Agile and Kanban are powerful methodologies designed to enhance project management and team productivity by promoting continuous delivery and flexibility. Agile focuses on iterative development and collaboration, while Kanban emphasizes visual workflow management and limiting work in progress to improve efficiency. Explore this article to understand how integrating Agile and Kanban can optimize your project's success.
Table of Comparison
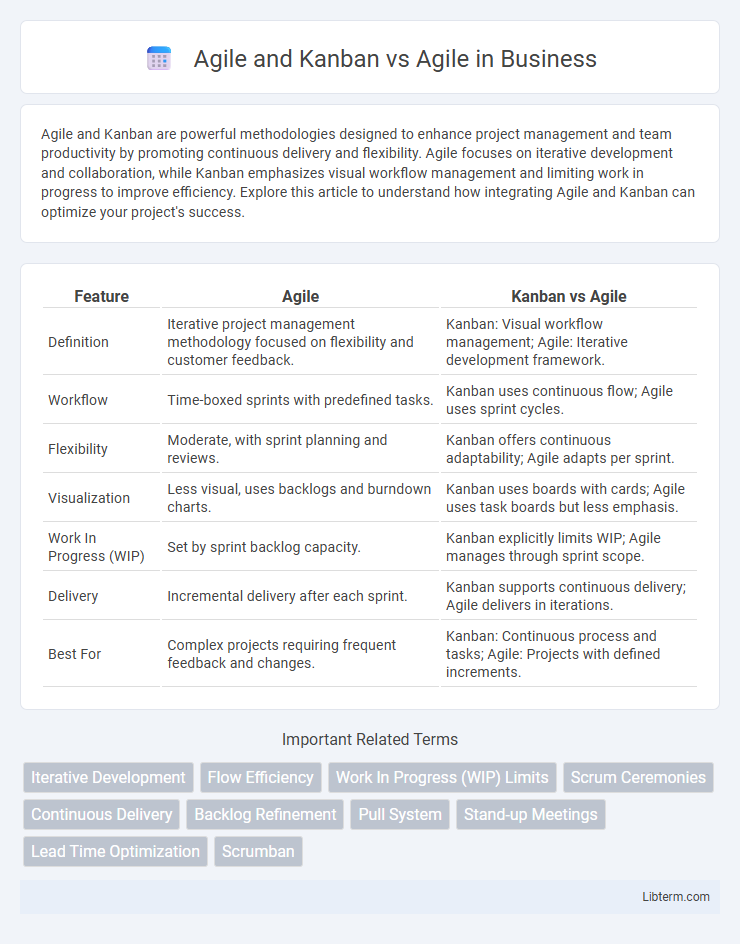
| Feature | Agile | Kanban vs Agile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Iterative project management methodology focused on flexibility and customer feedback. | Kanban: Visual workflow management; Agile: Iterative development framework. |
| Workflow | Time-boxed sprints with predefined tasks. | Kanban uses continuous flow; Agile uses sprint cycles. |
| Flexibility | Moderate, with sprint planning and reviews. | Kanban offers continuous adaptability; Agile adapts per sprint. |
| Visualization | Less visual, uses backlogs and burndown charts. | Kanban uses boards with cards; Agile uses task boards but less emphasis. |
| Work In Progress (WIP) | Set by sprint backlog capacity. | Kanban explicitly limits WIP; Agile manages through sprint scope. |
| Delivery | Incremental delivery after each sprint. | Kanban supports continuous delivery; Agile delivers in iterations. |
| Best For | Complex projects requiring frequent feedback and changes. | Kanban: Continuous process and tasks; Agile: Projects with defined increments. |
Understanding Agile: Core Principles and Practices
Agile is a project management methodology centered on iterative development, customer collaboration, and responsiveness to change, emphasizing core principles like individuals and interactions over processes and tools. Kanban, a visual workflow management tool, complements Agile by focusing on continuous delivery and limiting work in progress to optimize flow and efficiency. Understanding Agile's core practices involves embracing flexibility, iterative planning, regular feedback, and adaptive problem-solving to enhance team collaboration and product quality.
Introduction to Kanban: Key Concepts
Kanban is a visual workflow management method designed to improve efficiency by balancing demand with available capacity through the use of cards and boards. Unlike traditional Agile frameworks that emphasize iterative sprints, Kanban focuses on continuous delivery by limiting work-in-progress (WIP) to prevent bottlenecks. Core concepts include visualizing work, managing flow, and implementing explicit policies to optimize productivity and responsiveness.
Agile Methodologies: Scrum vs Other Frameworks
Agile methodologies encompass various frameworks, with Scrum and Kanban being prominent examples each serving unique project management needs. Scrum emphasizes iterative development through sprints and defined roles, fostering team collaboration and regular feedback, while Kanban focuses on continuous workflow improvement and visual task management without prescribed timeboxes. Comparing Scrum to other Agile frameworks highlights differences in structure, adaptability, and process control, enabling teams to select the approach that best aligns with their project goals and organizational culture.
What Sets Kanban Apart from Traditional Agile
Kanban distinguishes itself from traditional Agile methodologies by emphasizing continuous workflow visualization and limiting work in progress (WIP) to enhance efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. Unlike iterative Scrum sprints in Agile, Kanban operates on a continuous delivery model, allowing teams to adapt more fluidly to changing priorities without fixed-length cycles. The Kanban board's real-time transparency fosters incremental improvements, making it ideal for environments requiring flexibility and steady throughput.
Agile and Kanban: Similarities and Differences
Agile and Kanban both emphasize iterative progress and flexibility in project management, with Agile focusing on time-boxed sprints and cross-functional team collaboration, while Kanban provides a visual workflow system that limits work in progress to optimize efficiency. Agile methodologies like Scrum promote fixed-length iterations and predefined roles, whereas Kanban offers continuous delivery without prescribed roles or time constraints. Both frameworks improve transparency, adaptability, and customer feedback integration, but Kanban is often favored for its flow-based approach and ease of implementation in existing processes.
Workflow Visualization: Boards in Agile and Kanban
Workflow visualization in Agile typically uses Scrum boards to represent sprint backlogs and track tasks through predefined stages like To Do, In Progress, and Done, enabling iterative progress monitoring. Kanban employs a continuous flow board with columns that reflect each step of the process, such as Backlog, Development, Testing, and Deployment, emphasizing work-in-progress limits to optimize throughput. Both methods leverage visual boards for task transparency, but Kanban's board uniquely focuses on continuous delivery and reducing cycle time without fixed iterations.
Managing Work in Progress: Agile vs Kanban Approaches
Agile methodologies prioritize iterative progress through time-boxed sprints, limiting work in progress (WIP) by focusing on completing set user stories within each cycle. Kanban emphasizes continuous workflow management with explicit WIP limits for each stage, visualizing tasks on a board to optimize throughput and identify bottlenecks. Managing WIP in Agile relies on sprint planning and prioritization, while Kanban provides real-time flexibility and incremental delivery by controlling WIP through continuous pull-based task allocation.
Team Roles and Responsibilities in Agile vs Kanban
Agile frameworks emphasize cross-functional team roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team members, each with specific responsibilities to manage iterations and deliverables. Kanban focuses on visualizing workflow and continuous delivery, with less rigidly defined roles, empowering team members to manage tasks collaboratively and optimize flow. Agile roles are structured around iterative planning and review ceremonies, whereas Kanban promotes flexible task ownership and responsibility without prescribed role definitions.
Choosing the Right Framework: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right framework between Agile and Kanban requires evaluating factors such as team size, project complexity, and workflow flexibility. Agile is ideal for projects needing iterative development with clearly defined sprints, while Kanban suits continuous delivery and tasks requiring real-time prioritization. Understanding stakeholder collaboration, delivery deadlines, and adaptability needs ensures optimal framework selection for efficiency and product quality.
Conclusion: When to Use Agile, Kanban, or Both
Agile is ideal for projects requiring flexibility, iterative progress, and regular stakeholder feedback, especially in software development and dynamic environments. Kanban suits workflows needing continuous delivery, visual management, and limits on work in progress, often used in support, maintenance, or operational teams. Combining Agile and Kanban is effective when iterative planning aligns with real-time task tracking and flow optimization, leveraging Agile's adaptability and Kanban's visualization strengths.
Agile and Kanban Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com