Partnerships can amplify business growth by combining resources, expertise, and networks to achieve common goals more efficiently. Effective collaboration fosters innovation and opens new market opportunities that might be difficult to access alone. Discover how building strategic partnerships can transform Your business by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
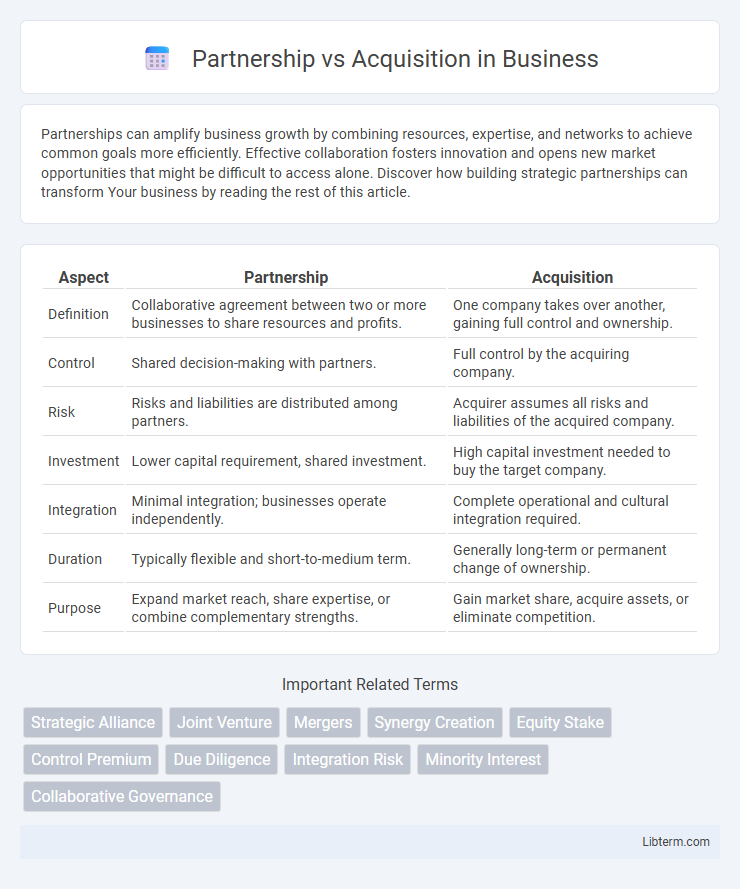
| Aspect | Partnership | Acquisition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative agreement between two or more businesses to share resources and profits. | One company takes over another, gaining full control and ownership. |
| Control | Shared decision-making with partners. | Full control by the acquiring company. |
| Risk | Risks and liabilities are distributed among partners. | Acquirer assumes all risks and liabilities of the acquired company. |
| Investment | Lower capital requirement, shared investment. | High capital investment needed to buy the target company. |
| Integration | Minimal integration; businesses operate independently. | Complete operational and cultural integration required. |
| Duration | Typically flexible and short-to-medium term. | Generally long-term or permanent change of ownership. |
| Purpose | Expand market reach, share expertise, or combine complementary strengths. | Gain market share, acquire assets, or eliminate competition. |
Introduction to Partnership and Acquisition
Partnership and acquisition are two strategic business approaches for growth and expansion. A partnership involves two or more companies collaborating to share resources, risks, and profits while maintaining separate identities. Acquisition occurs when one company purchases another, gaining full control and integrating its operations into the parent organization.
Defining Partnership: Key Features
Partnerships involve two or more entities collaborating to achieve shared goals while maintaining their independence, characterized by joint decision-making, shared risks, and mutual benefits. Key features include pooling resources and expertise, aligning strategic objectives, and establishing clear communication channels to ensure cooperation. Unlike acquisitions, partnerships do not entail ownership transfer, preserving each party's autonomy and operational control.
Understanding Acquisition: Core Concepts
Acquisition involves one company purchasing another to gain full control, often resulting in integration of assets, liabilities, and operations. It typically requires thorough due diligence, financial evaluation, and legal agreements to ensure strategic alignment and value creation. Understanding acquisition core concepts helps businesses navigate risks, optimize synergies, and enhance market position through decisive ownership transfer.
Strategic Goals: Partnership vs Acquisition
Partnerships enable organizations to align strategic goals through shared resources and collaborative innovation, fostering long-term growth without full ownership transfer. Acquisitions achieve strategic objectives by granting immediate control over assets and market access, often accelerating expansion and competitive positioning. Choosing between partnership and acquisition depends on desired control level, integration complexity, and speed of achieving strategic business outcomes.
Advantages of Forming Partnerships
Forming partnerships offers advantages such as shared resources, reduced financial risk, and access to complementary expertise, enabling businesses to leverage each other's strengths efficiently. Partnerships facilitate faster market entry and innovation through collaborative efforts without the complexities and costs of full ownership transfer seen in acquisitions. These strategic alliances enhance flexibility and allow companies to maintain their independence while benefiting from mutual growth opportunities.
Benefits and Challenges of Acquisition
Acquisition offers benefits such as immediate access to new markets, enhanced competitive advantage, and streamlined integration of resources and technologies. Challenges include high financial costs, cultural integration issues, and potential loss of key talent during the transition. Strategic alignment and thorough due diligence are critical to overcoming these obstacles and maximizing acquisition success.
Risk Factors in Partnerships and Acquisitions
Partnerships involve shared risks such as conflicting goals, unequal resource contributions, and potential legal liabilities from joint decisions. Acquisitions carry risks including cultural integration challenges, overvaluation of the acquired company, and regulatory hurdles that may delay or block the transaction. Both strategies require thorough due diligence to mitigate financial, operational, and reputational risks inherent in combining or collaborating business entities.
Financial Implications: Cost Comparison
Partnerships typically involve lower upfront costs compared to acquisitions, as they do not require full purchase payments or extensive due diligence fees. Acquisitions often incur significant expenses including purchase price, legal fees, integration costs, and potential debt financing. Cost comparison reveals partnerships maintain cash flow flexibility, while acquisitions demand substantial capital outlay impacting financial statements and valuation metrics.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Partnerships and acquisitions differ significantly in legal and regulatory considerations, with partnerships requiring formal agreements outlining roles, liabilities, and profit-sharing under contract law, while acquisitions involve complex regulatory scrutiny such as antitrust laws and securities regulations. Acquisitions typically necessitate compliance with merger control notifications, due diligence processes, and potential approval from competition authorities to prevent market monopolies. Legal risks vary as partnerships maintain separate entities sharing risks, whereas acquisitions transfer assets and liabilities, demanding comprehensive contractual and regulatory diligence.
Making the Right Choice: Partnership or Acquisition?
Choosing between partnership and acquisition depends on business goals, resource availability, and market conditions. Partnerships enable shared risks and collaboration without relinquishing control, ideal for strategic alliances and innovation. Acquisitions provide full control and rapid market entry but require significant investment and integration efforts, making them suitable for scaling and consolidating market position.
Partnership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com