An invoice is a crucial document that details the sale of goods or services, specifying quantities, prices, and payment terms to ensure clear communication between buyer and seller. Properly managing your invoices helps maintain accurate financial records and supports timely payments, improving cash flow and business relationships. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to create, manage, and utilize invoices effectively for your business success.
Table of Comparison
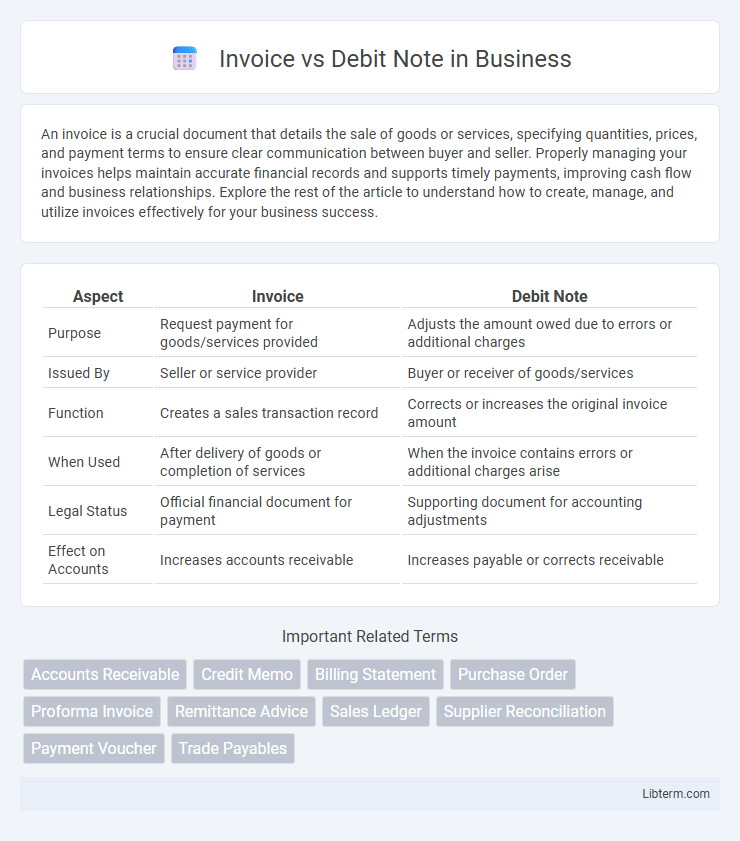
| Aspect | Invoice | Debit Note |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Request payment for goods/services provided | Adjusts the amount owed due to errors or additional charges |
| Issued By | Seller or service provider | Buyer or receiver of goods/services |
| Function | Creates a sales transaction record | Corrects or increases the original invoice amount |
| When Used | After delivery of goods or completion of services | When the invoice contains errors or additional charges arise |
| Legal Status | Official financial document for payment | Supporting document for accounting adjustments |
| Effect on Accounts | Increases accounts receivable | Increases payable or corrects receivable |
Understanding Invoices: Definition and Purpose
An invoice is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the products or services provided along with their prices, quantities, and total amount payable. It serves as a formal request for payment and is essential for accounting, tax reporting, and legal purposes. Understanding invoices involves recognizing their role in documenting transactions and facilitating payment processing within business operations.
What is a Debit Note? Key Features Explained
A debit note is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating a request for a credit adjustment due to returned goods or overcharged invoices. Key features include its role in correcting billing errors, specifying the amount debited, and linking to the original invoice for transparency. It serves as proof for accounting adjustments and helps maintain accurate financial records between businesses.
Key Differences Between Invoice and Debit Note
An invoice is a commercial document issued by a seller to request payment for goods or services provided, specifying quantities, prices, and terms. A debit note is sent by a buyer to a seller, indicating a request for adjustment or correction to a previously issued invoice, often due to returned goods or discrepancies. Key differences include purpose--invoice initiates payment, debit note requests correction--and timing, with invoices issued at sale and debit notes issued post-sale for adjustments.
When to Use an Invoice vs a Debit Note
Use an invoice to request payment for goods or services provided, typically issued after delivery or completion of a contract. A debit note is used to correct or adjust a previously issued invoice, reflecting changes such as price increases, additional fees, or returned goods. Businesses should issue a debit note when disputing invoice discrepancies or requesting payment modifications after the original invoice is sent.
Legal Requirements for Invoices and Debit Notes
Invoices must include specific legal elements such as the seller's and buyer's details, a unique invoice number, date of issue, description of goods or services, quantity, unit price, total amount, and applicable taxes to comply with tax authorities. Debit notes require legal documentation of the reason for additional charges or adjustments, referencing the original invoice, and must align with accounting standards to ensure accurate financial records. Both documents must adhere to jurisdiction-specific regulations, such as VAT/GST laws, to be valid for tax deductions and audits.
Common Scenarios: Invoice vs Debit Note in Practice
Invoices are issued to request payment for goods or services rendered, serving as detailed records of sales transactions, whereas debit notes are used to adjust previously issued invoices, often to correct billing errors or return goods. Common scenarios include suppliers sending debit notes to buyers when additional charges arise post-invoice, such as price adjustments or quantity discrepancies, ensuring accurate financial records and payment reconciliation. Businesses rely on these documents to maintain transparency in accounts payable and receivable, facilitating audit trails and compliance with accounting standards.
Essential Elements of an Invoice
An invoice must include essential elements such as the invoice number, date of issuance, seller and buyer details, description of goods or services, quantity, unit price, total amount payable, applicable taxes, payment terms, and due date. These components establish a legally valid request for payment and ensure transparency in the transaction between parties. Accurate inclusion of these elements differentiates an invoice from a debit note, which primarily adjusts or corrects financial entries without specifying full transaction details.
Essential Elements of a Debit Note
A debit note must include essential elements such as the date of issue, unique debit note number, purchaser and seller details, and a clear description of goods or services being returned or adjusted. It should specify the quantity, price, and reasons for the debit, such as discrepancies or returns, alongside the total amount debited. Including references to the original invoice and payment terms enhances clarity and legal validity in financial transactions.
Impact on Accounting and Bookkeeping
An invoice serves as a formal request for payment, increasing accounts receivable and revenue recognition in accounting records. A debit note adjusts previously recorded transactions, often correcting invoices or increasing payable amounts, thus impacting accounts payable and financial accuracy. Proper handling of both documents ensures precise bookkeeping, accurate financial statements, and compliance with accounting standards.
Choosing the Right Document: Best Practices
Selecting the appropriate document between an invoice and a debit note hinges on the nature of the transaction; invoices request payment for goods or services rendered, while debit notes adjust previous invoices due to discrepancies or returned goods. Best practices for choosing the right document include verifying the transaction type, ensuring accurate reference to original documents, and maintaining compliance with accounting standards to avoid disputes. Proper usage streamlines financial processes, enhances record accuracy, and supports transparent communication between buyers and sellers.
Invoice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com