Incremental innovation focuses on making small, continuous improvements to existing products, services, or processes to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction. By leveraging current knowledge and resources, businesses can reduce risks associated with radical changes while steadily advancing their market position. Discover how your company can capitalize on incremental innovation to achieve sustainable growth throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
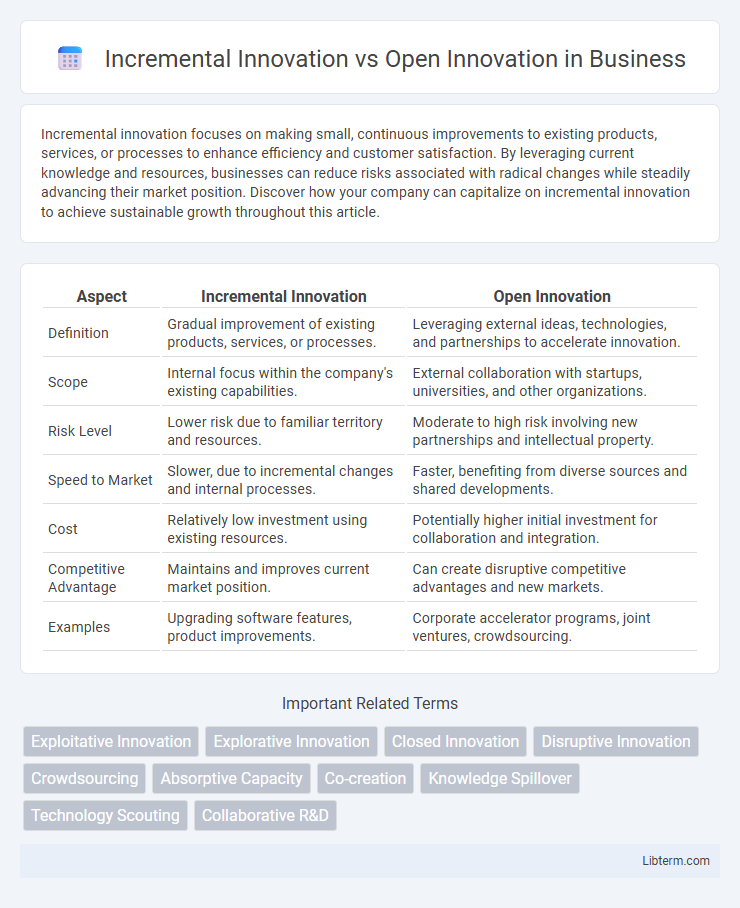
| Aspect | Incremental Innovation | Open Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual improvement of existing products, services, or processes. | Leveraging external ideas, technologies, and partnerships to accelerate innovation. |
| Scope | Internal focus within the company's existing capabilities. | External collaboration with startups, universities, and other organizations. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to familiar territory and resources. | Moderate to high risk involving new partnerships and intellectual property. |
| Speed to Market | Slower, due to incremental changes and internal processes. | Faster, benefiting from diverse sources and shared developments. |
| Cost | Relatively low investment using existing resources. | Potentially higher initial investment for collaboration and integration. |
| Competitive Advantage | Maintains and improves current market position. | Can create disruptive competitive advantages and new markets. |
| Examples | Upgrading software features, product improvements. | Corporate accelerator programs, joint ventures, crowdsourcing. |
Understanding Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves making continuous, small-scale improvements to existing products, services, or processes, enhancing efficiency and customer value without drastic changes. This type of innovation leverages existing knowledge and resources within the organization, reducing risk and cost compared to radical innovation. Companies using incremental innovation benefit from steady growth and the ability to respond quickly to market feedback, maintaining competitiveness over time.
Defining Open Innovation
Open Innovation is a strategic approach where organizations collaborate with external partners, such as startups, universities, and customers, to accelerate the development and commercialization of new ideas and technologies. This model contrasts with Incremental Innovation, which emphasizes gradual improvements within internal R&D departments. Open Innovation leverages external knowledge sources and intellectual property, enhancing flexibility and reducing time-to-market for breakthrough solutions.
Key Differences Between Incremental and Open Innovation
Incremental innovation focuses on making small, continuous improvements to existing products, services, or processes within an organization, aiming to enhance efficiency and performance gradually. Open innovation involves leveraging external ideas, technologies, and collaborations beyond the company's boundaries to accelerate development and bring diverse insights into the innovation process. Key differences include the scope of idea sources, with incremental innovation relying internally while open innovation integrates external contributions, and the scale of change, where incremental innovation targets gradual enhancements, contrasted by open innovation's potential for groundbreaking advancements.
Advantages of Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation offers advantages such as lower risk and cost by enhancing existing products or processes, allowing companies to build on proven technologies and customer feedback. This approach accelerates time-to-market, improves product quality, and fosters continuous improvement, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Firms leveraging incremental innovation maintain competitive advantage through steady, manageable advancements without the disruption associated with radical changes.
Benefits of Open Innovation
Open innovation accelerates product development by leveraging external expertise, reducing time-to-market and R&D costs. It fosters collaboration across industries, driving more diverse ideas and breakthrough solutions compared to incremental innovation's internal iteration. Companies adopting open innovation gain competitive advantage through access to a broader innovation ecosystem and enhanced scalability.
Challenges in Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation faces challenges such as limited breakthrough potential and difficulty in addressing rapidly changing market demands. Organizations may struggle with resource allocation and maintaining motivation for continuous small improvements without dramatic results. This contrasts with open innovation, which leverages external ideas to overcome the constraints of incremental progress.
Obstacles to Open Innovation
Open Innovation faces obstacles such as intellectual property risks, lack of trust among partners, and complex coordination challenges between internal teams and external collaborators. Companies often encounter difficulties in balancing knowledge sharing with competitive advantage and managing cultural differences that hinder seamless collaboration. These barriers slow down the integration of external ideas compared to the more controlled, step-by-step enhancements typical of Incremental Innovation.
Real-World Examples: Incremental vs Open Innovation
Incremental innovation is exemplified by Apple's iterative improvements to the iPhone, enhancing features and user experience with each new model. Open innovation is demonstrated by Procter & Gamble's Connect + Develop program, which sources ideas and technologies externally to accelerate product development. These approaches highlight how firms leverage internal refinement or external collaboration to sustain competitive advantage.
Choosing the Right Innovation Approach
Selecting the right innovation approach depends on organizational goals and resource availability, with incremental innovation prioritizing gradual improvements to existing products and processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing risk. Open innovation leverages external knowledge, collaboration, and diverse perspectives to accelerate breakthrough development and access new markets. Balancing incremental and open innovation strategies enables firms to foster sustained growth while navigating competitive and technological challenges.
Future Trends in Innovation Strategies
Incremental innovation emphasizes continuous, small-scale improvements to existing products or processes, driving steady growth and efficiency in the short term. Open innovation leverages external ideas, partnerships, and knowledge sharing, enhancing adaptability and accelerating breakthrough developments. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining incremental innovation's stability with open innovation's collaborative potential, supported by AI-driven analytics and digital platforms to optimize idea sourcing and implementation.
Incremental Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com