Green bonds are innovative financial instruments designed to fund projects that have positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture. These bonds attract investors eager to support eco-friendly initiatives while earning returns, driving the growth of the green finance market worldwide. Explore this article to understand how green bonds can align with your investment goals and contribute to a sustainable future.
Table of Comparison
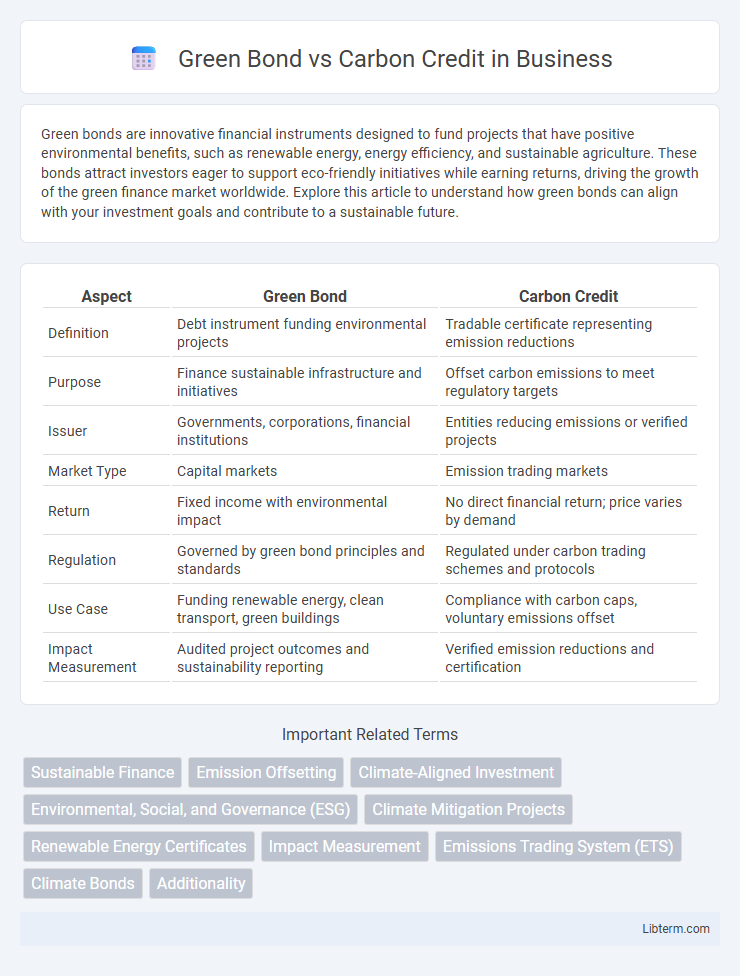
| Aspect | Green Bond | Carbon Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debt instrument funding environmental projects | Tradable certificate representing emission reductions |
| Purpose | Finance sustainable infrastructure and initiatives | Offset carbon emissions to meet regulatory targets |
| Issuer | Governments, corporations, financial institutions | Entities reducing emissions or verified projects |
| Market Type | Capital markets | Emission trading markets |
| Return | Fixed income with environmental impact | No direct financial return; price varies by demand |
| Regulation | Governed by green bond principles and standards | Regulated under carbon trading schemes and protocols |
| Use Case | Funding renewable energy, clean transport, green buildings | Compliance with carbon caps, voluntary emissions offset |
| Impact Measurement | Audited project outcomes and sustainability reporting | Verified emission reductions and certification |
Introduction to Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
Green bonds are fixed-income financial instruments designed to raise capital specifically for environmentally sustainable projects, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and energy efficiency improvements. Carbon credits represent a tradeable permit that allows the holder to emit one metric ton of carbon dioxide or an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases, functioning as a market-based tool to incentivize emissions reductions. Both mechanisms play crucial roles in addressing climate change by mobilizing private investment and regulating carbon emissions through complementary financial strategies.
Defining Green Bonds
Green bonds are fixed-income financial instruments specifically designed to fund projects that have positive environmental or climate benefits, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. Unlike carbon credits, which represent a tradable permit to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, green bonds raise capital for environmentally responsible initiatives without directly offsetting emissions. The growing global market for green bonds reflects increased investor demand for sustainable investment opportunities aligned with climate change mitigation goals.
Understanding Carbon Credits
Carbon credits represent a tradable permit or certificate allowing the holder to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, serving as a market-driven mechanism to incentivize emission reductions. These credits are generated from projects that reduce, remove, or avoid emissions, such as reforestation, renewable energy installations, or methane capture initiatives, and are verified through stringent standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard. Understanding carbon credits involves recognizing their role in offsetting emissions by enabling companies or individuals to invest in environmental projects that compensate for their greenhouse gas footprint.
Key Differences Between Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
Green bonds are debt instruments issued to finance projects with environmental benefits, primarily targeting renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure, while carbon credits represent tradable permits allowing the holder to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases. Green bonds provide upfront capital for green projects and typically offer financial returns to investors, whereas carbon credits function within cap-and-trade systems to incentivize emission reductions by enabling companies to offset their carbon footprint. The fundamental difference lies in their purpose: green bonds fund environmentally friendly projects, whereas carbon credits directly regulate and limit greenhouse gas emissions through market-based mechanisms.
Market Trends: Green Bond Issuance vs Carbon Credit Trading
Green bond issuance has surged globally, reaching over $500 billion in 2023, driven by escalating investor demand for sustainable finance and regulatory support. In contrast, carbon credit trading volumes on major exchanges, such as the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), have fluctuated around 2 billion metric tons of CO2 annually, influenced by price volatility and evolving carbon market mechanisms. The green bond market exhibits steady growth with diversified investment portfolios, while carbon credit trading remains highly sensitive to policy changes and market sentiment.
Environmental Impact: Green Bonds vs Carbon Credits
Green Bonds finance eco-friendly projects such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure, leading to long-term environmental benefits by reducing emissions and supporting green innovation. Carbon Credits represent a market-based mechanism allowing companies to offset their carbon emissions by investing in verified carbon reduction or removal projects, directly contributing to global emissions targets. While Green Bonds drive proactive investment in sustainability, Carbon Credits focus on compensating and neutralizing existing carbon footprints.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
Regulatory frameworks governing green bonds primarily involve standards set by bodies such as the Climate Bonds Initiative and adherence to the Green Bond Principles by the International Capital Market Association, ensuring transparency in the use of proceeds and reporting. Carbon credit regulations are managed through international agreements like the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, alongside regional cap-and-trade systems that define verification, issuance, and trading processes. Both frameworks emphasize stringent monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) protocols to maintain environmental integrity and investor confidence in climate finance markets.
Investment Opportunities and Risks
Green bonds offer investors fixed-income opportunities funding environmentally sustainable projects, providing predictable returns but subject to interest rate and project execution risks. Carbon credits represent tradable permits enabling companies to offset emissions, introducing market volatility and regulatory uncertainty. Both investment types appeal to ESG-focused portfolios but require careful risk assessment linked to regulatory frameworks and market dynamics.
Case Studies: Successful Green Bond and Carbon Credit Projects
The Masdar City Green Bond in Abu Dhabi successfully raised $600 million to fund renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure, demonstrating effective capital deployment in clean technology. In parallel, the Jari Para REDD+ project in Brazil has generated millions of carbon credits by preventing deforestation, successfully linking conservation efforts with market-based incentives. Both initiatives highlight scalable models where green finance and carbon markets drive measurable environmental impact and economic benefits.
Future Outlook for Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
The future outlook for green bonds is promising with a projected annual growth rate exceeding 20%, driven by increasing investor demand for sustainable finance and regulatory support from governments worldwide. Carbon credits are expected to expand as global carbon markets mature, with voluntary and compliance markets anticipating significant price stabilization and increased transaction volumes by 2030. Both instruments will play complementary roles in achieving net-zero targets, fostering investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and emission reduction technologies.
Green Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com