Licensing grants you legal permission to use intellectual property under defined terms, protecting both creators and users. Understanding the nuances of different licensing types, such as open-source, proprietary, or creative commons, ensures compliance and maximizes business potential. Explore the rest of the article to learn how licensing can impact your projects and safeguard your innovations.
Table of Comparison
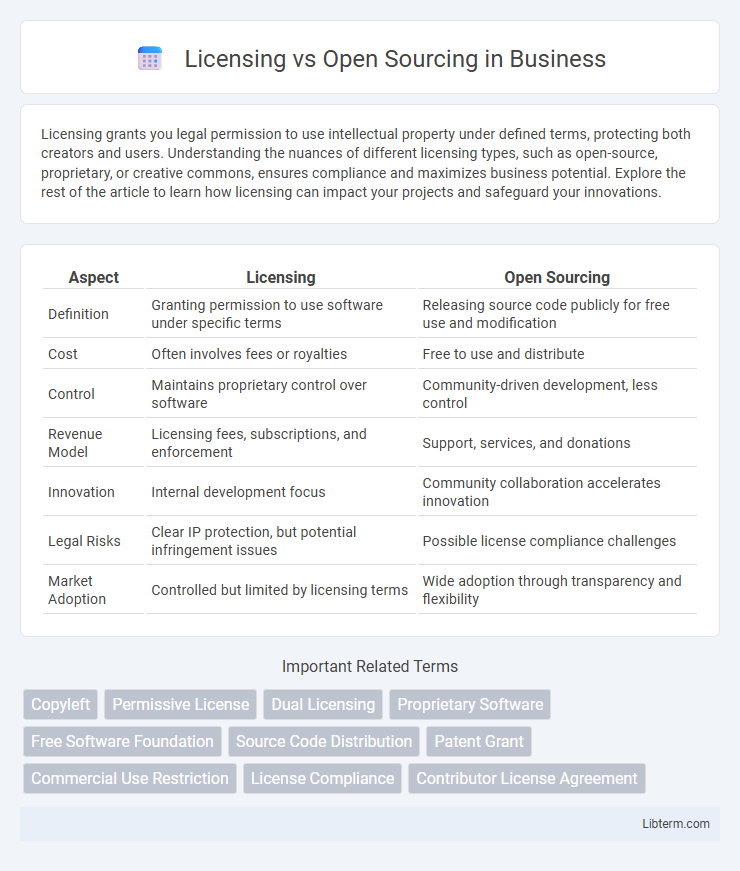
| Aspect | Licensing | Open Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Granting permission to use software under specific terms | Releasing source code publicly for free use and modification |
| Cost | Often involves fees or royalties | Free to use and distribute |
| Control | Maintains proprietary control over software | Community-driven development, less control |
| Revenue Model | Licensing fees, subscriptions, and enforcement | Support, services, and donations |
| Innovation | Internal development focus | Community collaboration accelerates innovation |
| Legal Risks | Clear IP protection, but potential infringement issues | Possible license compliance challenges |
| Market Adoption | Controlled but limited by licensing terms | Wide adoption through transparency and flexibility |
Introduction to Licensing and Open Sourcing
Licensing defines the legal permissions and restrictions for using, modifying, and distributing software, ensuring creators retain control over their intellectual property. Open sourcing involves releasing software source code publicly under licenses that promote collaboration, transparency, and community-driven development. Understanding the distinctions between proprietary licenses and various open source licenses, such as MIT, GPL, and Apache, is crucial for developers and organizations when choosing software distribution models.
Defining Software Licensing
Software licensing defines the legal framework granting users permission to use, modify, and distribute software under specified conditions. Unlike open sourcing, which makes source code publicly available for free modification and sharing, licensing can impose restrictions to protect intellectual property rights. Understanding software licensing terms is crucial for developers and organizations to ensure compliance and avoid legal risks.
What Does Open Sourcing Mean?
Open sourcing means making software's source code freely available to the public, allowing users to view, modify, and distribute it under specific licenses such as MIT, GPL, or Apache. It fosters collaboration, transparency, and innovation by enabling developers to contribute improvements and adapt the software to various needs. Unlike traditional licensing that restricts usage and distribution, open source licenses grant more freedom while ensuring compliance with defined terms.
Key Differences Between Licensing and Open Sourcing
Licensing typically restricts software usage, modification, and distribution through specific legal agreements, while open sourcing grants users free access to the source code under permissive or copyleft licenses. Licensing models like proprietary licenses enforce strict control over intellectual property, unlike open source licenses such as MIT, GPL, or Apache which promote collaboration and transparency. Key differences include the level of user freedom, with licensing often limiting modifications, whereas open sourcing encourages community contributions and innovation.
Benefits of Licensed Software
Licensed software provides guaranteed legal protection and clear usage rights, reducing the risk of copyright infringement and unauthorized redistribution. It often includes professional support, regular updates, and security patches, ensuring reliability and enhanced user experience. Businesses benefit from licensed software through compliance assurance, improved software performance, and access to dedicated customer service.
Advantages of Open Source Solutions
Open source solutions offer unparalleled transparency, allowing developers to inspect, modify, and enhance the source code freely, which accelerates innovation and fosters community collaboration. These solutions reduce costs significantly by eliminating licensing fees while providing greater flexibility and customization tailored to specific organizational needs. The vibrant open source ecosystem enhances security through continuous peer review and rapid vulnerability patching, ensuring robust and reliable software performance.
Common Licensing Models Explained
Common licensing models include proprietary licenses, which restrict usage and modification rights, and open-source licenses that promote free use, distribution, and alteration of software. Popular open-source licenses such as MIT, GNU General Public License (GPL), and Apache License differ in terms of copyleft requirements, patent grants, and attribution obligations. Choosing the right license depends on whether developers prioritize control and monetization or collaboration and transparency in software development.
Popular Open Source Licenses
Popular open source licenses like the MIT License, GNU General Public License (GPL), and Apache License define how software can be freely used, modified, and distributed while protecting developers' rights. The MIT License offers minimal restrictions, promoting maximum freedom for commercial and private use, whereas the GPL enforces copyleft provisions requiring derivative works to remain open source. Apache License balances permissiveness with patent protections, making it a preferred choice for enterprise-level open source projects.
Choosing Between Licensing and Open Sourcing
Choosing between licensing and open sourcing hinges on control, collaboration, and distribution goals. Licensing offers proprietary control over software usage, enabling monetization and restriction of modifications, while open sourcing fosters community collaboration and transparency by allowing free access and modification. Consider the desired balance of intellectual property protection, user engagement, and innovation speed when determining which approach aligns best with your project's objectives.
Future Trends in Software Distribution
Licensing models are evolving with an emphasis on hybrid approaches that combine proprietary and open-source elements to maximize flexibility and control. Open sourcing continues to gain traction as collaborative development accelerates innovation, supported by expanding ecosystems and community-driven contributions. Future software distribution trends highlight increased reliance on cloud-based platforms and containerization, enhancing accessibility and scalability across diverse environments.
Licensing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com