Asset-based strategies focus on leveraging your existing resources and investments to maximize financial growth and stability. By understanding how to optimize asset allocation, you can improve cash flow, reduce risks, and enhance overall portfolio performance. Explore the full article to discover effective asset-based approaches tailored for your financial success.
Table of Comparison
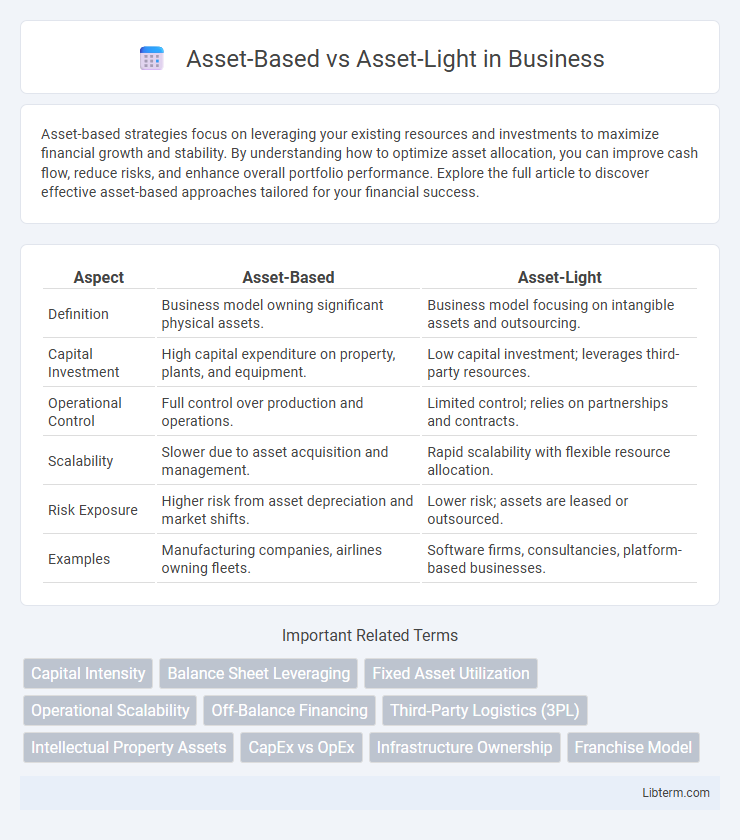
| Aspect | Asset-Based | Asset-Light |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model owning significant physical assets. | Business model focusing on intangible assets and outsourcing. |
| Capital Investment | High capital expenditure on property, plants, and equipment. | Low capital investment; leverages third-party resources. |
| Operational Control | Full control over production and operations. | Limited control; relies on partnerships and contracts. |
| Scalability | Slower due to asset acquisition and management. | Rapid scalability with flexible resource allocation. |
| Risk Exposure | Higher risk from asset depreciation and market shifts. | Lower risk; assets are leased or outsourced. |
| Examples | Manufacturing companies, airlines owning fleets. | Software firms, consultancies, platform-based businesses. |
Introduction to Asset-Based and Asset-Light Models
Asset-based models rely heavily on owning physical assets such as properties, equipment, or inventory, enabling direct control over operations and value creation. Asset-light models prioritize leveraging third-party assets or partnerships, focusing on service, technology, or brand management rather than ownership. Companies adopt asset-light strategies to enhance scalability, reduce capital expenditure, and increase operational flexibility in competitive markets.
Definition of Asset-Based Business Model
An asset-based business model relies on the ownership and control of physical assets such as property, equipment, or inventory, which are essential to the company's value creation and operations. This model enables direct control over production, delivery, and quality, often resulting in higher capital expenditure and operational complexity. Companies in manufacturing, real estate, and transportation commonly adopt asset-based strategies to maintain competitive advantages through tangible resources.
Key Features of Asset-Light Business Model
The asset-light business model emphasizes minimal ownership of physical assets, leveraging partnerships, outsourcing, and technology to reduce capital expenditure and enhance scalability. Key features include lower fixed costs, higher operational flexibility, and faster market entry, allowing companies to adapt quickly to changing demands. This approach prioritizes intangible assets like brand, intellectual property, and customer relationships, enabling efficient resource allocation and improved return on investment.
Advantages of Asset-Based Strategies
Asset-based strategies offer greater control over operations and quality through direct ownership of physical assets such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution networks. This approach enhances reliability and consistency in service delivery while enabling faster response times to market changes or customer demands. Holding tangible assets also provides collateral value, facilitating easier access to financing and investment opportunities for business expansion.
Benefits of Adopting Asset-Light Approaches
Asset-light approaches enhance operational flexibility by reducing dependence on physical assets, enabling faster market adaptation and scalability. Lower capital expenditure and minimized maintenance costs improve financial efficiency and risk management. This model supports innovation and strategic partnerships by allowing companies to focus resources on core competencies and customer experience.
Risks and Challenges of Asset-Based Organizations
Asset-based organizations face significant risks such as high capital expenditure, asset obsolescence, and reduced operational flexibility, which can impact financial stability during market downturns. Managing physical assets requires ongoing maintenance and regulatory compliance, increasing operational complexity and costs. These challenges limit the ability to scale quickly or pivot strategies, making asset-based models less adaptive to rapid industry changes compared to asset-light organizations.
Limitations of Asset-Light Models
Asset-light models often face limitations such as reduced control over supply chain and quality assurance, leading to potential inconsistencies in product or service delivery. The reliance on third-party partnerships increases vulnerability to external risks and can limit the ability to swiftly adapt to market changes. This model may also experience higher operational risks due to less direct oversight and potential challenges in scaling while maintaining brand integrity.
Industry Examples: Asset-Based vs Asset-Light
Asset-based companies such as FedEx and UPS own and operate extensive physical assets like trucks, planes, and warehouses, enabling tight control over logistics and delivery services. In contrast, asset-light firms like Airbnb and Uber rely on third-party resources--property owners and drivers--allowing rapid scalability with lower capital investment and operational risk. The choice between asset-based and asset-light models significantly impacts cost structure, operational flexibility, and competitive strategy within industries like transportation, hospitality, and manufacturing.
How to Choose the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right model between asset-based and asset-light depends on your business's capital availability, operational control needs, and risk tolerance. Asset-based models require significant investment in physical assets, offering greater control and potential for higher margins, while asset-light models leverage third-party resources to reduce capital expenditure and increase flexibility. Evaluate your industry dynamics, scalability goals, and long-term strategic priorities to determine which model aligns best with your growth and operational efficiency objectives.
Future Trends in Business Models: Asset-Based and Asset-Light
Future business models increasingly favor asset-light strategies due to advancements in digital platforms and cloud computing, enabling companies to scale rapidly without heavy capital investments in physical assets. Asset-based models maintain relevance in industries requiring significant physical infrastructure, such as manufacturing and logistics, where asset ownership ensures control and operational efficiency. Hybrid approaches are emerging, blending asset-light agility with selective asset holdings to optimize flexibility, cost management, and competitive advantage in evolving markets.
Asset-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com