors make informed decisions. Unlike sentiment analysis, which gauges market emotions and public opinion, fundamental analysis relies on quantitative data and qualitative factors to determine the true worth of an asset.
Core Differences Between Sentiment and Fundamental Analysis
Sentiment analysis evaluates market psychology by analyzing emotions and opinions expressed in news, social media, and investor behavior, providing insights into short-term price movements. Fundamental analysis examines a company's financial statements, market position, and economic factors to assess its intrinsic value and long-term growth potential. The core difference lies in sentiment analysis focusing on perception and market mood, while fundamental analysis relies on quantifiable financial metrics and economic data.
Data Sources for Sentiment Analysis vs Fundamental Analysis
Sentiment analysis primarily relies on unstructured data sources such as social media posts, news articles, blogs, and online forums to gauge public opinion and market sentiment, often leveraging natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze textual data. Fundamental analysis depends on structured financial data, including company earnings reports, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and macroeconomic indicators to assess a security's intrinsic value. The contrasting nature of these data sources highlights the qualitative, real-time insights of sentiment analysis versus the quantitative, historical financial metrics central to fundamental analysis.
Advantages of Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis leverages real-time data from social media, news, and market trends to capture investor emotions and market psychology, offering timely insights that traditional fundamental analysis may overlook. It enables traders to anticipate market movements by detecting shifts in public opinion and sentiment before they are reflected in financial statements or earnings reports. This method provides a dynamic advantage in volatile markets, allowing for quicker decision-making based on crowd behavior and sentiment trends.
Benefits of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis provides investors with a comprehensive evaluation of a company's intrinsic value by examining financial statements, industry conditions, and economic factors, enabling more informed long-term investment decisions. It identifies undervalued stocks through metrics like earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and return on equity (ROE), which supports portfolio stability and growth. Relying on fundamental analysis helps mitigate market noise and short-term volatility, offering a strategic advantage in understanding true business performance and potential.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
Sentiment analysis faces challenges such as data noise, misinterpretation of sarcasm, and limited context understanding, which can lead to inaccurate predictions in financial markets. Fundamental analysis struggles with limitations like reliance on historical financial data, vulnerability to unforeseen macroeconomic events, and the subjective nature of valuation models. Both approaches require continuous adaptation to evolving market conditions and integrating diverse datasets to improve decision-making accuracy.
Integrating Sentiment and Fundamental Analysis Strategies
Integrating sentiment analysis with fundamental analysis strategies enhances investment decision-making by combining quantitative financial metrics with real-time market sentiment data from social media, news, and earnings calls. This fusion enables investors to capture both the intrinsic value of assets and the impact of market psychology, improving prediction accuracy and risk management. Machine learning models that incorporate sentiment indicators alongside financial ratios and macroeconomic variables demonstrate higher returns and reduced volatility in portfolio performance.
Choosing the Right Approach for Investment Decisions
Sentiment analysis leverages real-time social media trends, news sentiment, and market mood to gauge short-term market movements, while fundamental analysis evaluates financial statements, economic indicators, and company performance for long-term investment value. Investors prioritizing quick responses to market changes may prefer sentiment analysis, whereas those emphasizing intrinsic value and growth potential typically rely on fundamental analysis. Selecting the right approach depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferred time horizons, with many successful strategies integrating both methods for comprehensive decision-making.
Sentiment Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com