Organizational flexibility enables companies to adapt swiftly to market changes by reshaping structures, processes, and workflows. Embracing a flexible approach fosters innovation, improves employee engagement, and enhances overall performance in dynamic environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for boosting your organization's flexibility.
Table of Comparison
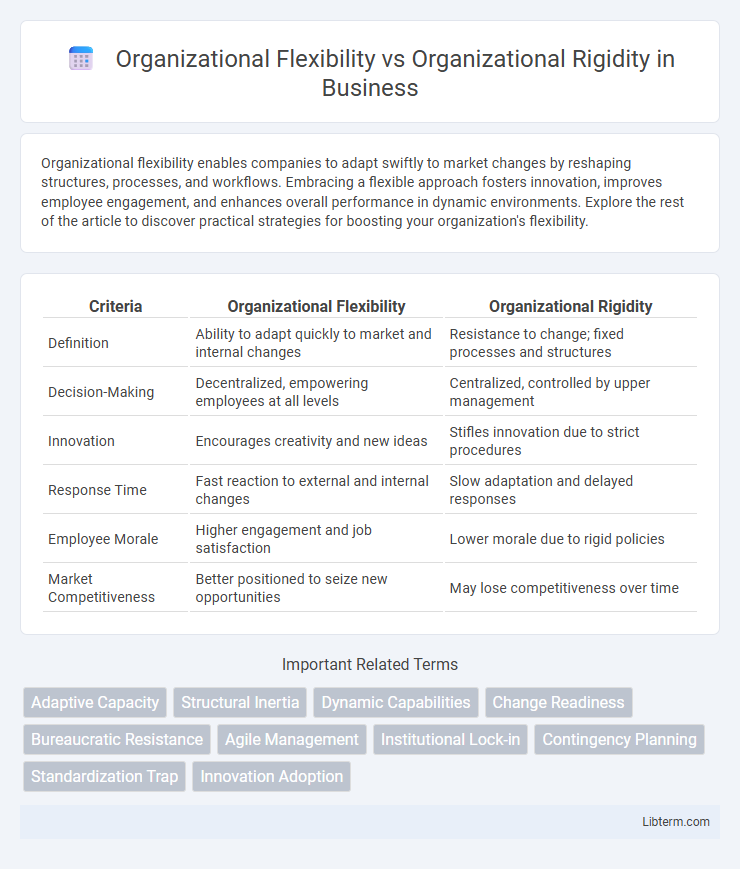
| Criteria | Organizational Flexibility | Organizational Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adapt quickly to market and internal changes | Resistance to change; fixed processes and structures |
| Decision-Making | Decentralized, empowering employees at all levels | Centralized, controlled by upper management |
| Innovation | Encourages creativity and new ideas | Stifles innovation due to strict procedures |
| Response Time | Fast reaction to external and internal changes | Slow adaptation and delayed responses |
| Employee Morale | Higher engagement and job satisfaction | Lower morale due to rigid policies |
| Market Competitiveness | Better positioned to seize new opportunities | May lose competitiveness over time |
Introduction to Organizational Flexibility and Rigidity
Organizational flexibility refers to a company's ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions, customer demands, and technological advancements while maintaining operational efficiency. In contrast, organizational rigidity denotes a fixed structure and resistance to change, often leading to slower decision-making processes and reduced innovation capacity. Understanding the balance between flexibility and rigidity is crucial for businesses aiming to sustain competitive advantage in dynamic environments.
Defining Organizational Flexibility
Organizational flexibility refers to a company's ability to adapt quickly to market changes, technological advancements, and shifting consumer demands through agile processes and responsive decision-making structures. This adaptability is characterized by decentralized management, cross-functional teams, and a culture that encourages innovation and continuous learning. High organizational flexibility enhances competitiveness and resilience in dynamic business environments.
Understanding Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity refers to the inability of a company to adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer preferences, often due to fixed structures, strict hierarchies, or resistant corporate culture. This inflexibility can lead to decreased innovation, slower decision-making processes, and reduced competitiveness, hindering long-term growth and responsiveness. Organizations exhibiting rigidity frequently face challenges in implementing change management initiatives and fail to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Key Differences Between Flexibility and Rigidity
Organizational flexibility emphasizes adaptability, allowing companies to respond quickly to market changes and foster innovation, while organizational rigidity is characterized by strict adherence to established procedures and resistance to change. Flexible organizations promote decentralized decision-making and dynamic workflows, enhancing employee empowerment and rapid problem-solving. Conversely, rigid organizations rely on hierarchical control and fixed processes, which can hinder responsiveness and limit growth opportunities.
Benefits of Organizational Flexibility
Organizational flexibility enhances adaptability, enabling businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and evolving customer demands. It fosters innovation by encouraging creative problem-solving and cross-functional collaboration among teams. Increased employee satisfaction and retention result from flexible work environments that accommodate diverse needs and promote work-life balance.
Drawbacks of Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity limits a company's ability to respond quickly to market changes, hindering innovation and adaptability. It often leads to employee dissatisfaction due to inflexible policies and bureaucratic decision-making processes. Such rigidity can result in lost competitive advantage as the organization struggles to implement new technologies or business models effectively.
Factors Influencing Organizational Adaptability
Organizational adaptability is influenced by factors such as leadership style, communication channels, and corporate culture that either promote flexibility or reinforce rigidity. Agile leadership encourages decentralized decision-making and continuous learning, enhancing responsiveness to market changes. In contrast, rigid organizational structures with strict hierarchies and inflexible policies often hinder timely adaptation and innovation.
Real-World Examples: Flexible vs. Rigid Organizations
Zappos exemplifies organizational flexibility by empowering employees to make customer-centric decisions without rigid protocols, resulting in high customer satisfaction and rapid innovation. In contrast, traditional manufacturing giants like General Motors have historically shown organizational rigidity with hierarchical decision-making and strict procedures, often slowing adaptation to market changes. Companies embracing flexibility tend to innovate faster and respond better to dynamic environments compared to rigid organizations constrained by bureaucratic structures.
Strategies to Promote Flexibility in the Workplace
Implementing cross-functional teams and encouraging continuous learning are effective strategies to promote organizational flexibility in the workplace. Adopting agile management practices allows companies to quickly adapt to market changes and innovate. Cultivating an open communication culture and empowering employees to make decisions enhances responsiveness and reduces rigidity.
Conclusion: Balancing Flexibility and Rigidity for Success
Balancing organizational flexibility and rigidity is crucial for sustainable success, allowing companies to adapt to market changes while maintaining necessary structure and control. Flexible organizations foster innovation and responsiveness, whereas rigidity ensures stability and efficient processes. Optimizing this balance enhances competitive advantage, workforce engagement, and long-term growth.
Organizational Flexibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com