Penetration pricing is a marketing strategy where a company sets a low initial price for a new product to attract customers and gain market share quickly. This approach aims to entice Your target audience by offering exceptional value compared to competitors, encouraging trial and fostering customer loyalty. Explore the rest of the article to discover how penetration pricing can boost your business growth and key considerations for its successful implementation.
Table of Comparison
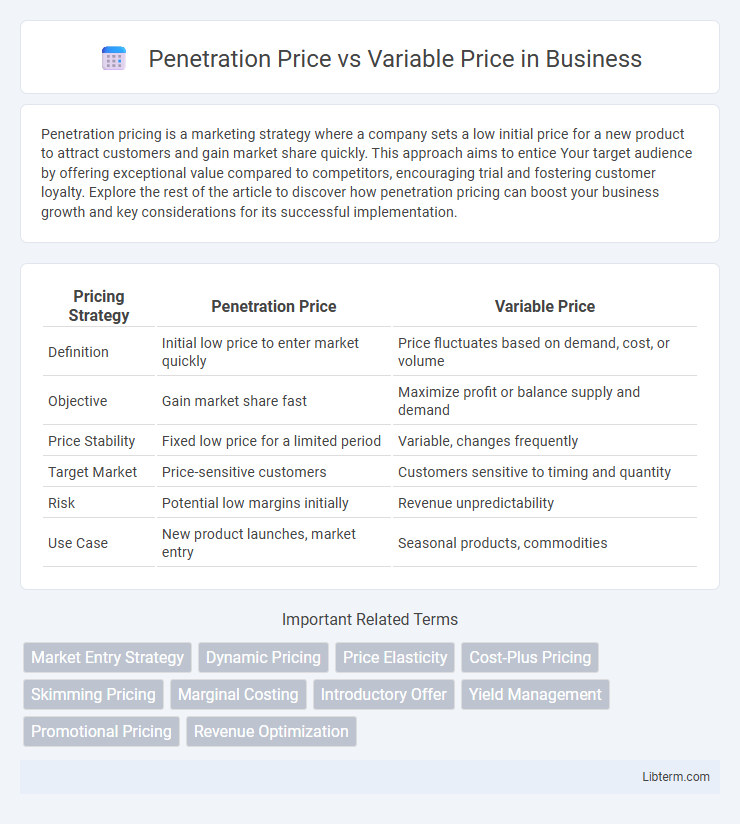
| Pricing Strategy | Penetration Price | Variable Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial low price to enter market quickly | Price fluctuates based on demand, cost, or volume |
| Objective | Gain market share fast | Maximize profit or balance supply and demand |
| Price Stability | Fixed low price for a limited period | Variable, changes frequently |
| Target Market | Price-sensitive customers | Customers sensitive to timing and quantity |
| Risk | Potential low margins initially | Revenue unpredictability |
| Use Case | New product launches, market entry | Seasonal products, commodities |
Introduction to Pricing Strategies
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share, making it effective for new product launches. Variable pricing adjusts prices based on factors like demand, customer segments, or purchase timing, optimizing revenue through flexibility. Both strategies play crucial roles in competitive market positioning and consumer behavior influence.
What is Penetration Pricing?
Penetration pricing is a marketing strategy where a product is introduced at a low price to quickly attract customers and gain market share. Unlike variable pricing, which fluctuates based on costs and demand, penetration pricing maintains a consistently low price to encourage adoption and discourage competitors. This approach is effective for new products entering competitive markets, aiming to build a strong customer base rapidly.
What is Variable Pricing?
Variable pricing refers to a dynamic strategy where prices fluctuate based on factors such as demand, customer segments, or market conditions, enabling businesses to maximize revenue. Unlike penetration pricing, which sets a low initial price to enter a market, variable pricing adjusts prices in real-time or across different channels to better match consumer willingness to pay. This approach is common in industries like airlines, hospitality, and e-commerce, where price sensitivity and inventory availability vary frequently.
Key Differences Between Penetration and Variable Pricing
Penetration pricing sets a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share, often below cost or competitors' prices, aiming for long-term profitability through volume sales. Variable pricing adjusts prices based on demand, customer segments, or purchase conditions, allowing flexibility and optimization of revenue per unit sold. The key difference lies in penetration pricing's strategy to establish market presence versus variable pricing's focus on maximizing revenue through price differentiation.
Advantages of Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing offers the advantage of rapidly attracting a large customer base by setting prices significantly lower than competitors, which increases market share swiftly. This strategy helps achieve economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and enhancing long-term profitability. Lower initial prices also create high barriers for new entrants, reinforcing the brand's market position.
Advantages of Variable Pricing
Variable pricing offers the advantage of aligning prices with real-time market demand and cost fluctuations, enhancing revenue management and profitability. It enables businesses to attract different customer segments by adjusting prices based on willingness to pay, leading to increased sales volume and market responsiveness. Unlike penetration pricing, which sets a fixed low entry price, variable pricing provides flexibility to optimize margins and compete effectively in dynamic markets.
Challenges and Risks of Each Pricing Model
Penetration pricing risks include slim profit margins during market entry and potential brand value erosion as consumers may associate low prices with lower quality, complicating future price increases. Variable pricing challenges involve customer dissatisfaction due to perceived unfairness and complexity in managing dynamic prices across segments, which can lead to mistrust and reduced loyalty. Both models require careful analysis of market demand elasticity and competitor responses to balance growth objectives and profitability.
When to Choose Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is ideal when entering a highly competitive market with price-sensitive customers, aiming to quickly gain market share by setting an initially low price below competitors. This strategy works well for new products requiring rapid adoption and brand visibility, especially in markets with elastic demand where volume can offset lower margins. Choosing penetration pricing helps establish customer loyalty and deters competitors from entering due to reduced profit incentives.
When to Implement Variable Pricing
Variable pricing is best implemented when businesses face fluctuating demand or seasonal variations, enabling dynamic adjustments to maximize revenue and optimize inventory turnover. This strategy suits markets with diverse customer segments willing to pay different prices or when cost structures change frequently due to raw material or labor variations. Companies in hospitality, airlines, or retail often use variable pricing during peak periods or off-seasons to balance supply and demand effectively.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Business
Choosing between penetration pricing and variable pricing depends on your business goals, market competition, and customer behavior. Penetration pricing can quickly attract market share with low initial prices, while variable pricing allows more flexibility by adjusting prices based on demand, cost, or customer segment. Evaluating your product lifecycle, cost structure, and target audience ensures the optimal pricing strategy that maximizes profit and market positioning.
Penetration Price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com