Automation streamlines repetitive tasks, boosting efficiency and reducing human error in various industries. By leveraging advanced technologies like AI and robotics, businesses can enhance productivity and focus on strategic goals. Discover how automation can transform your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
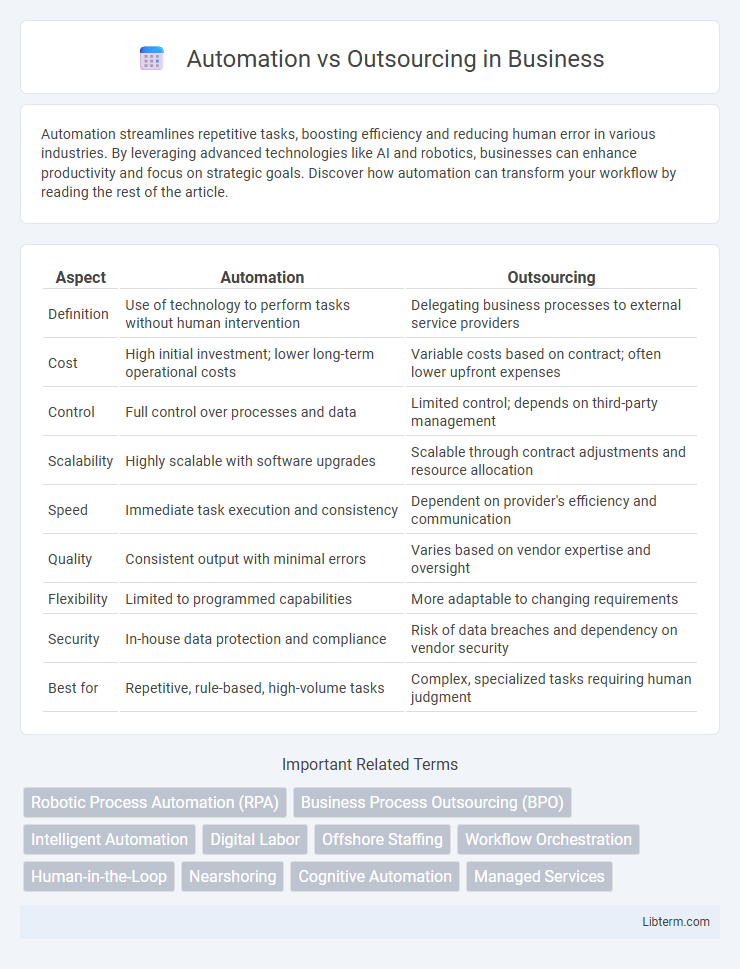
| Aspect | Automation | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention | Delegating business processes to external service providers |
| Cost | High initial investment; lower long-term operational costs | Variable costs based on contract; often lower upfront expenses |
| Control | Full control over processes and data | Limited control; depends on third-party management |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with software upgrades | Scalable through contract adjustments and resource allocation |
| Speed | Immediate task execution and consistency | Dependent on provider's efficiency and communication |
| Quality | Consistent output with minimal errors | Varies based on vendor expertise and oversight |
| Flexibility | Limited to programmed capabilities | More adaptable to changing requirements |
| Security | In-house data protection and compliance | Risk of data breaches and dependency on vendor security |
| Best for | Repetitive, rule-based, high-volume tasks | Complex, specialized tasks requiring human judgment |
Introduction to Automation and Outsourcing
Automation leverages advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, robotics, and software to perform repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Outsourcing involves contracting external organizations or vendors to handle specific business functions, enabling companies to focus on core competencies while lowering operational costs. Both strategies aim to optimize resource allocation and improve overall productivity within enterprises.
Defining Automation: Key Features and Benefits
Automation involves using technology such as software robots, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to perform repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, reducing human intervention. Key features of automation include task consistency, scalability, real-time data processing, and integration capabilities with existing systems. Benefits encompass cost savings, increased productivity, error reduction, and enhanced business agility, enabling companies to focus resources on strategic initiatives.
What is Outsourcing? Scope and Advantages
Outsourcing involves contracting external organizations to handle specific business processes or services, reducing internal workload and operational costs. Its scope includes functions like customer support, IT services, manufacturing, and payroll processing, enabling companies to access specialized expertise and technology. Advantages of outsourcing include cost savings, enhanced focus on core activities, scalability, and improved efficiency through leveraging third-party capabilities.
Core Differences Between Automation and Outsourcing
Automation leverages technology such as artificial intelligence and robotics to perform repetitive tasks with precision and efficiency, reducing human intervention and operational costs. Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or functions to third-party service providers, focusing on leveraging external expertise and labor. Core differences include automation's emphasis on process control through software or machines, while outsourcing centers on transferring work to external teams to optimize resource allocation.
Cost Implications: Automation vs Outsourcing
Automation reduces long-term operational costs by minimizing human error and increasing productivity through advanced technologies like AI and robotics. Outsourcing often involves variable expenses, including vendor fees and contract management, which may fluctuate based on service level agreements and labor market conditions. Companies must evaluate the initial capital investment for automation against the ongoing costs and risks associated with outsourcing to optimize budget efficiency.
Impact on Workforce and Employment
Automation transforms the workforce by replacing repetitive tasks with intelligent machines, leading to efficiency gains but reducing demand for low-skilled labor. Outsourcing shifts jobs to external providers, often in lower-cost regions, which can lead to domestic job displacement but also creates specialized employment opportunities abroad. Both strategies reshape employment dynamics, necessitating reskilling and adaptation to evolving labor market demands.
Scalability and Flexibility Compared
Automation offers unparalleled scalability by enabling businesses to rapidly increase output without proportional increases in labor costs, making it ideal for handling large volumes of repetitive tasks efficiently. Outsourcing provides flexibility through access to specialized skills and the ability to adjust resource levels quickly based on project demands or seasonal fluctuations. Combining automation with outsourcing can optimize operational scalability and adaptability, supporting dynamic business environments and accelerating growth.
Common Use Cases in Business Operations
Automation in business operations is commonly used for repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer service through chatbots, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Outsourcing focuses on leveraging external expertise for specialized functions like IT support, payroll management, and digital marketing, enabling cost savings and access to global talent. Both approaches optimize workflows but differ in implementation: automation relies on technology to streamline internal processes, while outsourcing delegates tasks to third-party providers.
Challenges and Risks of Each Approach
Automation presents challenges such as high initial investment, complex integration with existing systems, and potential job displacement causing workforce resistance. Outsourcing involves risks like loss of control over quality, dependence on third-party vendors, and possible security breaches due to data handling by external providers. Both approaches require careful risk management to ensure operational efficiency and safeguard business continuity.
Choosing the Right Solution: Automation, Outsourcing, or Both?
Choosing the right solution between automation and outsourcing depends on factors such as cost-efficiency, scalability, and business objectives. Automation excels in repetitive, rule-based tasks by reducing human error and increasing speed, while outsourcing provides access to specialized skills and flexibility for complex or non-core functions. Combining automation with outsourcing can optimize operational efficiency by leveraging technology for routine processes and expert human resources for strategic activities.
Automation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com