Qualitative analysis offers deep insights into complex data by exploring patterns, themes, and meanings beyond numerical values. It helps you understand behaviors, experiences, and motivations through detailed observation and interpretation. Discover how qualitative analysis can transform your research by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
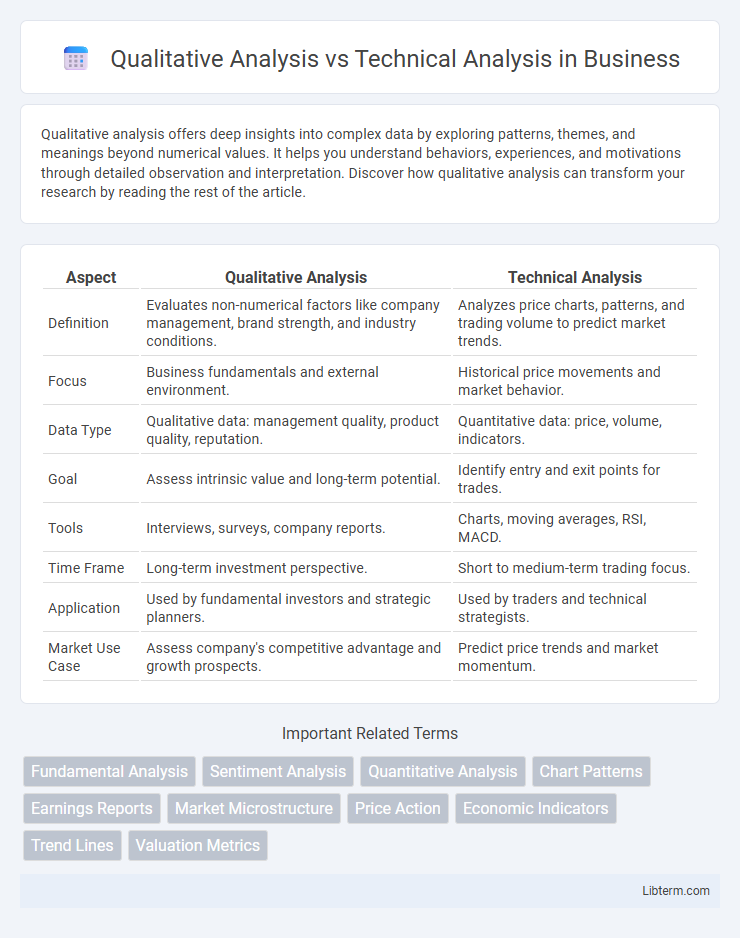
| Aspect | Qualitative Analysis | Technical Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates non-numerical factors like company management, brand strength, and industry conditions. | Analyzes price charts, patterns, and trading volume to predict market trends. |
| Focus | Business fundamentals and external environment. | Historical price movements and market behavior. |
| Data Type | Qualitative data: management quality, product quality, reputation. | Quantitative data: price, volume, indicators. |
| Goal | Assess intrinsic value and long-term potential. | Identify entry and exit points for trades. |
| Tools | Interviews, surveys, company reports. | Charts, moving averages, RSI, MACD. |
| Time Frame | Long-term investment perspective. | Short to medium-term trading focus. |
| Application | Used by fundamental investors and strategic planners. | Used by traders and technical strategists. |
| Market Use Case | Assess company's competitive advantage and growth prospects. | Predict price trends and market momentum. |
Introduction to Qualitative and Technical Analysis
Qualitative analysis evaluates non-numerical factors such as company management, brand reputation, competitive advantages, and market conditions to assess investment potential. Technical analysis involves studying historical price movements, trading volume, and chart patterns to predict future price trends and market behavior. Both approaches provide distinct insights, with qualitative analysis focusing on intrinsic value and technical analysis emphasizing market sentiment and timing.
Defining Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis evaluates non-numeric factors such as company management, brand strength, industry trends, and competitive advantages to assess investment potential. This approach emphasizes understanding the underlying business model, corporate governance, and market positioning to identify long-term value drivers. Unlike technical analysis, qualitative analysis relies on subjective judgment and in-depth research rather than historical price patterns or statistical data.
Defining Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing statistical trends from trading activity, such as price movement and volume. It relies on chart patterns, indicators, and historical data to predict future market behavior. Unlike qualitative analysis, which assesses fundamental factors like company management and financial health, technical analysis strictly focuses on market-generated information to guide trading decisions.
Key Differences Between Qualitative and Technical Analysis
Qualitative analysis evaluates financial statements, management quality, and market conditions to assess a company's intrinsic value, emphasizing subjective factors like leadership, brand strength, and economic environment. Technical analysis relies on historical price data, chart patterns, and trading volumes to predict future price movements, focusing on market psychology and trends through tools like moving averages and RSI indicators. The key difference lies in qualitative's fundamental approach versus technical's data-driven, pattern-recognition methodology.
Advantages of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis offers a comprehensive understanding of market sentiment by examining company leadership, industry trends, and competitive advantages, which cannot be quantified through charts or price data alone. It provides insights into management quality, brand value, and customer loyalty, enabling investors to assess long-term growth potential beyond historical price movements. This approach is especially valuable in identifying emerging companies and disruptive innovations before they are reflected in technical indicators.
Benefits of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis offers the significant benefit of identifying market trends and price patterns through historical data, which helps traders make informed decisions based on real-time price movements. It utilizes tools like moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and candlestick charts to predict future market behavior, enhancing timing accuracy for entries and exits. This method provides a systematic approach to risk management by setting stop-loss levels and profit targets based on support and resistance zones.
Limitations of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis faces limitations such as subjectivity, where interpretations of data can vary widely among analysts, leading to inconsistent conclusions. It also struggles with scalability, making it difficult to apply uniformly across large datasets or numerous assets without losing nuanced insights. Furthermore, the reliance on non-quantifiable information can result in challenges when trying to backtest or validate findings against historical market data.
Drawbacks of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis often faces criticism due to its reliance on historical price data, which may not accurately predict future market movements in volatile or unpredictable environments. The method can lead to false signals and overtrading, increasing the risk of significant financial losses. Unlike qualitative analysis, technical analysis lacks consideration of fundamental factors like company performance or macroeconomic trends, limiting its effectiveness in comprehensive decision-making.
When to Use Qualitative vs Technical Analysis
Qualitative analysis excels when understanding market sentiment, company management quality, or industry trends, making it ideal for long-term investment decisions. Technical analysis is more effective for short-term trading, leveraging price patterns and volume data to identify entry and exit points. Investors typically use qualitative analysis during fundamental research and technical analysis for timing market moves.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing the right approach between qualitative analysis and technical analysis depends on the investor's goals and market perspective. Qualitative analysis offers insights into company fundamentals, management quality, and industry positioning, ideal for long-term value investing. Technical analysis focuses on price patterns and market trends to identify entry and exit points, making it suitable for short-term trading strategies.
Qualitative Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com