Agile and Scrum are frameworks designed to enhance project management by promoting flexibility, collaboration, and iterative progress. Scrum breaks projects into manageable sprints, allowing teams to adapt rapidly to changes and deliver value consistently. Discover how these methodologies can transform your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
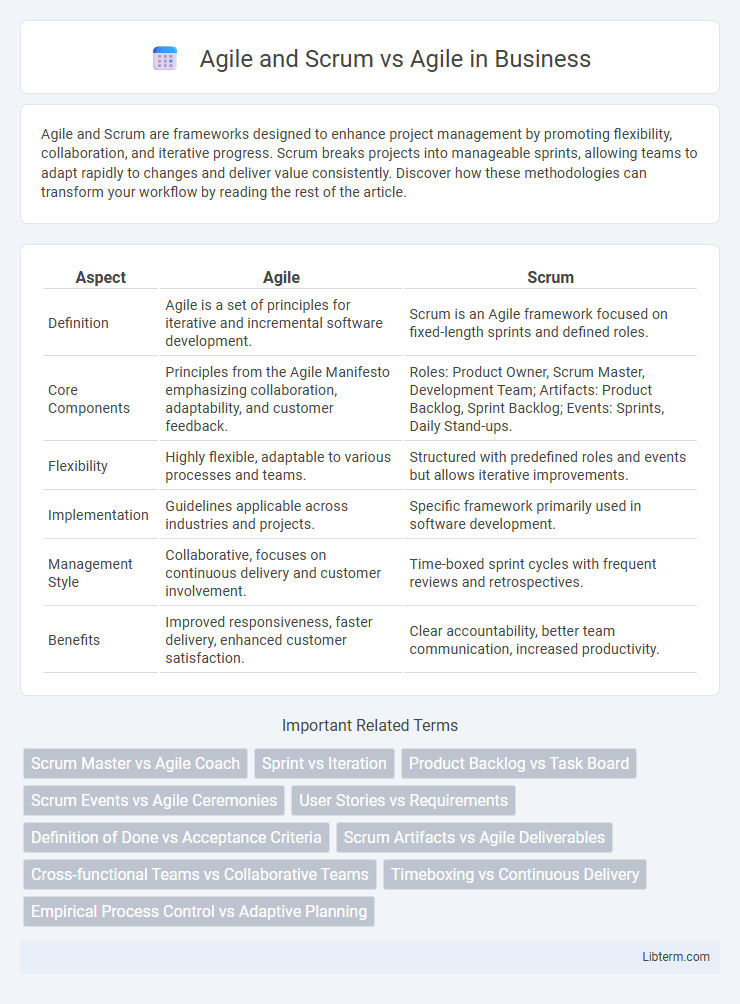
| Aspect | Agile | Scrum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agile is a set of principles for iterative and incremental software development. | Scrum is an Agile framework focused on fixed-length sprints and defined roles. |
| Core Components | Principles from the Agile Manifesto emphasizing collaboration, adaptability, and customer feedback. | Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team; Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog; Events: Sprints, Daily Stand-ups. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adaptable to various processes and teams. | Structured with predefined roles and events but allows iterative improvements. |
| Implementation | Guidelines applicable across industries and projects. | Specific framework primarily used in software development. |
| Management Style | Collaborative, focuses on continuous delivery and customer involvement. | Time-boxed sprint cycles with frequent reviews and retrospectives. |
| Benefits | Improved responsiveness, faster delivery, enhanced customer satisfaction. | Clear accountability, better team communication, increased productivity. |
Understanding Agile: Core Principles and Values
Agile is a comprehensive project management philosophy centered on adaptive planning, iterative development, and customer collaboration, rooted in the Agile Manifesto's core principles and values. Scrum represents a specific Agile framework emphasizing fixed-length sprints, cross-functional teams, and defined roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner to facilitate transparency and continuous improvement. Understanding Agile's values such as individuals and interactions over processes and tools is essential to effectively implement Scrum practices within any Agile environment.
What is Scrum? An Agile Framework Explained
Scrum is an Agile framework designed to manage complex projects by promoting iterative progress through fixed-length cycles called sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. It emphasizes roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team to enhance collaboration, accountability, and continuous delivery of value. Agile represents a broader philosophy centered on adaptive planning and flexible responses, while Scrum provides a structured methodology to implement Agile principles effectively.
Key Differences: Agile Mindset vs Scrum Methodology
Agile represents a flexible mindset centered on iterative progress, collaboration, and customer-centric delivery, while Scrum is a structured methodology within Agile that defines specific roles, events, and artifacts to implement those principles. Agile emphasizes values and principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, fostering adaptability and continuous improvement across various frameworks. Scrum provides a concrete process framework, including sprints, daily stand-ups, and sprint reviews, to operationalize Agile values into actionable practices.
Roles and Responsibilities in Agile vs Scrum
Agile frameworks emphasize collaborative roles such as product owners, development teams, and stakeholders focused on continuous delivery and adaptive planning. Scrum specifies distinct roles including the Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team, each with clearly defined responsibilities to facilitate sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and sprint reviews. The Scrum Master serves as a servant leader removing impediments, while Agile roles in other methodologies can be more fluid and adaptable depending on the project context.
Processes and Workflow Comparison: Agile and Scrum
Agile is a broad project management methodology emphasizing iterative development, customer collaboration, and flexibility, while Scrum is a specific Agile framework with defined roles, time-boxed sprints, and ceremonies such as daily stand-ups and sprint reviews. Agile processes are adaptable across various frameworks, allowing teams to customize workflow stages, whereas Scrum enforces a structured workflow with clear increments and sprint backlogs to manage tasks. Scrum's prescribed sprint cycles and roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner create a focused workflow that drives continuous improvement within Agile's overarching principles.
Agile without Scrum: When and Why
Agile without Scrum is ideal for projects requiring flexibility without strict frameworks, allowing teams to customize workflows based on specific needs and stakeholder feedback. This approach benefits innovative environments where iterative development and frequent adaptations drive success, without the overhead of Scrum ceremonies and roles. Organizations choose Agile without Scrum to maintain agility while avoiding the rigid structure and prescribed sprint cycles that Scrum mandates.
Benefits of Implementing Agile vs Scrum
Implementing Agile offers organizations increased flexibility, faster delivery, and enhanced customer collaboration by promoting iterative development and continuous feedback. Scrum, as a specific Agile framework, provides structured roles, ceremonies, and artifacts that help teams manage work efficiently and improve transparency. Choosing Agile broadly supports adaptability across various project types, while Scrum's framework maximizes team productivity and accountability through its defined processes.
Common Challenges in Agile and Scrum Adoption
Common challenges in Agile and Scrum adoption include resistance to cultural change, unclear roles and responsibilities, and insufficient training for team members. Organizations often struggle with maintaining consistent communication and managing scope creep during iterative development cycles. Addressing these challenges requires strong leadership commitment, continuous feedback mechanisms, and tailored Agile coaching to ensure effective implementation.
Choosing the Right Approach: Agile, Scrum, or Both?
Choosing the right approach between Agile, Scrum, or both depends on project complexity, team size, and flexibility requirements. Agile is a broad methodology emphasizing iterative development and customer collaboration, while Scrum is a specific Agile framework focusing on defined roles, time-boxed sprints, and regular ceremonies for continuous improvement. Organizations benefit most by adopting Agile principles for adaptability and incorporating Scrum practices to enhance structure and accountability.
Real-World Use Cases: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Agile frameworks like Scrum have been widely adopted across industries for software development, project management, and product delivery, enabling iterative progress and improved team collaboration. Real-world cases reveal Scrum's effectiveness in accelerating delivery cycles, enhancing transparency with daily stand-ups, and empowering cross-functional teams to adapt rapidly to changing requirements. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of organizational culture alignment, continuous stakeholder engagement, and the right balance between Agile rigidity and flexibility to maximize project outcomes.
Agile and Scrum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com