A Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a secure investment that offers a fixed interest rate over a specified term, usually ranging from a few months to several years. CDs are issued by banks and are insured, making them a low-risk option for growing your savings with predictable returns. Discover how choosing the right CD can benefit your financial strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
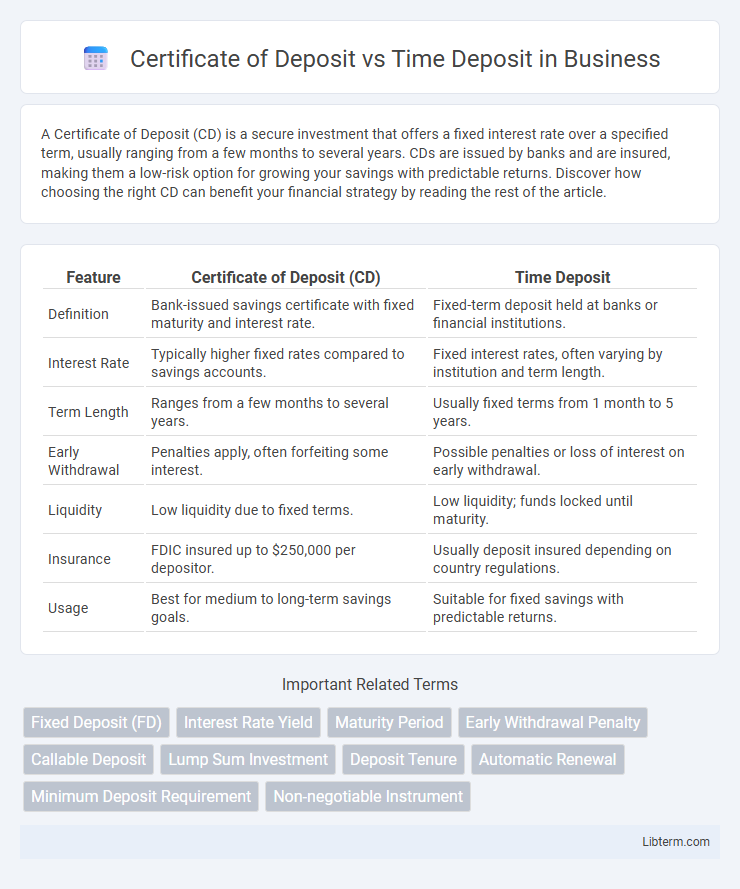
| Feature | Certificate of Deposit (CD) | Time Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bank-issued savings certificate with fixed maturity and interest rate. | Fixed-term deposit held at banks or financial institutions. |
| Interest Rate | Typically higher fixed rates compared to savings accounts. | Fixed interest rates, often varying by institution and term length. |
| Term Length | Ranges from a few months to several years. | Usually fixed terms from 1 month to 5 years. |
| Early Withdrawal | Penalties apply, often forfeiting some interest. | Possible penalties or loss of interest on early withdrawal. |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity due to fixed terms. | Low liquidity; funds locked until maturity. |
| Insurance | FDIC insured up to $250,000 per depositor. | Usually deposit insured depending on country regulations. |
| Usage | Best for medium to long-term savings goals. | Suitable for fixed savings with predictable returns. |
Introduction to Certificate of Deposit and Time Deposit
A Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a financial product offered by banks that locks in a fixed amount of money for a specified term at a guaranteed interest rate. Time Deposits, commonly known as fixed deposits in many countries, function similarly by requiring funds to be held for a predetermined period, earning interest that is often higher than regular savings accounts. Both CDs and Time Deposits provide secure investment opportunities with fixed returns, making them popular choices for risk-averse investors seeking stable growth.
Definition: What is a Certificate of Deposit?
A Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a financial product issued by banks that locks in a fixed amount of money for a specified term at a predetermined interest rate, offering higher returns compared to regular savings accounts. Unlike time deposits, which can vary by country, CDs are standardized instruments in the United States, typically insured by the FDIC up to $250,000. Certificates of Deposit require the investor to keep funds deposited until maturity to avoid penalties, emphasizing the benefit of guaranteed interest earnings through a legally binding contract.
Definition: What is a Time Deposit?
A time deposit is a financial account where funds are locked in for a fixed term, earning interest over that period. Unlike a Certificate of Deposit (CD), which is a specific type of time deposit offered by banks with fixed interest rates and maturity dates, time deposits can also include other fixed-term investment options. Time deposits provide a secure way to save money while earning predictable returns, usually requiring the funds to remain untouched until maturity to avoid penalties.
Key Differences Between Certificate of Deposit and Time Deposit
Certificate of Deposit (CD) and Time Deposit both refer to fixed-term savings instruments but differ primarily in terminology and regional usage. CDs are commonly used in the United States and often come with more flexible terms for early withdrawal, sometimes with penalties, while Time Deposits are prevalent in other countries like India and typically emphasize fixed maturity dates with strict withdrawal restrictions. Interest rates on CDs may vary based on term length and issuers, whereas Time Deposits usually offer fixed interest rates predefined at the contract's inception.
Interest Rates: CD vs Time Deposit
Certificate of Deposit (CD) interest rates often surpass those of standard Time Deposits due to fixed terms and early withdrawal penalties, encouraging longer commitments. CDs typically offer higher yields for terms ranging from three months to five years, while Time Deposits may provide more flexible durations but generally lower returns. Understanding the specific rate structures and maturity periods is essential for maximizing savings growth in these fixed-income instruments.
Maturity Periods and Terms Comparison
Certificate of Deposit (CD) and Time Deposit both offer fixed-term savings with predetermined maturity periods, typically ranging from one month to five years. CDs generally feature more flexible term options and may include penalties for early withdrawal, whereas Time Deposits often have stricter terms with less flexibility but comparable interest rates. Understanding the maturity periods and specific terms of each product is essential for aligning investment goals and liquidity needs.
Liquidity and Withdrawal Policies
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) typically have fixed terms ranging from a few months to several years, with early withdrawal penalties that reduce liquidity and can result in loss of earned interest. Time Deposits, often offered by banks outside the U.S., also lock funds for a specified period but may have more flexible withdrawal conditions, sometimes allowing partial withdrawals without severe penalties. Both instruments prioritize capital preservation but differ in liquidity access and penalty structures depending on the financial institution and regional banking regulations.
Safety and Risk Factors
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) and Time Deposits both offer low-risk investment options with principal protection, as they are typically insured by government agencies like the FDIC up to applicable limits. CDs often provide fixed interest rates and specified maturity dates, minimizing interest rate risk but possibly incurring penalties for early withdrawal, whereas Time Deposits may vary in terms and conditions depending on the institution, potentially affecting liquidity and return stability. Both instruments prioritize capital preservation, making them suitable for conservative investors seeking safety over high returns.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Each Option?
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) suit investors seeking fixed interest rates with set maturity dates, ideal for conservative savers prioritizing capital preservation and predictable returns. Time Deposits appeal to individuals and businesses looking for flexible terms with potentially negotiable interest rates, suitable for those willing to commit funds for varying periods while optimizing liquidity and yield. Both options cater to risk-averse investors but differ in accessibility and customization based on financial goals and cash flow needs.
Conclusion: Which Deposit is Right for You?
Choosing between a Certificate of Deposit (CD) and a Time Deposit depends on your financial goals and liquidity needs. CDs typically offer fixed interest rates with set terms, making them ideal for savers seeking predictable returns and low risk. Time deposits may provide flexibility in terms and maturities but generally require you to commit funds for a specific period, so evaluate your cash flow requirements before deciding.
Certificate of Deposit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com