Lean Startup focuses on rapid experimentation and validated learning to efficiently develop products that meet customer needs, while Six Sigma emphasizes reducing process variation and defects through statistical analysis and control. Both methodologies drive continuous improvement and operational excellence, but Lean Startup prioritizes agility and customer feedback, whereas Six Sigma centers on quality and consistency. Discover how integrating these approaches can optimize your business strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
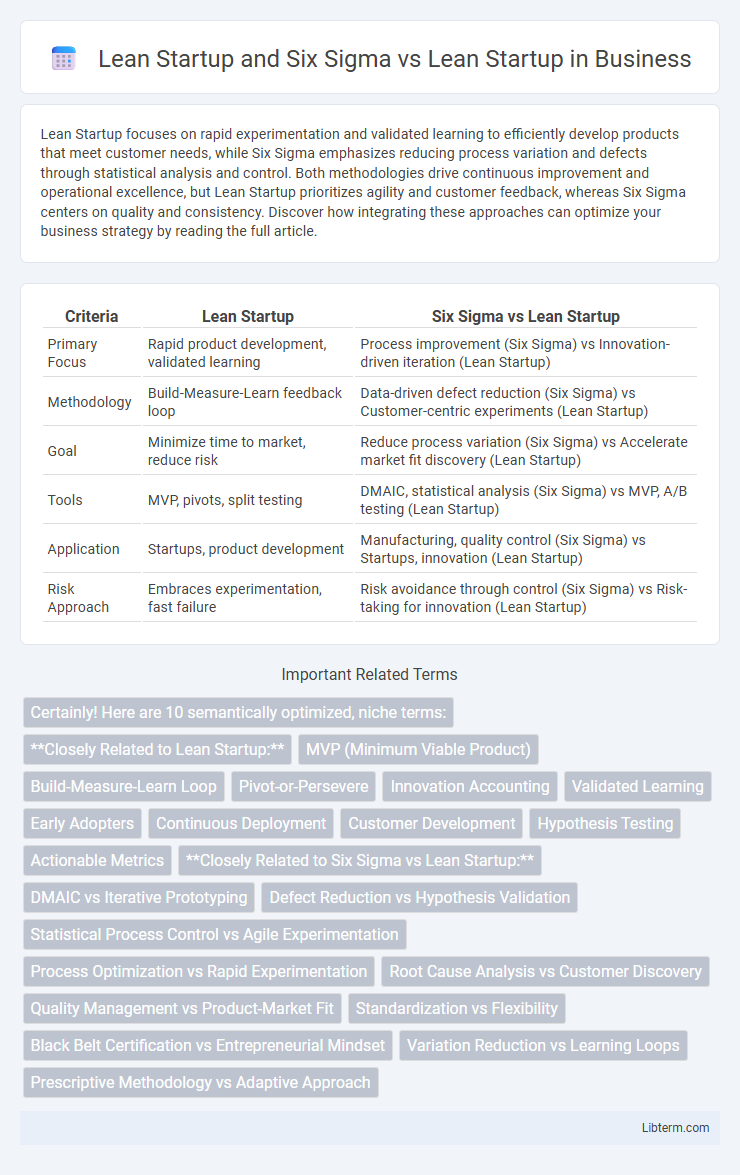
| Criteria | Lean Startup | Six Sigma vs Lean Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Rapid product development, validated learning | Process improvement (Six Sigma) vs Innovation-driven iteration (Lean Startup) |
| Methodology | Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop | Data-driven defect reduction (Six Sigma) vs Customer-centric experiments (Lean Startup) |
| Goal | Minimize time to market, reduce risk | Reduce process variation (Six Sigma) vs Accelerate market fit discovery (Lean Startup) |
| Tools | MVP, pivots, split testing | DMAIC, statistical analysis (Six Sigma) vs MVP, A/B testing (Lean Startup) |
| Application | Startups, product development | Manufacturing, quality control (Six Sigma) vs Startups, innovation (Lean Startup) |
| Risk Approach | Embraces experimentation, fast failure | Risk avoidance through control (Six Sigma) vs Risk-taking for innovation (Lean Startup) |
Introduction to Lean Startup Methodology
Lean Startup methodology emphasizes rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to quickly adapt to market needs, reducing waste and uncertainty in new ventures. Six Sigma focuses on process improvement through data-driven techniques and defect reduction, aiming for near-perfect quality in production processes. While Lean Startup prioritizes agility and customer feedback to accelerate innovation, Six Sigma targets operational efficiency and consistency within established systems.
Core Principles of Lean Startup
Lean Startup centers on rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to minimize market risks and discover viable business models quickly. Its core principles include building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring user feedback, and learning through continuous pivoting or persevering. Unlike Six Sigma's emphasis on reducing process variation and defects through statistical analysis, Lean Startup prioritizes agility and customer-centric innovation to accelerate growth and adaptation.
What is Six Sigma? Key Concepts Explained
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at improving process quality by identifying and eliminating defects, striving for near perfection with a target of 3.4 defects per million opportunities. Key concepts include DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), which structures problem-solving and process improvement, and the emphasis on statistical analysis to reduce variation and enhance consistency. While Lean Startup focuses on rapid experimentation and validated learning to develop products, Six Sigma concentrates on optimizing existing processes through rigorous data analysis and quality management techniques.
Comparing Lean Startup and Six Sigma
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative product development to minimize market risk and accelerate innovation. Six Sigma focuses on improving process quality by identifying and eliminating defects using data-driven methodologies and statistical analysis. While Lean Startup drives agility and market fit through continuous learning, Six Sigma ensures precision and efficiency by reducing variability and enhancing operational performance.
Objectives: Innovation vs. Process Improvement
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid innovation and customer feedback to develop viable products quickly, driving market disruption and agility. Six Sigma, in contrast, targets process improvement by reducing defects and variability through data-driven methodologies. While Lean Startup fosters creative experimentation to validate business models, Six Sigma focuses on optimizing efficiency and quality within established processes.
Tools and Techniques: Lean Startup vs. Six Sigma
Lean Startup employs tools like Build-Measure-Learn feedback loops, rapid prototyping, and validated learning to accelerate product development and market fit analysis. Six Sigma utilizes data-driven techniques such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), statistical process control, and root cause analysis to reduce process variation and improve quality. The Lean Startup approach emphasizes agility and customer feedback for innovation, while Six Sigma focuses on precision, defect reduction, and process optimization through rigorous measurement.
Implementation Challenges: Lean Startup and Six Sigma
Lean Startup faces implementation challenges such as navigating uncertainty in product-market fit, requiring rapid experimentation and iteration to validate hypotheses. Six Sigma implementation challenges include the need for extensive training, data-driven decision-making, and overcoming resistance to change in process standardization. Combining Lean Startup with Six Sigma demands balancing flexibility and rigor, which can complicate cultural adoption and resource allocation.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies of Lean Startup demonstrate rapid product iterations based on customer feedback, exemplified by Dropbox's early minimal viable product approach that accelerated market entry and customer validation. In contrast, Six Sigma case studies such as General Electric reveal significant process improvements and cost reductions through rigorous data-driven methodologies and defect reduction strategies. Comparing both reveals Lean Startup's agility in innovation-focused environments, while Six Sigma excels in operational excellence and quality control within established manufacturing and services sectors.
Integrating Lean Startup with Six Sigma
Integrating Lean Startup with Six Sigma combines rapid innovation cycles with data-driven quality improvements, accelerating product development while reducing defects and variability. Lean Startup's iterative testing and validated learning processes complement Six Sigma's structured methodologies like DMAIC to optimize efficiency and customer value. This integration empowers organizations to scale innovations effectively by balancing experimentation speed with rigorous process control.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate methodology depends on organizational goals and project scope, where Lean Startup excels in fostering rapid innovation and customer feedback during product development. Six Sigma offers a data-driven approach to minimize defects and improve process efficiency, ideal for mature operations focused on quality control. Companies seeking agility and iteration benefit from Lean Startup, while those prioritizing precision and consistency should consider Six Sigma.
Lean Startup and Six Sigma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com