Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy focused on continuous, incremental improvement in both personal and professional settings, emphasizing efficiency and waste reduction. It fosters a culture where every individual actively participates in enhancing processes, resulting in higher quality and productivity. Discover how implementing Kaizen principles can transform your workflow by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
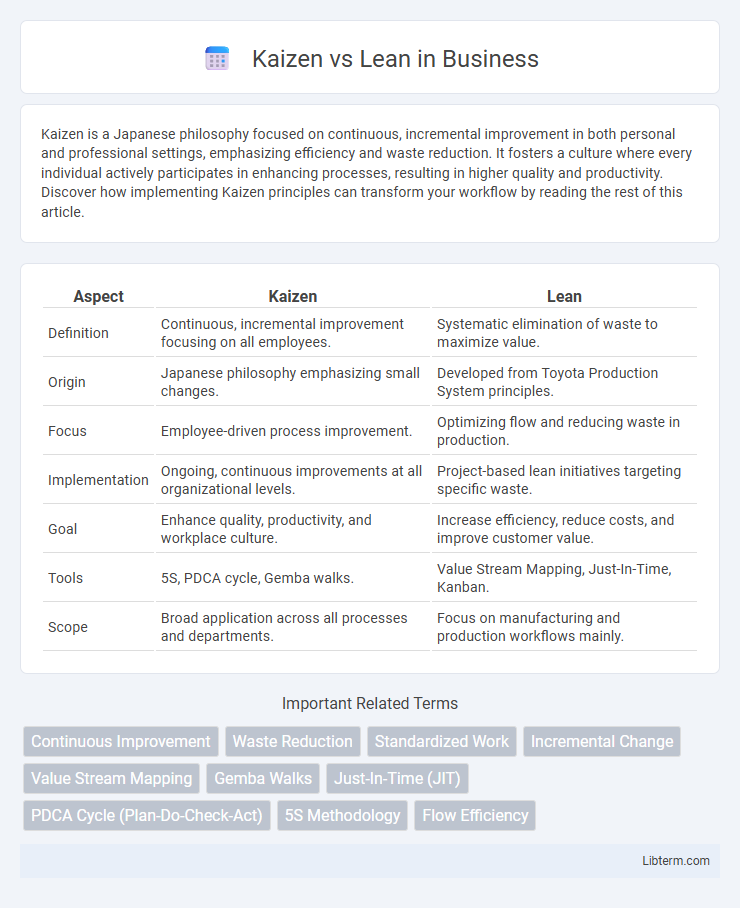
| Aspect | Kaizen | Lean |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous, incremental improvement focusing on all employees. | Systematic elimination of waste to maximize value. |
| Origin | Japanese philosophy emphasizing small changes. | Developed from Toyota Production System principles. |
| Focus | Employee-driven process improvement. | Optimizing flow and reducing waste in production. |
| Implementation | Ongoing, continuous improvements at all organizational levels. | Project-based lean initiatives targeting specific waste. |
| Goal | Enhance quality, productivity, and workplace culture. | Increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer value. |
| Tools | 5S, PDCA cycle, Gemba walks. | Value Stream Mapping, Just-In-Time, Kanban. |
| Scope | Broad application across all processes and departments. | Focus on manufacturing and production workflows mainly. |
Introduction to Kaizen and Lean
Kaizen is a continuous improvement methodology originating from Japan, emphasizing small, incremental changes that enhance efficiency and quality within organizations. Lean, derived from the Toyota Production System, focuses on maximizing customer value by eliminating waste and optimizing workflows across processes. Both frameworks aim to improve operational performance but differ in scope and application, with Kaizen concentrating on ongoing employee-driven improvements and Lean targeting systematic waste reduction.
Origins and Historical Background
Kaizen originated in post-World War II Japan as a continuous improvement approach developed by Japanese businesses to enhance productivity and quality incrementally. Lean methodology traces its roots to the Toyota Production System of the 1940s and 1950s, emphasizing waste reduction, efficient workflows, and value stream mapping. Both philosophies emerged from the need to rebuild and optimize manufacturing processes, but Kaizen focuses on ongoing small improvements while Lean centers on eliminating waste and improving overall system efficiency.
Core Principles of Kaizen
Kaizen centers on continuous, incremental improvements driven by employee involvement and a culture of constant feedback. Its core principles include eliminating waste, standardizing processes, and empowering workers to identify inefficiencies and suggest solutions. Lean, while sharing the goal of waste reduction, emphasizes value stream mapping and optimizing overall flow across the production process.
Fundamental Concepts of Lean
Lean centers on maximizing customer value by minimizing waste and enhancing workflow efficiency through continuous improvement and respect for people. Key concepts include value stream mapping to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, just-in-time production to reduce inventory costs, and empowering employees to contribute to process improvements. Lean principles aim to create more value with fewer resources by fostering a culture of ongoing optimization and quality enhancement.
Key Differences Between Kaizen and Lean
Kaizen emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements driven by employee involvement, fostering a culture of ongoing change, while Lean focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing processes to enhance overall efficiency and value delivery. Kaizen's approach is iterative and people-centric, promoting small, daily improvements, whereas Lean employs structured methodologies like value stream mapping and just-in-time production to streamline workflows systematically. The primary distinction lies in Kaizen's focus on gradual cultural transformation versus Lean's strategic implementation of tools and principles to achieve process excellence.
Methodologies and Tools Comparison
Kaizen emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements through employee involvement using tools like 5S, PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), and root cause analysis to foster a culture of ongoing enhancement. Lean methodology focuses on maximizing value by eliminating waste with tools such as Value Stream Mapping, Just-In-Time (JIT) production, and Kanban to streamline processes and improve efficiency. Both methodologies complement each other by integrating Kaizen's cultural approach with Lean's structured waste reduction techniques for sustainable operational excellence.
Implementation Strategies
Kaizen implementation strategies emphasize continuous, incremental improvements through employee involvement and standardized processes, fostering a culture of ongoing feedback and problem-solving at all organizational levels. Lean implementation focuses on value stream mapping, waste elimination, and just-in-time production to streamline workflows and optimize resource allocation, often starting with pilot projects in key areas. Both approaches require strong leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, and regular performance measurement to ensure sustainable operational excellence.
Benefits of Kaizen vs Lean
Kaizen emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements involving all employees, fostering a culture of sustained innovation and employee engagement that drives quality and efficiency. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and streamlining processes to deliver faster value to customers, resulting in cost reduction and improved workflow. Both methodologies enhance operational performance, but Kaizen's strength lies in cultural transformation, while Lean excels in process optimization.
Challenges in Applying Kaizen and Lean
Implementing Kaizen and Lean methodologies faces challenges such as resistance to cultural change and lack of employee engagement, which can hinder continuous improvement efforts. Organizations often struggle with inadequate training and unclear communication, leading to inconsistent application of Kaizen principles and Lean tools like value stream mapping or 5S. Measuring progress and maintaining momentum require strong leadership commitment and alignment of processes with business goals to overcome operational inertia.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Kaizen emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements driven by employee involvement, ideal for organizations seeking cultural transformation and sustained growth. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing processes to enhance efficiency, suitable for companies needing rapid operational improvements and cost reduction. Selecting the right approach depends on organizational goals, existing culture, and the urgency of desired results, with some businesses benefiting from integrating both methodologies for comprehensive performance enhancement.
Kaizen Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com