Profit sharing incentivizes employees by distributing a portion of the company's earnings directly to them, enhancing motivation and productivity. This approach aligns individual and organizational goals, fostering a collaborative work environment that drives sustained business growth. Discover how implementing profit sharing can transform Your workplace dynamics in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
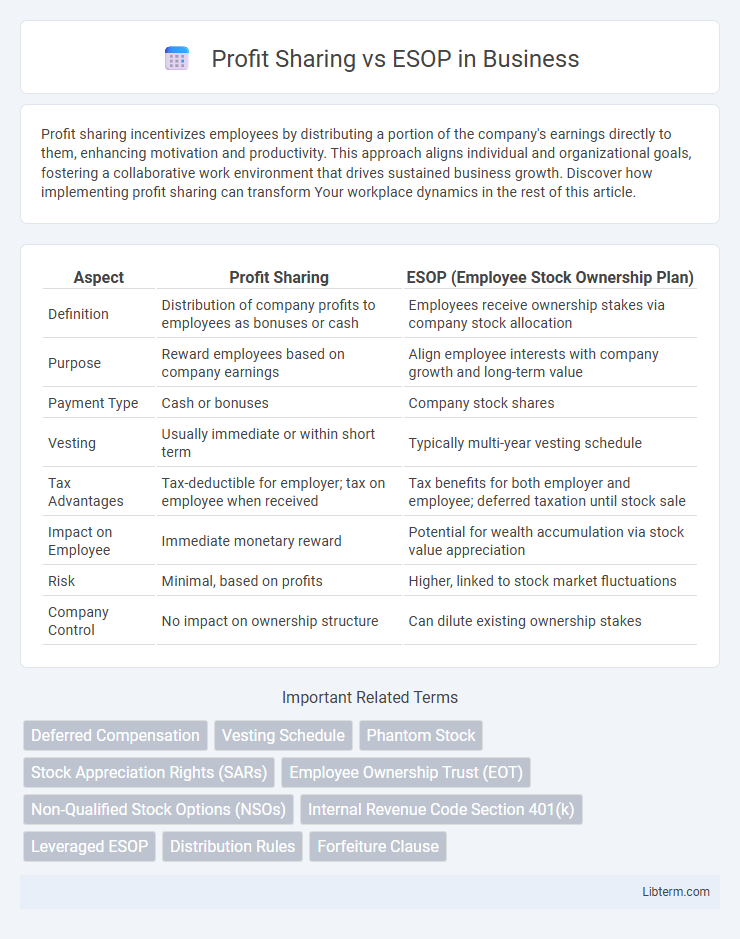
| Aspect | Profit Sharing | ESOP (Employee Stock Ownership Plan) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distribution of company profits to employees as bonuses or cash | Employees receive ownership stakes via company stock allocation |
| Purpose | Reward employees based on company earnings | Align employee interests with company growth and long-term value |
| Payment Type | Cash or bonuses | Company stock shares |
| Vesting | Usually immediate or within short term | Typically multi-year vesting schedule |
| Tax Advantages | Tax-deductible for employer; tax on employee when received | Tax benefits for both employer and employee; deferred taxation until stock sale |
| Impact on Employee | Immediate monetary reward | Potential for wealth accumulation via stock value appreciation |
| Risk | Minimal, based on profits | Higher, linked to stock market fluctuations |
| Company Control | No impact on ownership structure | Can dilute existing ownership stakes |
Introduction to Profit Sharing and ESOP
Profit sharing is a compensation strategy where employers distribute a portion of company profits to employees, enhancing motivation and aligning workforce performance with business success. Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) grant employees ownership stakes via company shares, fostering long-term investment in company growth and retirement benefits. Both profit sharing and ESOPs serve as powerful tools for employee engagement and retention, but differ in structure and impact on company equity.
Understanding Profit Sharing Plans
Profit Sharing Plans distribute a portion of company profits to employees, creating a direct link between company performance and employee rewards, which enhances motivation and retention. Unlike ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans), profit sharing does not involve ownership or stock issuance but rather cash bonuses or contributions to retirement accounts. These plans often offer flexibility in contribution amounts and eligibility, making them an attractive tool for businesses aiming to share financial successes without diluting ownership.
What is an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)?
An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a tax-qualified, defined-contribution benefit plan that provides employees with ownership interest in the company through allocated shares of stock. ESOPs align employee incentives with corporate performance by granting stock ownership, often used as a retirement benefit or to enhance employee motivation and retention. Unlike profit-sharing plans that distribute cash bonuses based on company earnings, ESOPs invest in company equity, potentially offering long-term financial gains tied to stock appreciation.
Key Differences Between Profit Sharing and ESOP
Profit sharing plans distribute company profits to employees based on predetermined formulas, often tied to salary or tenure, while ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans) allocate company stock to employees, creating ownership stakes. Profit sharing provides direct cash bonuses reflecting the company's profitability, whereas ESOPs focus on long-term wealth accumulation through stock appreciation and voting rights. Key differences include the nature of benefits--cash versus equity--and the impact on employee engagement, with ESOPs fostering a stronger sense of ownership and alignment with company goals.
Benefits of Profit Sharing for Employers and Employees
Profit sharing plans boost employee motivation and retention by directly linking compensation to company performance, creating a shared interest in business success. Employers benefit from enhanced productivity and reduced turnover costs, as profit sharing aligns workforce goals with organizational profitability. Employees gain financial rewards without upfront investment, encouraging a collaborative culture and fostering long-term commitment.
Advantages of ESOPs for Companies and Workforce
ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans) enhance company performance by aligning employee interests with shareholder value, fostering a culture of ownership and long-term commitment. They offer tax advantages, including tax-deductible contributions and potential deferral of capital gains, benefiting both companies and employees. ESOPs improve employee retention and motivation by providing a tangible stake in the company's success, unlike profit sharing, which delivers variable cash bonuses without equity ownership.
Tax Implications: Profit Sharing vs ESOP
Profit sharing plans offer employers tax deductions on contributions, while employees defer taxes until distributions are received, typically during retirement. ESOPs allow companies to deduct contributions used to buy shares and provide tax-deferred growth for employees, with potential capital gains tax advantages upon sale of stock. Both plans provide significant tax benefits, but ESOPs uniquely enable employees to accumulate equity with favorable tax treatment on dividends and stock sales.
Eligibility and Participation Criteria
Profit sharing plans typically allow eligibility for all employees who have completed a minimum service period, often one year, ensuring broad participation based on tenure. ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans) require employees to meet specific criteria such as minimum age and length of service, commonly one to two years, before gaining ownership stakes. Participation in profit sharing is generally more inclusive and discretionary, while ESOPs involve structured stock allocations tied to predefined eligibility rules.
Long-Term Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Profit sharing plans directly link employee compensation to company performance, fostering immediate motivation and aligning interests with business success. ESOPs offer employees ownership stakes, promoting long-term commitment by providing financial benefits through stock value appreciation and dividends. Studies show ESOP participants exhibit higher retention rates and increased loyalty, driven by a sense of ownership and potential wealth accumulation over time.
Choosing the Right Plan: Factors to Consider
Choosing between profit sharing and ESOP plans depends on factors such as company size, employee engagement goals, and tax implications. Profit sharing offers flexibility in contribution amounts tied to company performance, while ESOPs provide employees with ownership stakes, fostering long-term commitment. Evaluating financial capacity, administrative complexity, and desired employee incentives ensures the selection of the most effective plan for workforce motivation and retention.
Profit Sharing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com